Ethan Henderson
Benchmarking Egocentric Multimodal Goal Inference for Assistive Wearable Agents
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:There has been a surge of interest in assistive wearable agents: agents embodied in wearable form factors (e.g., smart glasses) who take assistive actions toward a user's goal/query (e.g. "Where did I leave my keys?"). In this work, we consider the important complementary problem of inferring that goal from multi-modal contextual observations. Solving this "goal inference" problem holds the promise of eliminating the effort needed to interact with such an agent. This work focuses on creating WAGIBench, a strong benchmark to measure progress in solving this problem using vision-language models (VLMs). Given the limited prior work in this area, we collected a novel dataset comprising 29 hours of multimodal data from 348 participants across 3,477 recordings, featuring ground-truth goals alongside accompanying visual, audio, digital, and longitudinal contextual observations. We validate that human performance exceeds model performance, achieving 93% multiple-choice accuracy compared with 84% for the best-performing VLM. Generative benchmark results that evaluate several families of modern vision-language models show that larger models perform significantly better on the task, yet remain far from practical usefulness, as they produce relevant goals only 55% of the time. Through a modality ablation, we show that models benefit from extra information in relevant modalities with minimal performance degradation from irrelevant modalities.
TorchAudio-Squim: Reference-less Speech Quality and Intelligibility measures in TorchAudio
Apr 04, 2023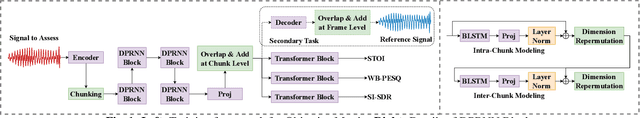
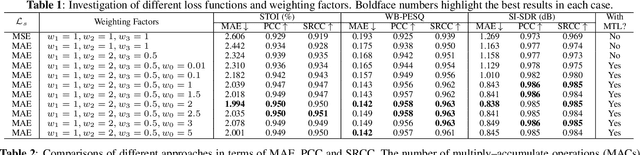
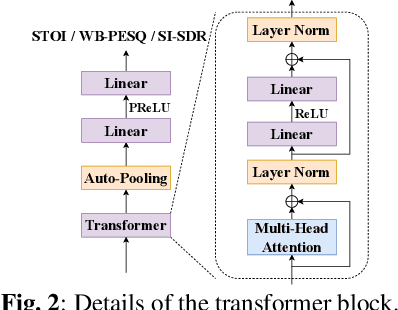
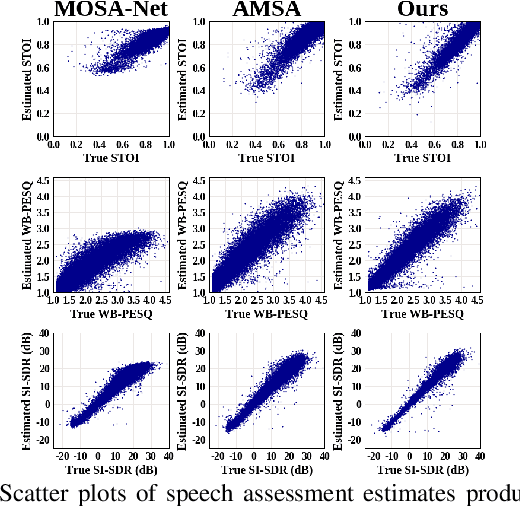
Abstract:Measuring quality and intelligibility of a speech signal is usually a critical step in development of speech processing systems. To enable this, a variety of metrics to measure quality and intelligibility under different assumptions have been developed. Through this paper, we introduce tools and a set of models to estimate such known metrics using deep neural networks. These models are made available in the well-established TorchAudio library, the core audio and speech processing library within the PyTorch deep learning framework. We refer to it as TorchAudio-Squim, TorchAudio-Speech QUality and Intelligibility Measures. More specifically, in the current version of TorchAudio-squim, we establish and release models for estimating PESQ, STOI and SI-SDR among objective metrics and MOS among subjective metrics. We develop a novel approach for objective metric estimation and use a recently developed approach for subjective metric estimation. These models operate in a ``reference-less" manner, that is they do not require the corresponding clean speech as reference for speech assessment. Given the unavailability of clean speech and the effortful process of subjective evaluation in real-world situations, such easy-to-use tools would greatly benefit speech processing research and development.
Chat2Map: Efficient Scene Mapping from Multi-Ego Conversations
Jan 04, 2023
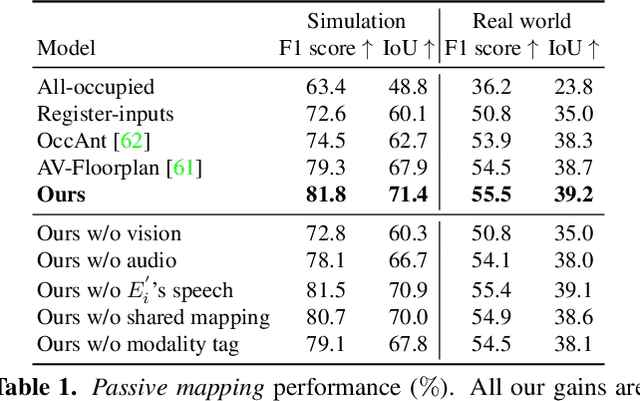

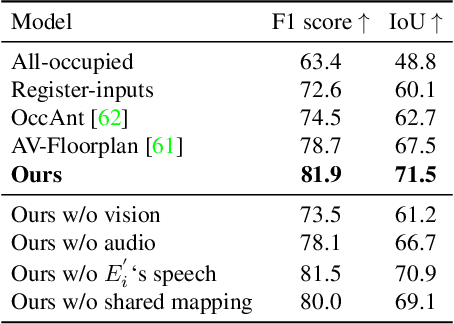
Abstract:Can conversational videos captured from multiple egocentric viewpoints reveal the map of a scene in a cost-efficient way? We seek to answer this question by proposing a new problem: efficiently building the map of a previously unseen 3D environment by exploiting shared information in the egocentric audio-visual observations of participants in a natural conversation. Our hypothesis is that as multiple people ("egos") move in a scene and talk among themselves, they receive rich audio-visual cues that can help uncover the unseen areas of the scene. Given the high cost of continuously processing egocentric visual streams, we further explore how to actively coordinate the sampling of visual information, so as to minimize redundancy and reduce power use. To that end, we present an audio-visual deep reinforcement learning approach that works with our shared scene mapper to selectively turn on the camera to efficiently chart out the space. We evaluate the approach using a state-of-the-art audio-visual simulator for 3D scenes as well as real-world video. Our model outperforms previous state-of-the-art mapping methods, and achieves an excellent cost-accuracy tradeoff. Project: http://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/chat2map.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge