Feizhao Zhang
Hierarchical Balance Packing: Towards Efficient Supervised Fine-tuning for Long-Context LLM
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Training Long-Context Large Language Models (LLMs) is challenging, as hybrid training with long-context and short-context data often leads to workload imbalances. Existing works mainly use data packing to alleviate this issue but fail to consider imbalanced attention computation and wasted communication overhead. This paper proposes Hierarchical Balance Packing (HBP), which designs a novel batch-construction method and training recipe to address those inefficiencies. In particular, the HBP constructs multi-level data packing groups, each optimized with a distinct packing length. It assigns training samples to their optimal groups and configures each group with the most effective settings, including sequential parallelism degree and gradient checkpointing configuration. To effectively utilize multi-level groups of data, we design a dynamic training pipeline specifically tailored to HBP, including curriculum learning, adaptive sequential parallelism, and stable loss. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly reduces training time over multiple datasets and open-source models while maintaining strong performance. For the largest DeepSeek-V2 (236B) MOE model, our method speeds up the training by 2.4$\times$ with competitive performance.
OmniBal: Towards Fast Instruct-tuning for Vision-Language Models via Omniverse Computation Balance
Jul 30, 2024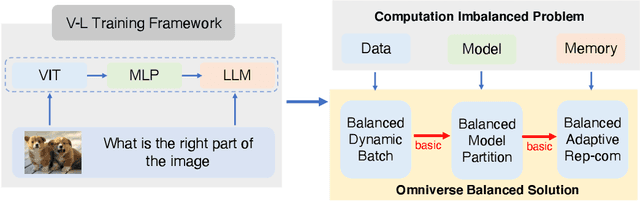

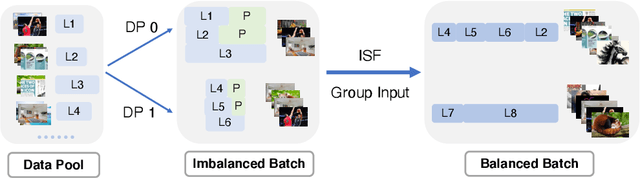
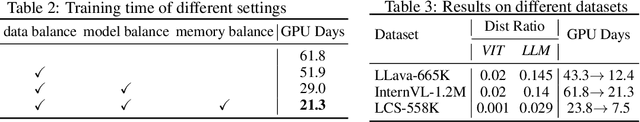
Abstract:Recently, vision-language instruct-tuning models have made significant progress due to their more comprehensive understanding of the world. In this work, we discovered that large-scale 3D parallel training on those models leads to an imbalanced computation load across different devices. The vision and language parts are inherently heterogeneous: their data distribution and model architecture differ significantly, which affects distributed training efficiency. We rebalanced the computational loads from data, model, and memory perspectives to address this issue, achieving more balanced computation across devices. These three components are not independent but are closely connected, forming an omniverse balanced training framework. Specifically, for the data, we grouped instances into new balanced mini-batches within and across devices. For the model, we employed a search-based method to achieve a more balanced partitioning. For memory optimization, we adaptively adjusted the re-computation strategy for each partition to utilize the available memory fully. We conducted extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of our method. Compared with the open-source training code of InternVL-Chat, we significantly reduced GPU days, achieving about 1.8x speed-up. Our method's efficacy and generalizability were further demonstrated across various models and datasets. Codes will be released at https://github.com/ModelTC/OmniBal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge