Francesco Verdoja
Relational Scene Graphs for Object Grounding of Natural Language Commands
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Robots are finding wider adoption in human environments, increasing the need for natural human-robot interaction. However, understanding a natural language command requires the robot to infer the intended task and how to decompose it into executable actions, and to ground those actions in the robot's knowledge of the environment, including relevant objects, agents, and locations. This challenge can be addressed by combining the capabilities of Large language models (LLMs) to understand natural language with 3D scene graphs (3DSGs) for grounding inferred actions in a semantic representation of the environment. However, many 3DSGs lack explicit spatial relations between objects, even though humans often rely on these relations to describe an environment. This paper investigates whether incorporating open- or closed-vocabulary spatial relations into 3DSGs can improve the ability of LLMs to interpret natural language commands. To address this, we propose an LLM-based pipeline for target object grounding from open-vocabulary language commands and a vision language model (VLM)-based pipeline to add open-vocabulary spatial edges to 3DSGs from images captured while mapping. Finally, two LLMs are evaluated in a study assessing their performance on the downstream task of target object grounding. Our study demonstrates that explicit spatial relations improve the ability of LLMs to ground objects. Moreover, open-vocabulary relation generation with VLMs proves feasible from robot-captured images, but their advantage over closed-vocabulary relations is found to be limited.
MoDeSuite: Robot Learning Task Suite for Benchmarking Mobile Manipulation with Deformable Objects
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Mobile manipulation is a critical capability for robots operating in diverse, real-world environments. However, manipulating deformable objects and materials remains a major challenge for existing robot learning algorithms. While various benchmarks have been proposed to evaluate manipulation strategies with rigid objects, there is still a notable lack of standardized benchmarks that address mobile manipulation tasks involving deformable objects. To address this gap, we introduce MoDeSuite, the first Mobile Manipulation Deformable Object task suite, designed specifically for robot learning. MoDeSuite consists of eight distinct mobile manipulation tasks covering both elastic objects and deformable objects, each presenting a unique challenge inspired by real-world robot applications. Success in these tasks requires effective collaboration between the robot's base and manipulator, as well as the ability to exploit the deformability of the objects. To evaluate and demonstrate the use of the proposed benchmark, we train two state-of-the-art reinforcement learning algorithms and two imitation learning algorithms, highlighting the difficulties encountered and showing their performance in simulation. Furthermore, we demonstrate the practical relevance of the suite by deploying the trained policies directly into the real world with the Spot robot, showcasing the potential for sim-to-real transfer. We expect that MoDeSuite will open a novel research domain in mobile manipulation involving deformable objects. Find more details, code, and videos at https://sites.google.com/view/modesuite/home.
MISC: Minimal Intervention Shared Control with Guaranteed Safety under Non-Convex Constraints
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Shared control combines human intention with autonomous decision-making, from low-level safety overrides to high-level task guidance, enabling systems that adapt to users while ensuring safety and performance. This enhances task effectiveness and user experience across domains such as assistive robotics, teleoperation, and autonomous driving. However, existing shared control methods, based on e.g. Model Predictive Control, Control Barrier Functions, or learning-based control, struggle with feasibility, scalability, or safety guarantees, particularly since the user input is unpredictable. To address these challenges, we propose an assistive controller framework based on Constrained Optimal Control Problem that incorporates an offline-computed Control Invariant Set, enabling online computation of control actions that ensure feasibility, strict constraint satisfaction, and minimal override of user intent. Moreover, the framework can accommodate structured class of non-convex constraints, which are common in real-world scenarios. We validate the approach through a large-scale user study with 66 participants--one of the most extensive in shared control research--using a computer game environment to assess task load, trust, and perceived control, in addition to performance. The results show consistent improvements across all these aspects without compromising safety and user intent.
REACT: Real-time Efficient Attribute Clustering and Transfer for Updatable 3D Scene Graph
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Modern-day autonomous robots need high-level map representations to perform sophisticated tasks. Recently, 3D scene graphs (3DSGs) have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional grid maps, blending efficient memory use and rich feature representation. However, most efforts to apply them have been limited to static worlds. This work introduces REACT, a framework that efficiently performs real-time attribute clustering and transfer to relocalize object nodes in a 3DSG. REACT employs a novel method for comparing object instances using an embedding model trained on triplet loss, facilitating instance clustering and matching. Experimental results demonstrate that REACT is able to relocalize objects while maintaining computational efficiency. The REACT framework's source code will be available as an open-source project, promoting further advancements in reusable and updatable 3DSGs.
Jointly Learning Cost and Constraints from Demonstrations for Safe Trajectory Generation
May 06, 2024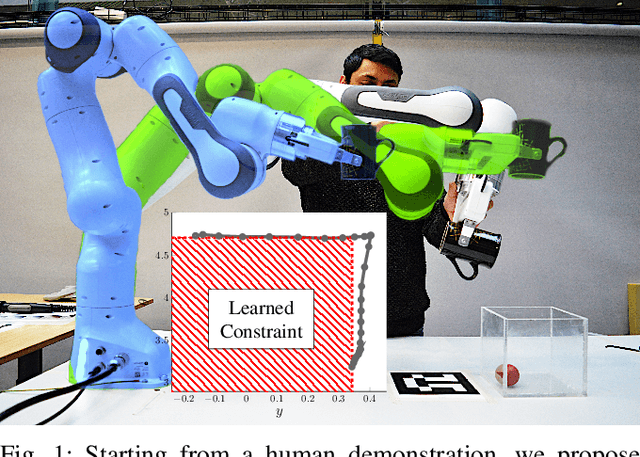
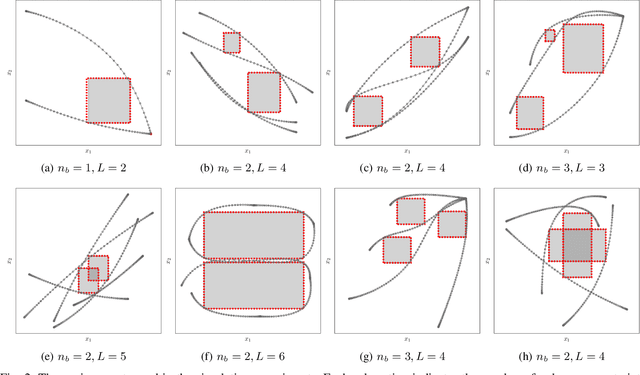
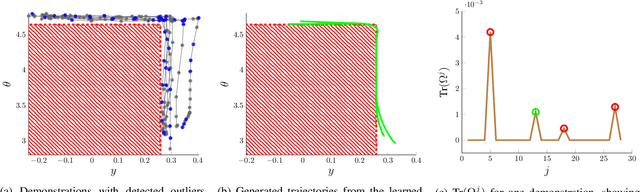
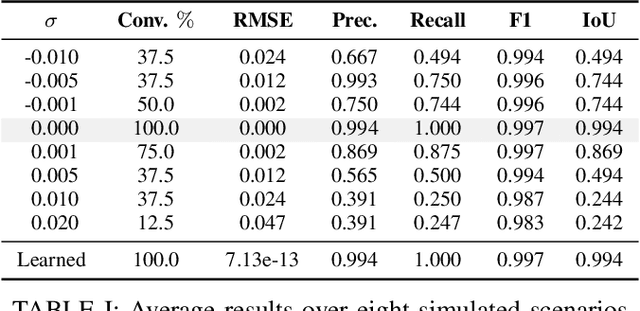
Abstract:Learning from Demonstration allows robots to mimic human actions. However, these methods do not model constraints crucial to ensure safety of the learned skill. Moreover, even when explicitly modelling constraints, they rely on the assumption of a known cost function, which limits their practical usability for task with unknown cost. In this work we propose a two-step optimization process that allow to estimate cost and constraints by decoupling the learning of cost functions from the identification of unknown constraints within the demonstrated trajectories. Initially, we identify the cost function by isolating the effect of constraints on parts of the demonstrations. Subsequently, a constraint leaning method is used to identify the unknown constraints. Our approach is validated both on simulated trajectories and a real robotic manipulation task. Our experiments show the impact that incorrect cost estimation has on the learned constraints and illustrate how the proposed method is able to infer unknown constraints, such as obstacles, from demonstrated trajectories without any initial knowledge of the cost.
Do Visual-Language Maps Capture Latent Semantics?
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Visual-language models (VLMs) have recently been introduced in robotic mapping by using the latent representations, i.e., embeddings, of the VLMs to represent the natural language semantics in the map. The main benefit is moving beyond a small set of human-created labels toward open-vocabulary scene understanding. While there is anecdotal evidence that maps built this way support downstream tasks, such as navigation, rigorous analysis of the quality of the maps using these embeddings is lacking. We investigate two critical properties of map quality: queryability and consistency. The evaluation of queryability addresses the ability to retrieve information from the embeddings. We investigate two aspects of consistency: intra-map consistency and inter-map consistency. Intra-map consistency captures the ability of the embeddings to represent abstract semantic classes, and inter-map consistency captures the generalization properties of the representation. In this paper, we propose a way to analyze the quality of maps created using VLMs, which forms an open-source benchmark to be used when proposing new open-vocabulary map representations. We demonstrate the benchmark by evaluating the maps created by two state-of-the-art methods, VLMaps and OpenScene, using two encoders, LSeg and OpenSeg, using real-world data from the Matterport3D data set. We find that OpenScene outperforms VLMaps with both encoders, and LSeg outperforms OpenSeg with both methods.
Object-oriented mapping in dynamic environments
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Grid maps, especially occupancy grid maps, are ubiquitous in many mobile robot applications. To simplify the process of learning the map, grid maps subdivide the world into a grid of cells, whose occupancies are independently estimated using only measurements in the perceptual field of the particular cell. However, the world consists of objects that span multiple cells, which means that measurements falling onto a cell provide evidence on the occupancy of other cells belonging to the same object. This correlation is not captured by current models. In this work, we present a way to generalize the update of grid maps relaxing the assumption of independence by modeling the relationship between the measurements and the occupancy of each cell as a set of latent variables, and jointly estimating those variables and the posterior of the map. Additionally, we propose a method to estimate the latent variables by clustering based on semantic labels and an extension to the Normal Distributions Transfer Occupancy Map (NDT-OM) to facilitate the proposed map update method. We perform comprehensive experiments of map creation and localization with real world data sets, and show that the proposed method creates better maps in highly dynamic environments compared to state-of-the-art methods. Finally, we demonstrate the ability of the proposed method to remove occluded objects from the map in a lifelong map update scenario.
Localization under consistent assumptions over dynamics
May 26, 2023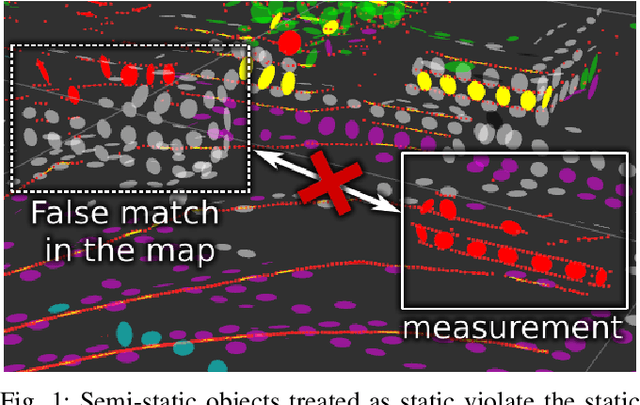
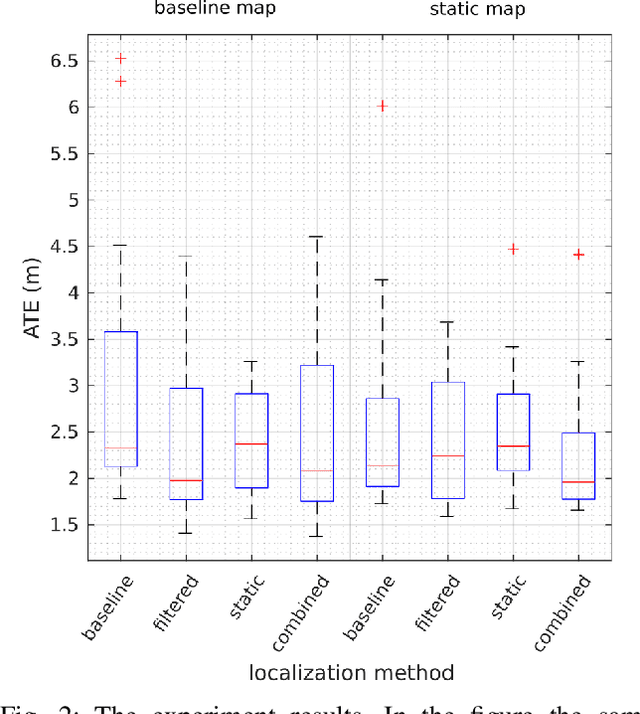
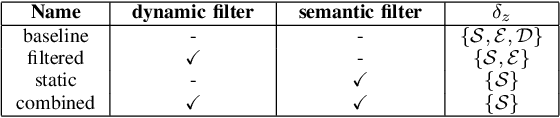
Abstract:Accurate maps are a prerequisite for virtually all autonomous vehicle tasks. Most state-of-the-art maps assume a static world, and therefore dynamic objects are filtered out of the measurements. However, this division ignores movable but non-moving, i.e. semi-static, objects, which are usually recorded in the map and treated as static objects, violating the static world assumption, causing error in the localization. In this paper, we present a method for modeling moving and movable objects for matching the map and the measurements consistently. This reduces the error resulting from inconsistent categorization and treatment of non-static measurements. A semantic segmentation network is used to categorize the measurements into static and semi-static classes, and a background subtraction-based filtering method is used to remove dynamic measurements. Experimental comparison against a state-of-the-art baseline solution using real-world data from Oxford Radar RobotCar data set shows that consistent assumptions over dynamics increase localization accuracy.
Constrained Generative Sampling of 6-DoF Grasps
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:Most state-of-the-art data-driven grasp sampling methods propose stable and collision-free grasps uniformly on the target object. For bin-picking, executing any of those grasps is sufficient. However, for completing specific tasks, such as squeezing out liquid from a bottle, we want the grasp to be on a specific part on the object body while avoiding other locations, such as the cap. In this work, we present a generative grasp sampling network, VCGS, capable of constrained 6-Degrees-of-Freedom (DoF) grasp sampling. In addition, we also curate a new dataset designed to train and evaluate methods for constrained grasping. The new dataset, called CONG, consists of over 14 million training samples of synthetically rendered point clouds and grasps at random target areas on 2889 objects. VCGS is benchmarked against GraspNet, a state-of-the-art unconstrained grasp sampler, in simulation and on a real robot. The results demonstrate that VCGS achieves a 10-15% higher grasp success rate than the baseline while being 2-3 times as sample efficient.
LSVL: Large-scale season-invariant visual localization for UAVs
Dec 07, 2022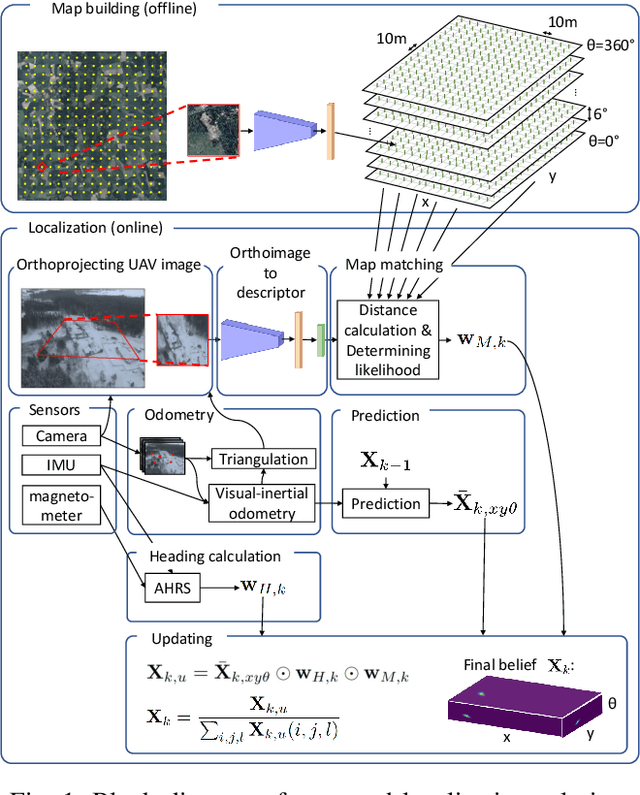
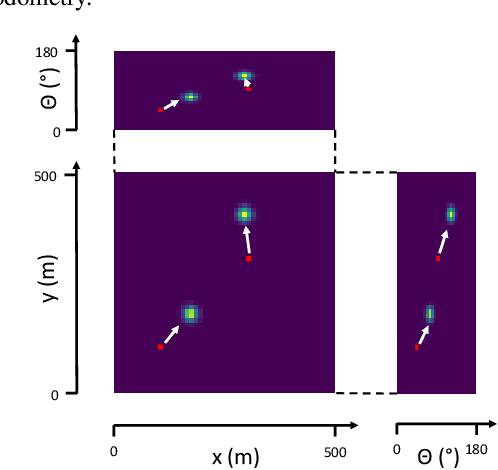
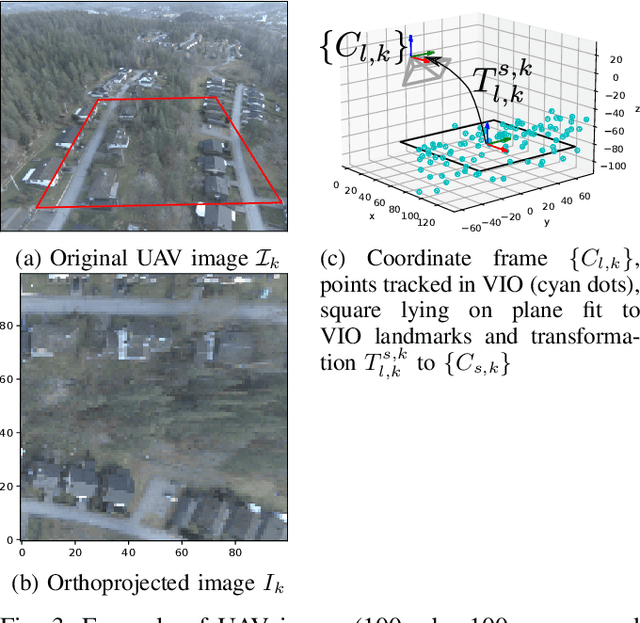
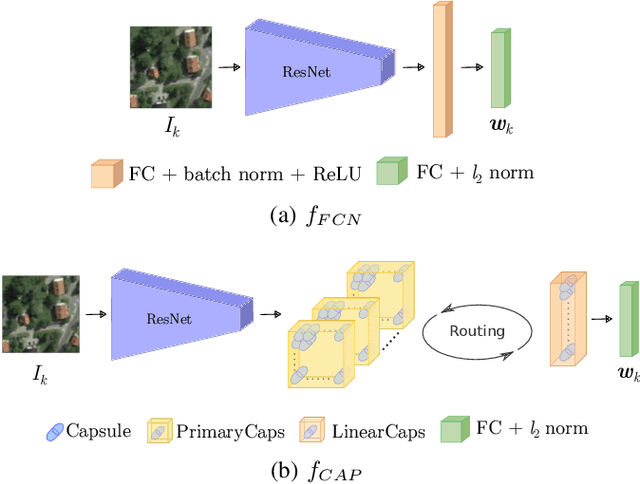
Abstract:Localization of autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) relies heavily on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), which are susceptible to interference. Especially in security applications, robust localization algorithms independent of GNSS are needed to provide dependable operations of autonomous UAVs also in interfered conditions. Typical non-GNSS visual localization approaches rely on known starting pose, work only on a small-sized map, or require known flight paths before a mission starts. We consider the problem of localization with no information on initial pose or planned flight path. We propose a solution for global visual localization on a map at scale up to 100 km2, based on matching orthoprojected UAV images to satellite imagery using learned season-invariant descriptors. We show that the method is able to determine heading, latitude and longitude of the UAV at 12.6-18.7 m lateral translation error in as few as 23.2-44.4 updates from an uninformed initialization, also in situations of significant seasonal appearance difference (winter-summer) between the UAV image and the map. We evaluate the characteristics of multiple neural network architectures for generating the descriptors, and likelihood estimation methods that are able to provide fast convergence and low localization error. We also evaluate the operation of the algorithm using real UAV data and evaluate running time on a real-time embedded platform. We believe this is the first work that is able to recover the pose of an UAV at this scale and rate of convergence, while allowing significant seasonal difference between camera observations and map.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge