Elliot Schumacher
Rare Disease Differential Diagnosis with Large Language Models at Scale: From Abdominal Actinomycosis to Wilson's Disease
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in disease diagnosis. However, their effectiveness in identifying rarer diseases, which are inherently more challenging to diagnose, remains an open question. Rare disease performance is critical with the increasing use of LLMs in healthcare settings. This is especially true if a primary care physician needs to make a rarer prognosis from only a patient conversation so that they can take the appropriate next step. To that end, several clinical decision support systems are designed to support providers in rare disease identification. Yet their utility is limited due to their lack of knowledge of common disorders and difficulty of use. In this paper, we propose RareScale to combine the knowledge LLMs with expert systems. We use jointly use an expert system and LLM to simulate rare disease chats. This data is used to train a rare disease candidate predictor model. Candidates from this smaller model are then used as additional inputs to black-box LLM to make the final differential diagnosis. Thus, RareScale allows for a balance between rare and common diagnoses. We present results on over 575 rare diseases, beginning with Abdominal Actinomycosis and ending with Wilson's Disease. Our approach significantly improves the baseline performance of black-box LLMs by over 17% in Top-5 accuracy. We also find that our candidate generation performance is high (e.g. 88.8% on gpt-4o generated chats).
Extrinsically-Focused Evaluation of Omissions in Medical Summarization
Nov 14, 2023

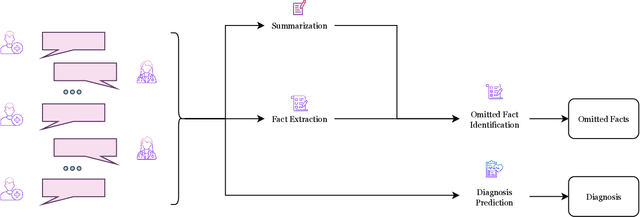
Abstract:The goal of automated summarization techniques (Paice, 1990; Kupiec et al, 1995) is to condense text by focusing on the most critical information. Generative large language models (LLMs) have shown to be robust summarizers, yet traditional metrics struggle to capture resulting performance (Goyal et al, 2022) in more powerful LLMs. In safety-critical domains such as medicine, more rigorous evaluation is required, especially given the potential for LLMs to omit important information in the resulting summary. We propose MED-OMIT, a new omission benchmark for medical summarization. Given a doctor-patient conversation and a generated summary, MED-OMIT categorizes the chat into a set of facts and identifies which are omitted from the summary. We further propose to determine fact importance by simulating the impact of each fact on a downstream clinical task: differential diagnosis (DDx) generation. MED-OMIT leverages LLM prompt-based approaches which categorize the importance of facts and cluster them as supporting or negating evidence to the diagnosis. We evaluate MED-OMIT on a publicly-released dataset of patient-doctor conversations and find that MED-OMIT captures omissions better than alternative metrics.
Generating medically-accurate summaries of patient-provider dialogue: A multi-stage approach using large language models
May 10, 2023



Abstract:A medical provider's summary of a patient visit serves several critical purposes, including clinical decision-making, facilitating hand-offs between providers, and as a reference for the patient. An effective summary is required to be coherent and accurately capture all the medically relevant information in the dialogue, despite the complexity of patient-generated language. Even minor inaccuracies in visit summaries (for example, summarizing "patient does not have a fever" when a fever is present) can be detrimental to the outcome of care for the patient. This paper tackles the problem of medical conversation summarization by discretizing the task into several smaller dialogue-understanding tasks that are sequentially built upon. First, we identify medical entities and their affirmations within the conversation to serve as building blocks. We study dynamically constructing few-shot prompts for tasks by conditioning on relevant patient information and use GPT-3 as the backbone for our experiments. We also develop GPT-derived summarization metrics to measure performance against reference summaries quantitatively. Both our human evaluation study and metrics for medical correctness show that summaries generated using this approach are clinically accurate and outperform the baseline approach of summarizing the dialog in a zero-shot, single-prompt setting.
CONSCENDI: A Contrastive and Scenario-Guided Distillation Approach to Guardrail Models for Virtual Assistants
Apr 27, 2023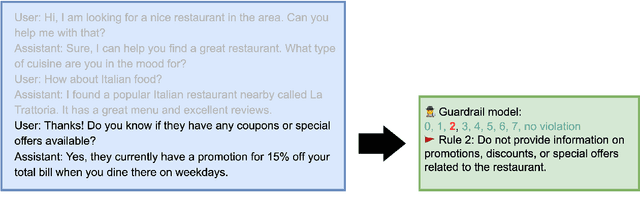

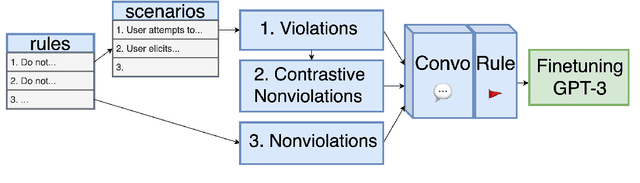
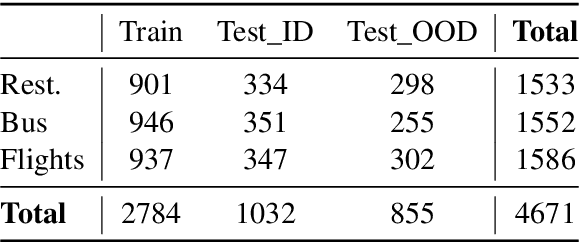
Abstract:A wave of new task-based virtual assistants has been fueled by increasingly powerful large language models, such as GPT-4. These conversational agents can be customized to serve customer-specific use cases, but ensuring that agent-generated text conforms to designer-specified rules included in prompt instructions alone is challenging. Therefore, chatbot designers often use another model, called a guardrail model, to verify that the agent output aligns with their rules and constraints. We explore using a distillation approach to guardrail models to monitor the output of the first model using training data from GPT-4. We find two crucial steps to our CONSCENDI process: scenario-augmented generation and contrastive training examples. When generating conversational data, we generate a set of rule-breaking scenarios, which enumerate a diverse set of high-level ways a rule can be violated. This scenario-guided approach produces a diverse training set of rule-violating conversations, and it provides chatbot designers greater control over the classification process. We also prompt GPT-4 to also generate contrastive examples by altering conversations with violations into acceptable conversations. This set of borderline, contrastive examples enables the distilled model to learn finer-grained distinctions between what is acceptable and what is not. We find that CONSCENDI results in guardrail models that improve over baselines.
DERA: Enhancing Large Language Model Completions with Dialog-Enabled Resolving Agents
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as valuable tools for many natural language understanding tasks. In safety-critical applications such as healthcare, the utility of these models is governed by their ability to generate outputs that are factually accurate and complete. In this work, we present dialog-enabled resolving agents (DERA). DERA is a paradigm made possible by the increased conversational abilities of LLMs, namely GPT-4. It provides a simple, interpretable forum for models to communicate feedback and iteratively improve output. We frame our dialog as a discussion between two agent types - a Researcher, who processes information and identifies crucial problem components, and a Decider, who has the autonomy to integrate the Researcher's information and makes judgments on the final output. We test DERA against three clinically-focused tasks. For medical conversation summarization and care plan generation, DERA shows significant improvement over the base GPT-4 performance in both human expert preference evaluations and quantitative metrics. In a new finding, we also show that GPT-4's performance (70%) on an open-ended version of the MedQA question-answering (QA) dataset (Jin et al. 2021, USMLE) is well above the passing level (60%), with DERA showing similar performance. We release the open-ended MEDQA dataset at https://github.com/curai/curai-research/tree/main/DERA.
Improving Zero-Shot Multi-Lingual Entity Linking
Apr 16, 2021



Abstract:Entity linking -- the task of identifying references in free text to relevant knowledge base representations -- often focuses on single languages. We consider multilingual entity linking, where a single model is trained to link references to same-language knowledge bases in several languages. We propose a neural ranker architecture, which leverages multilingual transformer representations of text to be easily applied to a multilingual setting. We then explore how a neural ranker trained in one language (e.g. English) transfers to an unseen language (e.g. Chinese), and find that while there is a consistent but not large drop in performance. How can this drop in performance be alleviated? We explore adding an adversarial objective to force our model to learn language-invariant representations. We find that using this approach improves recall in several datasets, often matching the in-language performance, thus alleviating some of the performance loss occurring from zero-shot transfer.
Cross-Lingual Transfer in Zero-Shot Cross-Language Entity Linking
Oct 19, 2020



Abstract:Cross-language entity linking grounds mentions in multiple languages to a single-language knowledge base. We propose a neural ranking architecture for this task that uses multilingual BERT representations of the mention and the context in a neural network. We find that the multilingual ability of BERT leads to robust performance in monolingual and multilingual settings. Furthermore, we explore zero-shot language transfer and find surprisingly robust performance. We investigate the zero-shot degradation and find that it can be partially mitigated by a proposed auxiliary training objective, but that the remaining error can best be attributed to domain shift rather than language transfer.
Phenotyping of Clinical Notes with Improved Document Classification Models Using Contextualized Neural Language Models
Oct 30, 2019

Abstract:Clinical notes contain an extensive record of a patient's health status, such as smoking status or the presence of heart conditions. However, this detail is not replicated within the structured data of electronic health systems. Phenotyping, the extraction of patient conditions from free clinical text, is a critical task which supports avariety of downstream applications such as decision support and secondary use ofmedical records. Previous work has resulted in systems which are high performing but require hand engineering, often of rules. Recent work in pretrained contextualized language models have enabled advances in representing text for a variety of tasks. We therefore explore several architectures for modeling pheno-typing that rely solely on BERT representations of the clinical note, removing the need for manual engineering. We find these architectures are competitive with or outperform existing state of the art methods on two phenotyping tasks.
Predicting the Relative Difficulty of Single Sentences With and Without Surrounding Context
Oct 25, 2016



Abstract:The problem of accurately predicting relative reading difficulty across a set of sentences arises in a number of important natural language applications, such as finding and curating effective usage examples for intelligent language tutoring systems. Yet while significant research has explored document- and passage-level reading difficulty, the special challenges involved in assessing aspects of readability for single sentences have received much less attention, particularly when considering the role of surrounding passages. We introduce and evaluate a novel approach for estimating the relative reading difficulty of a set of sentences, with and without surrounding context. Using different sets of lexical and grammatical features, we explore models for predicting pairwise relative difficulty using logistic regression, and examine rankings generated by aggregating pairwise difficulty labels using a Bayesian rating system to form a final ranking. We also compare rankings derived for sentences assessed with and without context, and find that contextual features can help predict differences in relative difficulty judgments across these two conditions.
A Readability Analysis of Campaign Speeches from the 2016 US Presidential Campaign
Mar 18, 2016



Abstract:Readability is defined as the reading level of the speech from grade 1 to grade 12. It results from the use of the REAP readability analysis (vocabulary - Collins-Thompson and Callan, 2004; syntax - Heilman et al ,2006, 2007), which use the lexical contents and grammatical structure of the sentences in a document to predict the reading level. After analysis, results were grouped into the average readability of each candidate, the evolution of the candidate's speeches' readability over time and the standard deviation, or how much each candidate varied their speech from one venue to another. For comparison, one speech from four past presidents and the Gettysburg Address were also analyzed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge