Francesco Guidi
Dual Orthogonal Projections-Based Multiuser Interference Cancellation for mmWave Beamforming in XL-MIMO Systems
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates multiuser interference (MUI) cancellation for millimeter-wave (mmWave) beamforming in extremely large-scale multiple-input multiple-output (XL-MIMO) communication systems. We propose a linear algorithm, termed iterative dual orthogonal projections (DOP), which alternates between two orthogonal projections: one to eliminate MUI and the other to refine combiners, ensuring a monotonic increase in spectral efficiency. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that, with each iteration, the signal power for each user increases monotonically, the equivalent noise power after receive combining decreases monotonically, and the spectral efficiency improves accordingly and converges rapidly, closely approaching the theoretical optimum determined by dirty paper coding (DPC), outperforming existing linear algorithms in spectral efficiency.
AREE-Based Decoupled Design of Hybrid Beamformers in mmWave XL-MIMO Systems
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Hybrid beamforming has been widely employed in mmWave communications such as vehicular-to-everything (V2X) scenarios, as a compromise between hardware complexity and spectral efficiency. However, the inherent coupling between analog and digital precoders in hybrid array architecture significantly limits the computational and spectral efficiency of existing algorithms. To address this issue, we propose an alternating residual error elimination (AREE) algorithm, which decomposes the hybrid beamforming problem into two low-dimensional subproblems, each exhibiting a favorable matrix structure that enables effective decoupling of analog and digital precoders from the matrix product formulation. These subproblems iteratively eliminate each other's residual errors, driving the original problem toward the optimal hybrid beamforming performance. The proposed initialization ensures rapid convergence, while a low-complexity geometric channel SVD algorithm is developed by transforming the high-dimensional sparse channel into a low-dimensional equivalent, thereby simplifying the derivation of subproblems. Simulation results demonstrate that the AREE algorithm effectively decouples analog and digital precoders with low complexity, achieves fast convergence, and offers higher spectral efficiency than existing beamforming methods.
Beam Focusing for Near-Field Multi-User Localization
Jul 24, 2024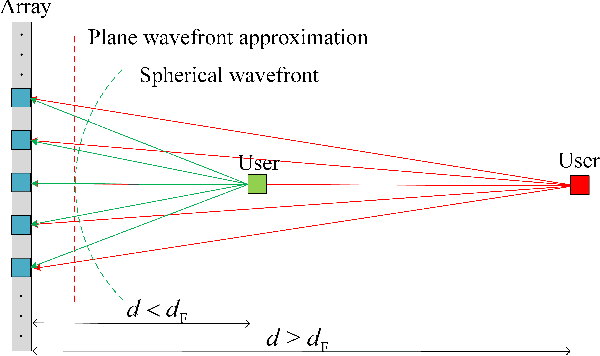
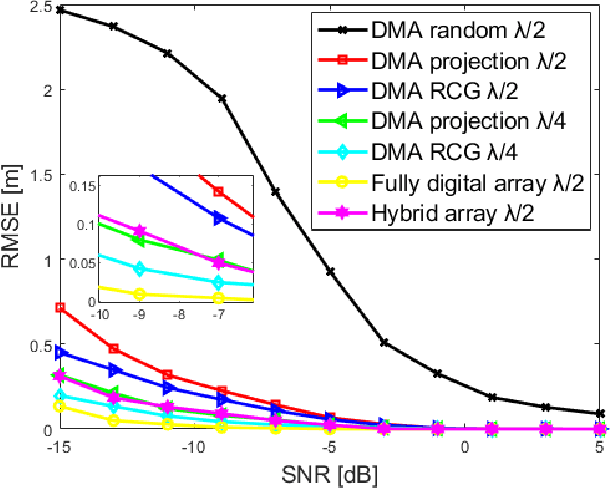
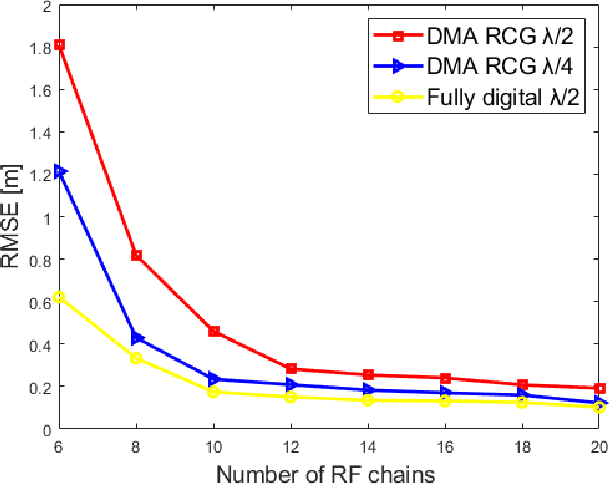
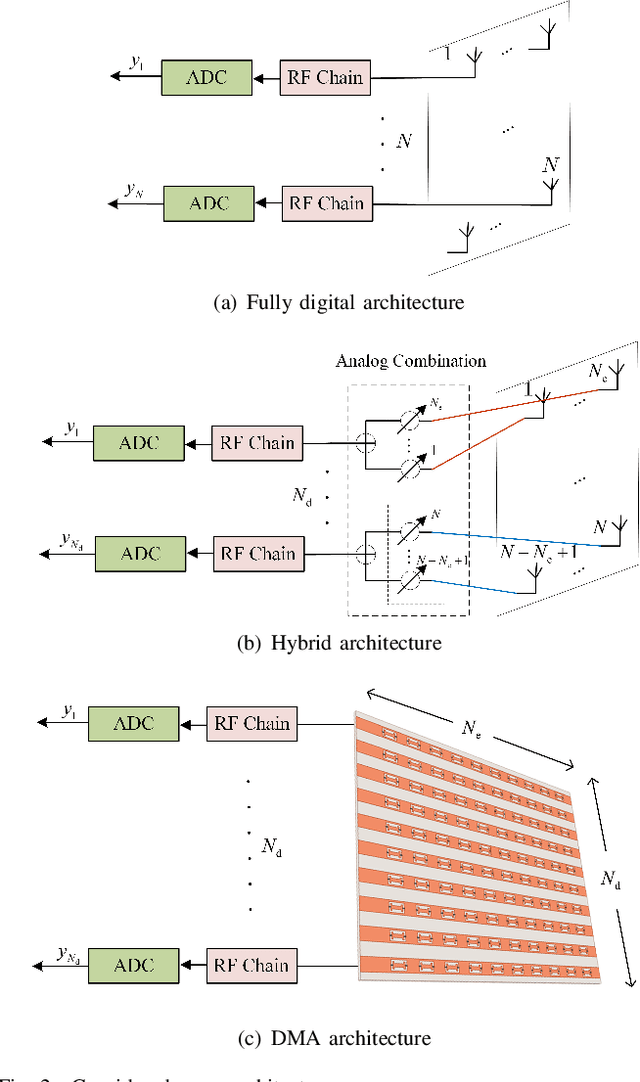
Abstract:Extremely large-scale antenna arrays are poised to play a pivotal role in sixth-generation (6G) networks. Utilizing such arrays often results in a near-field spherical wave transmission environment, enabling the generation of focused beams, which introduces new degrees of freedom for wireless localization. In this paper, we consider a beam-focusing design for localizing multiple sources in the radiating near-field. Our formulation accommodates various expected types of implementations of large antenna arrays, including hybrid analog/digital architectures and dynamic metasurface antennas (DMAs). We consider a direct localization estimation method exploiting curvature-of-arrival of impinging spherical wavefront to obtain user positions. In this regard, we adopt a two-stage approach configuring the array to optimize near-field positioning. In the first step, we focus only on adjusting the array coefficients to minimize the estimation error. We obtain a closed-form approximate solution based on projection and the better one based on the Riemann gradient algorithm. We then extend this approach to simultaneously localize and focus the beams via a sub-optimal iterative approach that does not rely on such knowledge. The simulation results show that near-field localization accuracy based on a hybrid array or DMA can achieve performance close to that of fully digital arrays at a lower cost, and DMAs can attain better performance than hybrid solutions with the same aperture.
A Deep-NN Beamforming Approach for Dual Function Radar-Communication THz UAV
May 27, 2024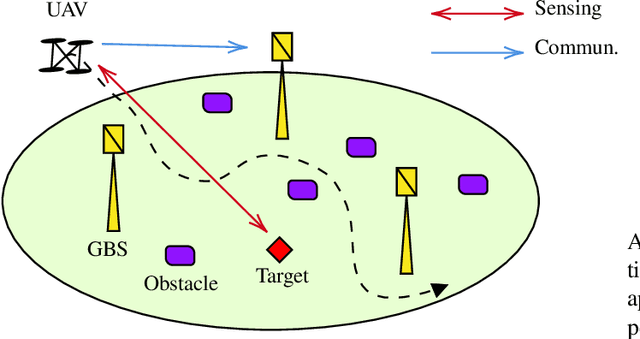
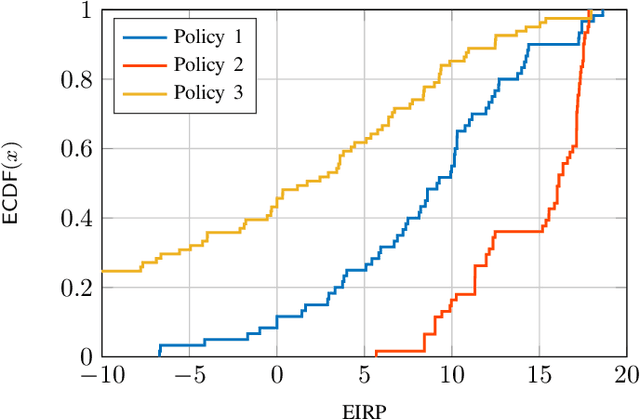
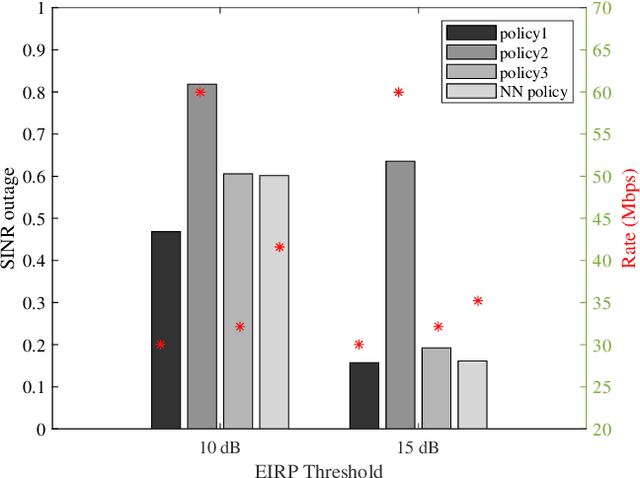
Abstract:In this paper, we consider a scenario with one UAV equipped with a ULA, which sends combined information and sensing signals to communicate with multiple GBS and, at the same time, senses potential targets placed within an interested area on the ground. We aim to jointly design the transmit beamforming with the GBS association to optimize communication performance while ensuring high sensing accuracy. We propose a predictive beamforming framework based on a dual DNN solution to solve the formulated nonconvex optimization problem. A first DNN is trained to produce the required beamforming matrix for any point of the UAV flying area in a reduced time compared to state-of-the-art beamforming optimizers. A second DNN is trained to learn the optimal mapping from the input features, power, and EIRP constraints to the GBS association decision. Finally, we provide an extensive simulation analysis to corroborate the proposed approach and show the benefits of EIRP, SINR performance and computational speed.
Holographic Imaging with XL-MIMO and RIS: Illumination and Reflection Design
Dec 18, 2023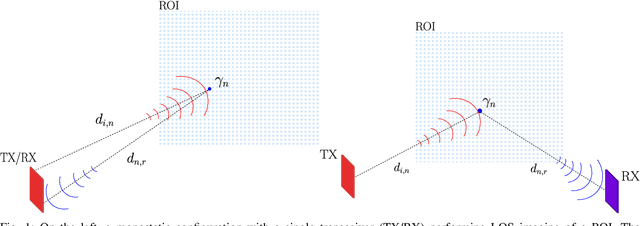

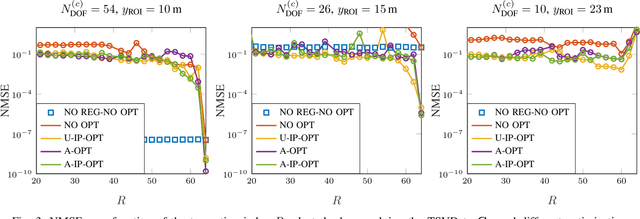
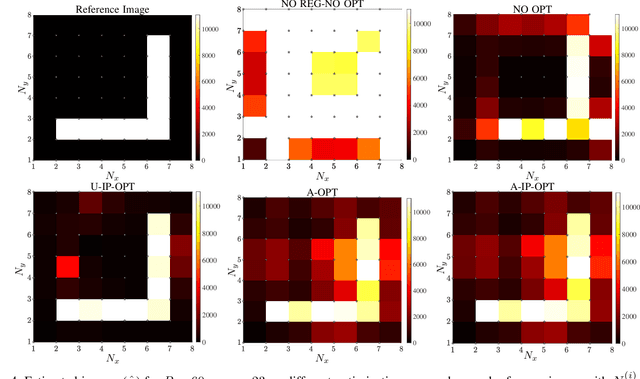
Abstract:This paper addresses a near-field imaging problem utilizing extremely large-scale multiple-input multiple-output (XL-MIMO) antennas and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) already in place for wireless communications. To this end, we consider a system with a fixed transmitting antenna array illuminating a region of interest (ROI) and a fixed receiving antenna array inferring the ROI's scattering coefficients. Leveraging XL-MIMO and high frequencies, the ROI is situated in the radiating near-field region of both antenna arrays, thus enhancing the degrees of freedom (DoF) of the illuminating and sensing channels available for imaging, here referred to as holographic imaging. To further boost the imaging performance, we optimize the illuminating waveform by solving a min-max optimization problem having the upper bound of the mean squared error (MSE) of the image estimate as the objective function. Additionally, we address the challenge of non-line-of-sight (NLOS) scenarios by considering the presence of a RIS and deriving its optimal reflection coefficients. Numerical results investigate the interplay between illumination optimization, geometric configuration (monostatic and bistatic), the DoF of the illuminating and sensing channels, image estimation accuracy, and image complexity.
Near and Far Field Model Mismatch: Implications on 6G Communications, Localization, and Sensing
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:The upcoming 6G technology is expected to operate in near-field (NF) radiating conditions thanks to high-frequency and electrically large antenna arrays. While several studies have already addressed this possibility, it is worth noting that NF models introduce heightened complexity, the justification for which is not always evident in terms of performance improvements. Therefore, this paper delves into the implications of the disparity between NF and far-field (FF) models concerning communication, localization, and sensing systems. Such disparity might lead to a degradation of performance metrics like localization accuracy, sensing reliability, and communication efficiency. Through an exploration of the effects arising from the mismatches between NF and FF models, this study seeks to illuminate the challenges confronting system designers and offer valuable insights into the balance between model accuracy, which typically requires a high complexity and achievable performance. To substantiate our perspective, we also incorporate a numerical performance assessment confirming the repercussions of the mismatch between NF and FF models.
Radio SLAM for 6G Systems at THz Frequencies: Design and Experimental Validation
Dec 23, 2022



Abstract:Next-generation wireless networks will see the convergence of communication and sensing, also exploiting the availability of large bandwidths in the Terahertz (THz) spectrum and electrically large antenna arrays on handheld devices. In particular, it is envisaged that user devices will be able to automatically scan their surroundings by steering a very narrow antenna beam and collecting echoes reflected by objects and walls to derive a map of indoors and infer users' trajectories using simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) techniques. In this paper, we address this scenario by proposing original radioSLAM (R-SLAM) algorithms, derived from image processing techniques, to map the environment and pinpoint the device position in the map starting from measurements sensed by a mobile THz radar. Initially, to fully understand the THz backscattering phenomenon, we provide an experimental characterization of the THz backscattering channel in indoor environments. Then, the performance of the proposed algorithms is assessed using real-world THz radar measurements and is compared with state-of-the-art SLAM techniques, demonstrating the superiority of the proposed approaches.
Near-field Localization with Dynamic Metasurface Antennas
Oct 28, 2022



Abstract:Sixth generation (6G) cellular communications are expected to support enhanced wireless localization capabilities. The widespread deployment of large arrays and high-frequency bandwidths give rise to new considerations for localization applications. First, emerging antenna architectures, such as dynamic metasurface antennas (DMAs), are expected to be frequently utilized thanks to the achievable high angular resolution and low hardware complexity. Further, wireless localization is likely to take place in the radiating near-field (Fresnel) region, which provides new degrees of freedom, because of the adoption of arrays with large apertures. While current studies mostly focus on the use of costly fully-digital antenna arrays, in this paper we investigate how DMAs can be applied for near-field localization of a single user. We use a direct positioning estimation method based on curvature-of-arrival of the impinging wavefront to obtain the user location, and characterize the effects of DMA tuning on the estimation accuracy. Next, we propose an algorithm for configuring the DMA to optimize near-field localization, by first tuning the adjustable DMA coefficients to minimize the estimation error using postulated knowledge of the actual user position. Finally, we propose a sub-optimal iterative algorithm that does not rely on such knowledge. Simulation results show that the DMA-based near-field localization accuracy could approach that of fully-digital arrays at lower cost.
6G Wireless Communications: From Far-field Beam Steering to Near-field Beam Focusing
Mar 24, 2022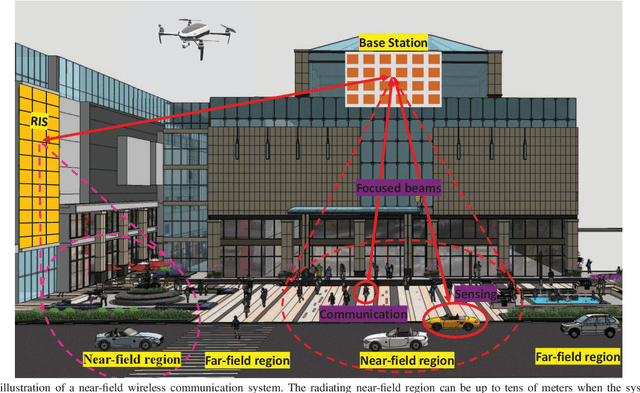
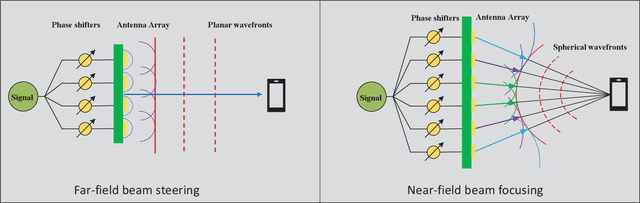
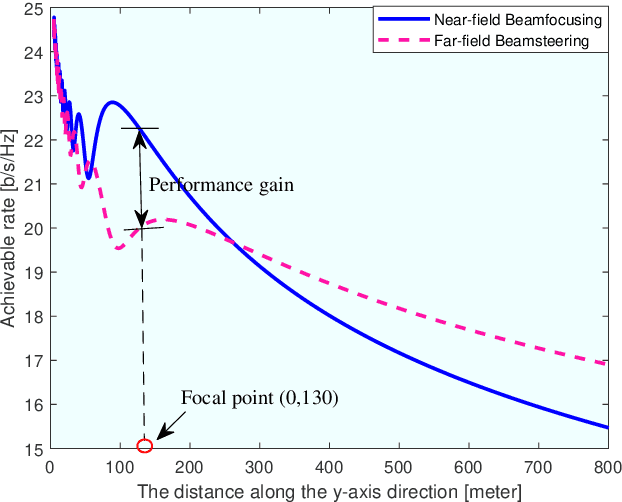
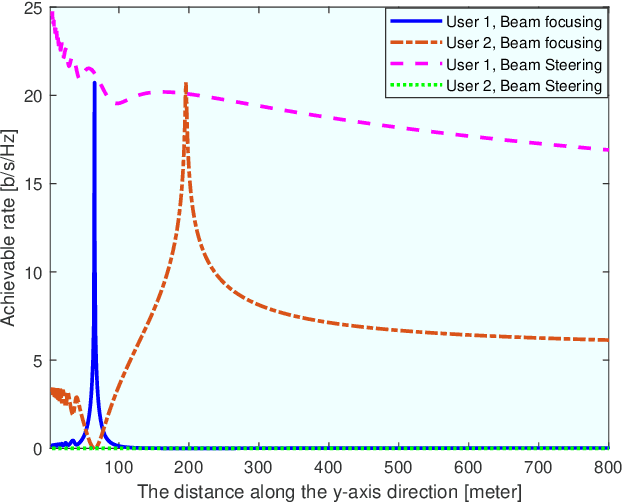
Abstract:6G networks will be required to support higher data rates, improved energy efficiency, lower latency, and more diverse users compared with 5G systems. To meet these requirements, extremely large antenna arrays and high-frequency signaling are envisioned to be key physical-layer technologies. The deployment of extremely large antenna arrays, especially in high-frequency bands, indicates that future 6G wireless networks are likely to operate in the radiating near-field (Fresnel) region, as opposed to the traditional far-field operation of current wireless technologies. In this article, we discuss the opportunities and challenges that arise in radiating near-field communications. We begin by discussing the key physical characteristics of near-field communications, where the standard plane-wave propagation assumption no longer holds, and clarify its implication on the modelling of wireless channels. Then, we elaborate on the ability to leverage spherical wavefronts via beam focusing, highlighting its advantages for 6G systems. We point out several appealing application scenarios which, with proper design, can benefit from near-field operation, including interference mitigation in multi-user communications, accurate localization and focused sensing, as well as wireless power transfer with minimal energy pollution. We conclude with discussing some of the design challenges and research directions that are yet to be explored to fully harness the potential of this emerging paradigm.
Near-Field Wireless Power Transfer with Dynamic Metasurface Antennas
Oct 10, 2021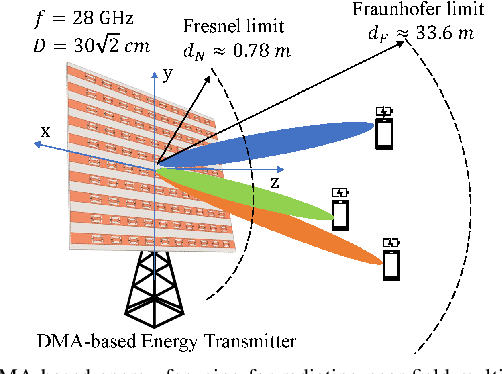
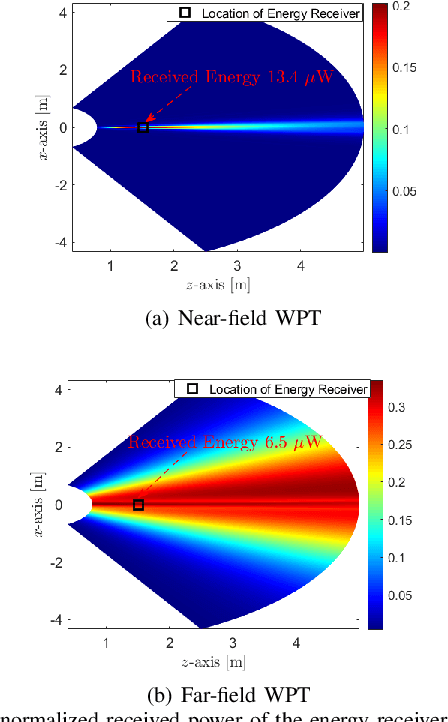
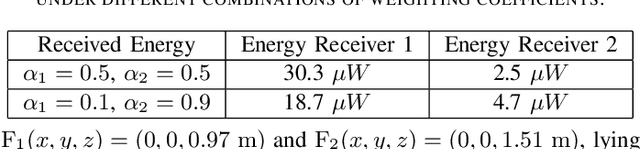
Abstract:Radio frequency wireless power transfer (WPT) enables charging low-power mobile devices without relying on wired infrastructure. Current existing WPT systems are typically designed assuming far-field propagation, where the radiated energy is steered in given angles, resulting in limited efficiency and possible radiation in undesired locations. When large arrays at high frequencies, such as DMA, are employed, WPT might take place in the radiating near-field (Fresnel) region where spherical wave propagation holds, rather than plane wave propagation as in the far-field. In this paper, we study WPT systems charging multiple devices in the Fresnel region, where the energy transmitter is equipped with an emerging DMA, exploring how the antenna configuration can exploit the spherical wavefront to generate focused energy beams. In particular, after presenting a mathematical model for DMA-based radiating near-field WPT systems, we characterize the weighted sum-harvested energy maximization problem of the considered system, and we propose an efficient solution to jointly design the DMA weights and digital precoding vector. Simulation results show that our design generates focused energy beams that are capable of improving energy transfer efficiency in the radiating near-field with minimal energy pollution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge