Feiyi Fan
Auto-Augmentation Contrastive Learning for Wearable-based Human Activity Recognition
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:For low-semantic sensor signals from human activity recognition (HAR), contrastive learning (CL) is essential to implement novel applications or generic models without manual annotation, which is a high-performance self-supervised learning (SSL) method. However, CL relies heavily on data augmentation for pairwise comparisons. Especially for low semantic data in the HAR area, conducting good performance augmentation strategies in pretext tasks still rely on manual attempts lacking generalizability and flexibility. To reduce the augmentation burden, we propose an end-to-end auto-augmentation contrastive learning (AutoCL) method for wearable-based HAR. AutoCL is based on a Siamese network architecture that shares the parameters of the backbone and with a generator embedded to learn auto-augmentation. AutoCL trains the generator based on the representation in the latent space to overcome the disturbances caused by noise and redundant information in raw sensor data. The architecture empirical study indicates the effectiveness of this design. Furthermore, we propose a stop-gradient design and correlation reduction strategy in AutoCL to enhance encoder representation learning. Extensive experiments based on four wide-used HAR datasets demonstrate that the proposed AutoCL method significantly improves recognition accuracy compared with other SOTA methods.
MLCask: Efficient Management of Component Evolution in Collaborative Data Analytics Pipelines
Oct 17, 2020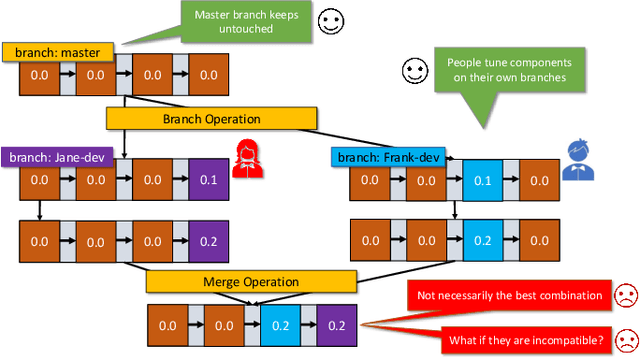
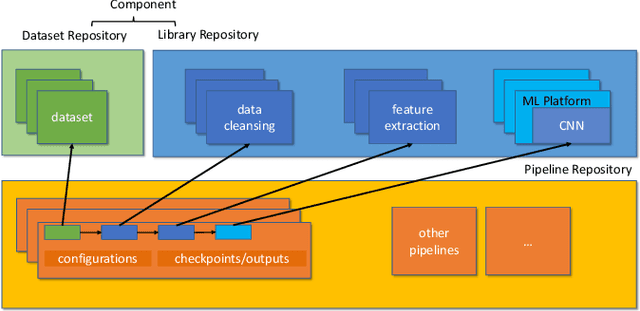
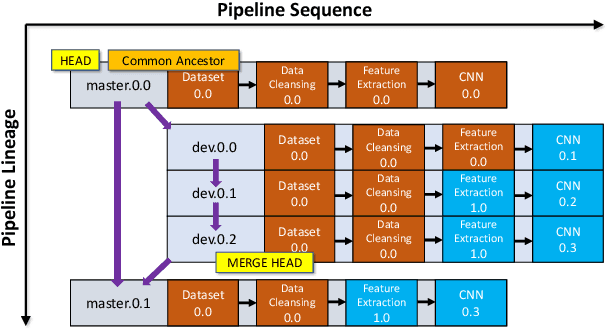
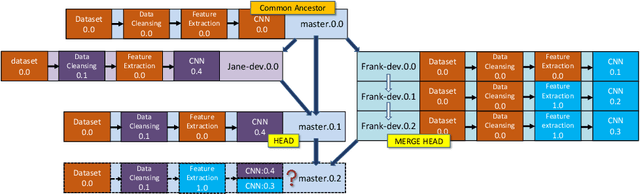
Abstract:With the ever-increasing adoption of machine learning for data analytics, maintaining a machine learning pipeline is becoming more complex as both the datasets and trained models evolve with time. In a collaborative environment, the changes and updates due to pipeline evolution often cause cumbersome coordination and maintenance work, raising the costs and making it hard to use. Existing solutions, unfortunately, do not address the version evolution problem, especially in a collaborative environment where non-linear version control semantics are necessary to isolate operations made by different user roles. The lack of version control semantics also incurs unnecessary storage consumption and lowers efficiency due to data duplication and repeated data pre-processing, which are avoidable. In this paper, we identify two main challenges that arise during the deployment of machine learning pipelines, and address them with the design of versioning for an end-to-end analytics system MLCask. The system supports multiple user roles with the ability to perform Git-like branching and merging operations in the context of the machine learning pipelines. We define and accelerate the metric-driven merge operation by pruning the pipeline search tree using reusable history records and pipeline compatibility information. Further, we design and implement the prioritized pipeline search, which gives preference to the pipelines that probably yield better performance. The effectiveness of MLCask is evaluated through an extensive study over several real-world deployment cases. The performance evaluation shows that the proposed merge operation is up to 7.8x faster and saves up to 11.9x storage space than the baseline method that does not utilize history records.
Attentive Geo-Social Group Recommendation
Nov 15, 2019



Abstract:Social activities play an important role in people's daily life since they interact. For recommendations based on social activities, it is vital to have not only the activity information but also individuals' social relations. Thanks to the geo-social networks and widespread use of location-aware mobile devices, massive geo-social data is now readily available for exploitation by the recommendation system. In this paper, a novel group recommendation method, called attentive geo-social group recommendation, is proposed to recommend the target user with both activity locations and a group of users that may join the activities. We present an attention mechanism to model the influence of the target user $u_T$ in candidate user groups that satisfy the social constraints. It helps to retrieve the optimal user group and activity topic candidates, as well as explains the group decision-making process. Once the user group and topics are retrieved, a novel efficient spatial query algorithm SPA-DF is employed to determine the activity location under the constraints of the given user group and activity topic candidates. The proposed method is evaluated in real-world datasets and the experimental results show that the proposed model significantly outperforms baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge