Emanuele Dalsasso
EPFL
SMARTIES: Spectrum-Aware Multi-Sensor Auto-Encoder for Remote Sensing Images
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:From optical sensors to microwave radars, leveraging the complementary strengths of remote sensing (RS) sensors is crucial for achieving dense spatio-temporal monitoring of our planet. In contrast, recent deep learning models, whether task-specific or foundational, are often specific to single sensors or to fixed combinations: adapting such models to different sensory inputs requires both architectural changes and re-training, limiting scalability and generalization across multiple RS sensors. On the contrary, a single model able to modulate its feature representations to accept diverse sensors as input would pave the way to agile and flexible multi-sensor RS data processing. To address this, we introduce SMARTIES, a generic and versatile foundation model lifting sensor-specific/dependent efforts and enabling scalability and generalization to diverse RS sensors: SMARTIES projects data from heterogeneous sensors into a shared spectrum-aware space, enabling the use of arbitrary combinations of bands both for training and inference. To obtain sensor-agnostic representations, we train a single, unified transformer model reconstructing masked multi-sensor data with cross-sensor token mixup. On both single- and multi-modal tasks across diverse sensors, SMARTIES outperforms previous models that rely on sensor-specific pretraining. Our code and pretrained models are available at https://gsumbul.github.io/SMARTIES.
CanadaFireSat: Toward high-resolution wildfire forecasting with multiple modalities
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Canada experienced in 2023 one of the most severe wildfire seasons in recent history, causing damage across ecosystems, destroying communities, and emitting large quantities of CO2. This extreme wildfire season is symptomatic of a climate-change-induced increase in the length and severity of the fire season that affects the boreal ecosystem. Therefore, it is critical to empower wildfire management in boreal communities with better mitigation solutions. Wildfire probability maps represent an important tool for understanding the likelihood of wildfire occurrence and the potential severity of future wildfires. The massive increase in the availability of Earth observation data has enabled the development of deep learning-based wildfire forecasting models, aiming at providing precise wildfire probability maps at different spatial and temporal scales. A main limitation of such methods is their reliance on coarse-resolution environmental drivers and satellite products, leading to wildfire occurrence prediction of reduced resolution, typically around $\sim 0.1${\deg}. This paper presents a benchmark dataset: CanadaFireSat, and baseline methods for high-resolution: 100 m wildfire forecasting across Canada, leveraging multi-modal data from high-resolution multi-spectral satellite images (Sentinel-2 L1C), mid-resolution satellite products (MODIS), and environmental factors (ERA5 reanalysis data). Our experiments consider two major deep learning architectures. We observe that using multi-modal temporal inputs outperforms single-modal temporal inputs across all metrics, achieving a peak performance of 60.3% in F1 score for the 2023 wildfire season, a season never seen during model training. This demonstrates the potential of multi-modal deep learning models for wildfire forecasting at high-resolution and continental scale.
Multi-Scale and Multimodal Species Distribution Modeling
Nov 06, 2024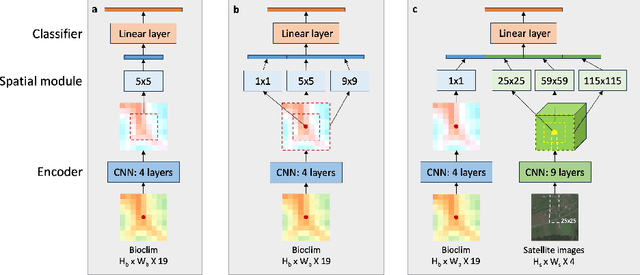
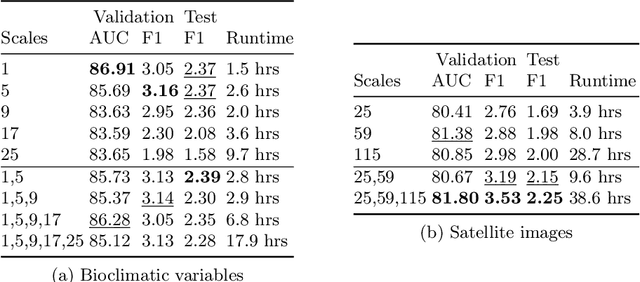
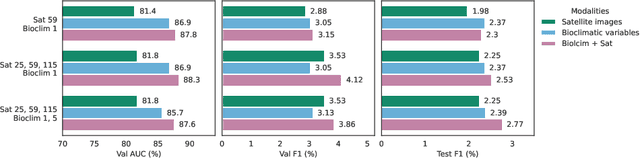
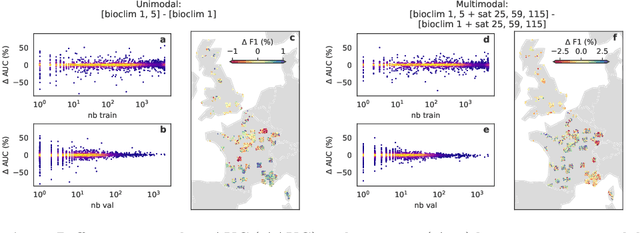
Abstract:Species distribution models (SDMs) aim to predict the distribution of species by relating occurrence data with environmental variables. Recent applications of deep learning to SDMs have enabled new avenues, specifically the inclusion of spatial data (environmental rasters, satellite images) as model predictors, allowing the model to consider the spatial context around each species' observations. However, the appropriate spatial extent of the images is not straightforward to determine and may affect the performance of the model, as scale is recognized as an important factor in SDMs. We develop a modular structure for SDMs that allows us to test the effect of scale in both single- and multi-scale settings. Furthermore, our model enables different scales to be considered for different modalities, using a late fusion approach. Results on the GeoLifeCLEF 2023 benchmark indicate that considering multimodal data and learning multi-scale representations leads to more accurate models.
POLO -- Point-based, multi-class animal detection
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Automated wildlife surveys based on drone imagery and object detection technology are a powerful and increasingly popular tool in conservation biology. Most detectors require training images with annotated bounding boxes, which are tedious, expensive, and not always unambiguous to create. To reduce the annotation load associated with this practice, we develop POLO, a multi-class object detection model that can be trained entirely on point labels. POLO is based on simple, yet effective modifications to the YOLOv8 architecture, including alterations to the prediction process, training losses, and post-processing. We test POLO on drone recordings of waterfowl containing up to multiple thousands of individual birds in one image and compare it to a regular YOLOv8. Our experiments show that at the same annotation cost, POLO achieves improved accuracy in counting animals in aerial imagery.
Multi-Scale Grouped Prototypes for Interpretable Semantic Segmentation
Sep 14, 2024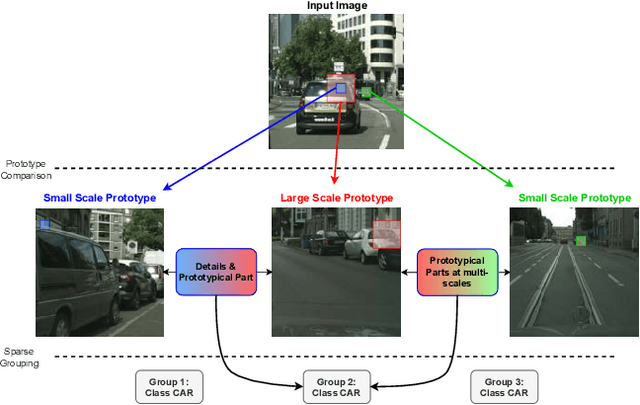
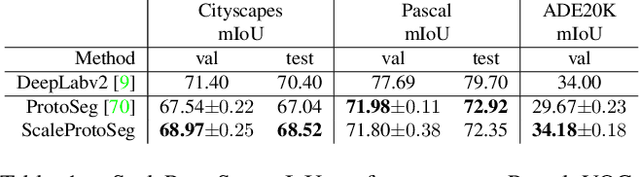
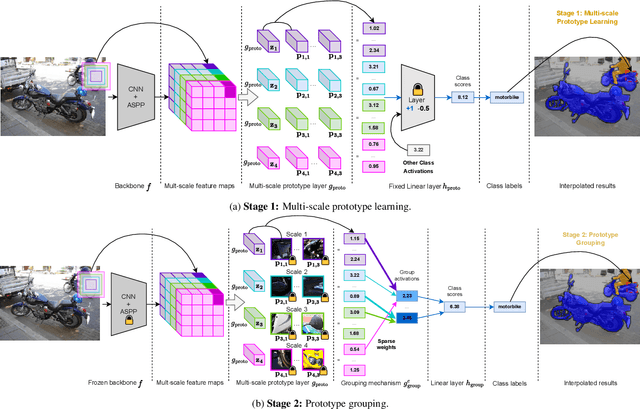
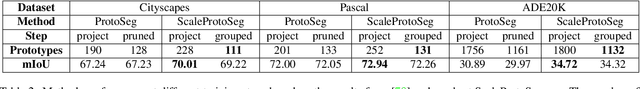
Abstract:Prototypical part learning is emerging as a promising approach for making semantic segmentation interpretable. The model selects real patches seen during training as prototypes and constructs the dense prediction map based on the similarity between parts of the test image and the prototypes. This improves interpretability since the user can inspect the link between the predicted output and the patterns learned by the model in terms of prototypical information. In this paper, we propose a method for interpretable semantic segmentation that leverages multi-scale image representation for prototypical part learning. First, we introduce a prototype layer that explicitly learns diverse prototypical parts at several scales, leading to multi-scale representations in the prototype activation output. Then, we propose a sparse grouping mechanism that produces multi-scale sparse groups of these scale-specific prototypical parts. This provides a deeper understanding of the interactions between multi-scale object representations while enhancing the interpretability of the segmentation model. The experiments conducted on Pascal VOC, Cityscapes, and ADE20K demonstrate that the proposed method increases model sparsity, improves interpretability over existing prototype-based methods, and narrows the performance gap with the non-interpretable counterpart models. Code is available at github.com/eceo-epfl/ScaleProtoSeg.
Just Project! Multi-Channel Despeckling, the Easy Way
Aug 21, 2024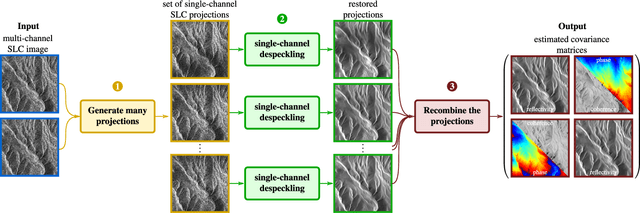
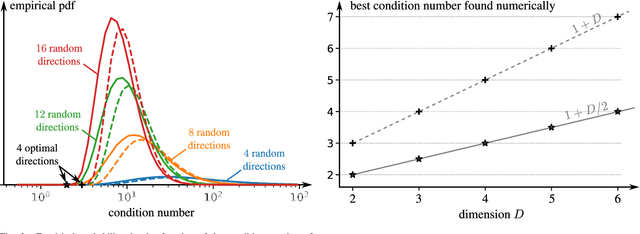
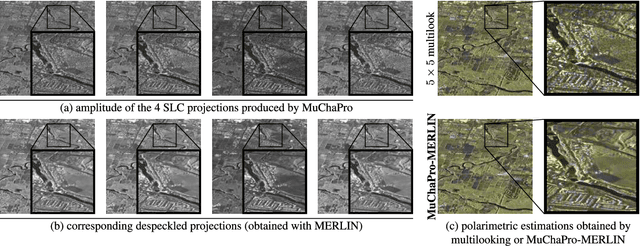
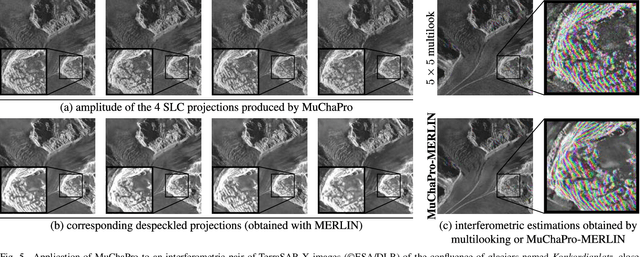
Abstract:Reducing speckle fluctuations in multi-channel SAR images is essential in many applications of SAR imaging such as polarimetric classification or interferometric height estimation. While single-channel despeckling has widely benefited from the application of deep learning techniques, extensions to multi-channel SAR images are much more challenging.This paper introduces MuChaPro, a generic framework that exploits existing single-channel despeckling methods. The key idea is to generate numerous single-channel projections, restore these projections, and recombine them into the final multi-channel estimate. This simple approach is shown to be effective in polarimetric and/or interferometric modalities. A special appeal of MuChaPro is the possibility to apply a self-supervised training strategy to learn sensor-specific networks for single-channel despeckling.
Leveraging Vision-Language Foundation Models for Fine-Grained Downstream Tasks
Jul 13, 2023



Abstract:Vision-language foundation models such as CLIP have shown impressive zero-shot performance on many tasks and datasets, especially thanks to their free-text inputs. However, they struggle to handle some downstream tasks, such as fine-grained attribute detection and localization. In this paper, we propose a multitask fine-tuning strategy based on a positive/negative prompt formulation to further leverage the capacities of the vision-language foundation models. Using the CLIP architecture as baseline, we show strong improvements on bird fine-grained attribute detection and localization tasks, while also increasing the classification performance on the CUB200-2011 dataset. We provide source code for reproducibility purposes: it is available at https://github.com/FactoDeepLearning/MultitaskVLFM.
Multi-temporal speckle reduction with self-supervised deep neural networks
Jul 25, 2022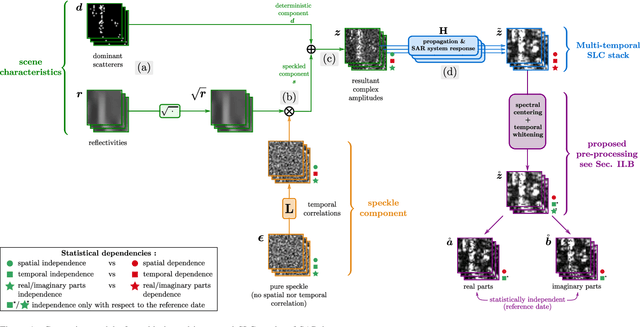
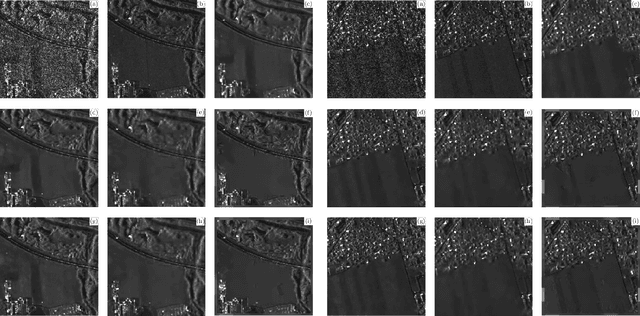
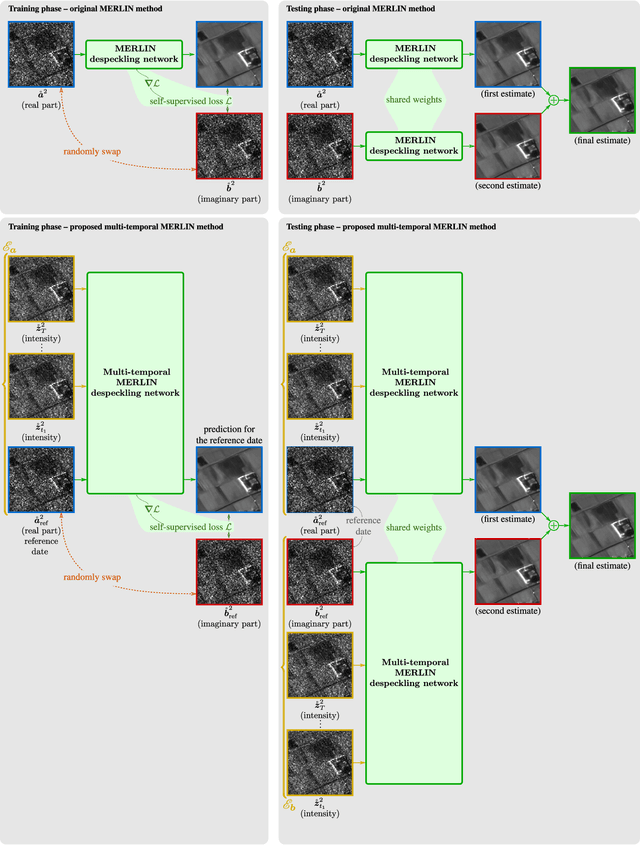
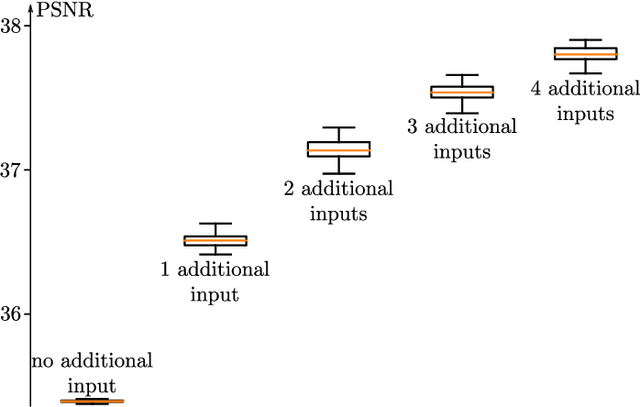
Abstract:Speckle filtering is generally a prerequisite to the analysis of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images. Tremendous progress has been achieved in the domain of single-image despeckling. Latest techniques rely on deep neural networks to restore the various structures and textures peculiar to SAR images. The availability of time series of SAR images offers the possibility of improving speckle filtering by combining different speckle realizations over the same area. The supervised training of deep neural networks requires ground-truth speckle-free images. Such images can only be obtained indirectly through some form of averaging, by spatial or temporal integration, and are imperfect. Given the potential of very high quality restoration reachable by multi-temporal speckle filtering, the limitations of ground-truth images need to be circumvented. We extend a recent self-supervised training strategy for single-look complex SAR images, called MERLIN, to the case of multi-temporal filtering. This requires modeling the sources of statistical dependencies in the spatial and temporal dimensions as well as between the real and imaginary components of the complex amplitudes. Quantitative analysis on datasets with simulated speckle indicates a clear improvement of speckle reduction when additional SAR images are included. Our method is then applied to stacks of TerraSAR-X images and shown to outperform competing multi-temporal speckle filtering approaches. The code of the trained models is made freely available on the Gitlab of the IMAGES team of the LTCI Lab, T\'el\'ecom Paris Institut Polytechnique de Paris (https://gitlab.telecom-paris.fr/ring/multi-temporal-merlin/).
Fast strategies for multi-temporal speckle reduction of Sentinel-1 GRD images
Jul 22, 2022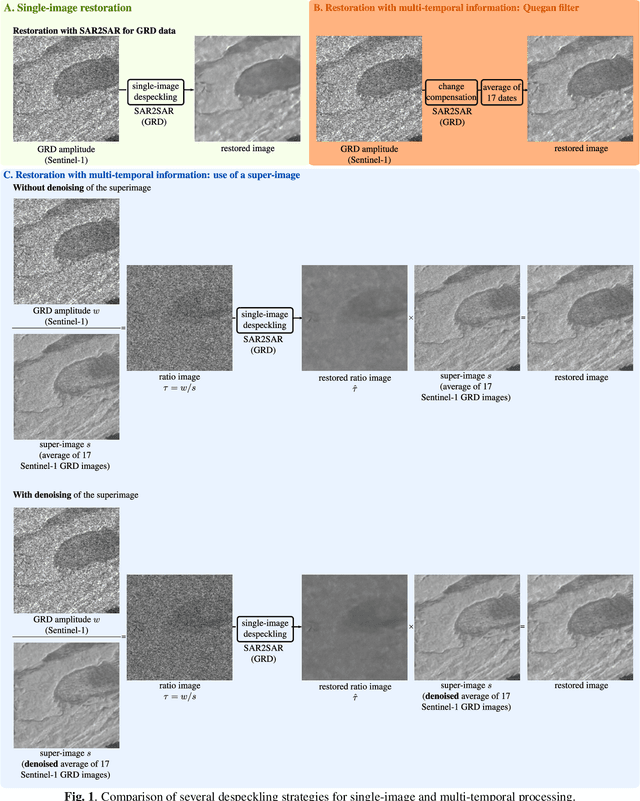
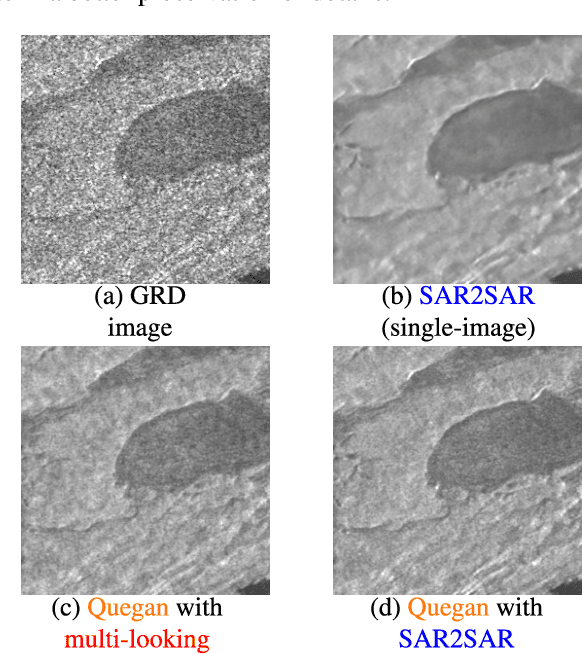
Abstract:Reducing speckle and limiting the variations of the physical parameters in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images is often a key-step to fully exploit the potential of such data. Nowadays, deep learning approaches produce state of the art results in single-image SAR restoration. Nevertheless, huge multi-temporal stacks are now often available and could be efficiently exploited to further improve image quality. This paper explores two fast strategies employing a single-image despeckling algorithm, namely SAR2SAR, in a multi-temporal framework. The first one is based on Quegan filter and replaces the local reflectivity pre-estimation by SAR2SAR. The second one uses SAR2SAR to suppress speckle from a ratio image encoding the multi-temporal information under the form of a "super-image", i.e. the temporal arithmetic mean of a time series. Experimental results on Sentinel-1 GRD data show that these two multi-temporal strategies provide improved filtering results while adding a limited computational cost.
As if by magic: self-supervised training of deep despeckling networks with MERLIN
Nov 15, 2021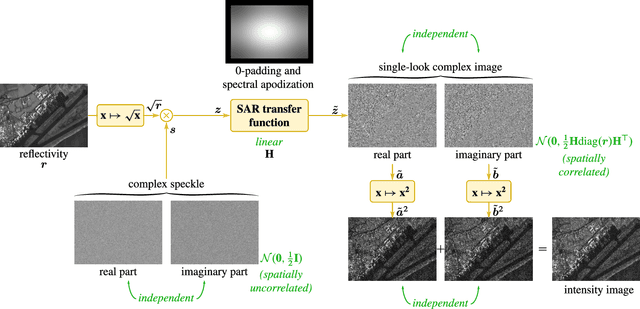
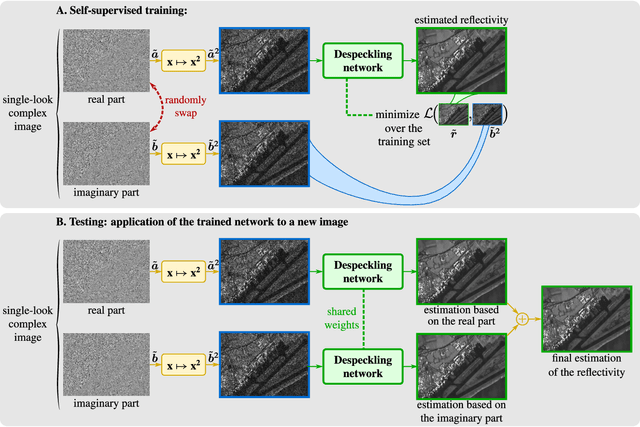
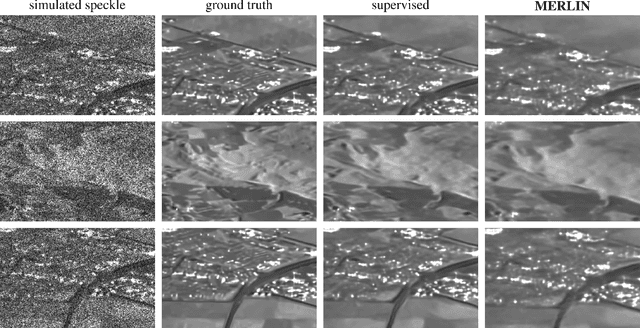
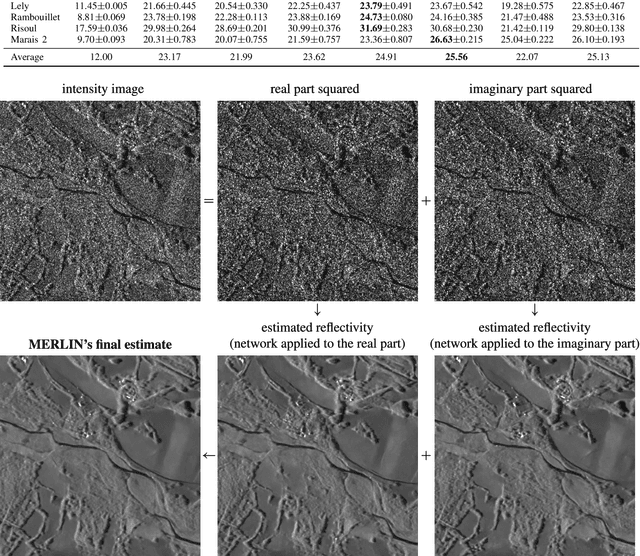
Abstract:Speckle fluctuations seriously limit the interpretability of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images. Speckle reduction has thus been the subject of numerous works spanning at least four decades. Techniques based on deep neural networks have recently achieved a new level of performance in terms of SAR image restoration quality. Beyond the design of suitable network architectures or the selection of adequate loss functions, the construction of training sets is of uttermost importance. So far, most approaches have considered a supervised training strategy: the networks are trained to produce outputs as close as possible to speckle-free reference images. Speckle-free images are generally not available, which requires resorting to natural or optical images or the selection of stable areas in long time series to circumvent the lack of ground truth. Self-supervision, on the other hand, avoids the use of speckle-free images. We introduce a self-supervised strategy based on the separation of the real and imaginary parts of single-look complex SAR images, called MERLIN (coMplex sElf-supeRvised despeckLINg), and show that it offers a straightforward way to train all kinds of deep despeckling networks. Networks trained with MERLIN take into account the spatial correlations due to the SAR transfer function specific to a given sensor and imaging mode. By requiring only a single image, and possibly exploiting large archives, MERLIN opens the door to hassle-free as well as large-scale training of despeckling networks. The code of the trained models is made freely available at https://gitlab.telecom-paris.fr/RING/MERLIN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge