Eilif Muller
seq-JEPA: Autoregressive Predictive Learning of Invariant-Equivariant World Models
May 06, 2025Abstract:Current self-supervised algorithms mostly rely on transformations such as data augmentation and masking to learn visual representations. This is achieved by inducing invariance or equivariance with respect to these transformations after encoding two views of an image. This dominant two-view paradigm can limit the flexibility of learned representations for downstream adaptation by creating performance trade-offs between invariance-related tasks such as image classification and more fine-grained equivariance-related tasks. In this work, we introduce \emph{seq-JEPA}, a world modeling paradigm based on joint-embedding predictive architecture that leverages architectural inductive biases to resolve this trade-off. Without requiring an additional equivariance predictor or loss term, seq-JEPA simultaneously learns two architecturally segregated representations: one equivariant to the specified transformations and another invariant to them and suited for tasks such as classification. To do so, our model processes a short sequence of different views (observations) of an input image. Each encoded view is concatenated with embeddings corresponding to the relative transformation (action) producing the next observation in the sequence. A transformer encoder outputs an aggregate representation of this sequence, which is subsequently conditioned on the action leading to the next observation to predict its representation. Empirically, seq-JEPA achieves strong performance on equivariant benchmarks and image classification without sacrificing one for the other. Additionally, our framework excels at tasks that inherently require aggregating a sequence of observations, such as path integration across actions and predictive learning across eye movements.
Generating Diverse Realistic Laughter for Interactive Art
Nov 04, 2021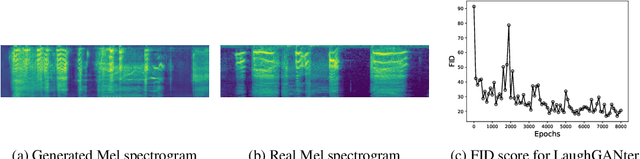
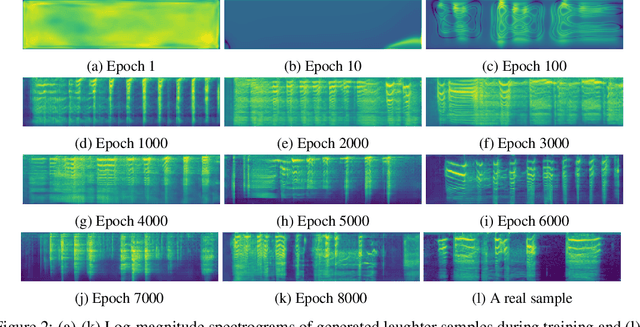
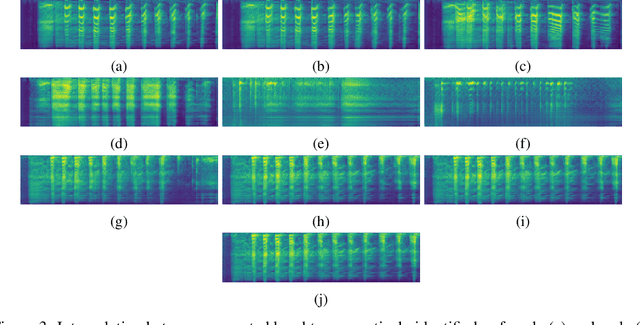
Abstract:We propose an interactive art project to make those rendered invisible by the COVID-19 crisis and its concomitant solitude reappear through the welcome melody of laughter, and connections created and explored through advanced laughter synthesis approaches. However, the unconditional generation of the diversity of human emotional responses in high-quality auditory synthesis remains an open problem, with important implications for the application of these approaches in artistic settings. We developed LaughGANter, an approach to reproduce the diversity of human laughter using generative adversarial networks (GANs). When trained on a dataset of diverse laughter samples, LaughGANter generates diverse, high quality laughter samples, and learns a latent space suitable for emotional analysis and novel artistic applications such as latent mixing/interpolation and emotional transfer.
Predicting Infectiousness for Proactive Contact Tracing
Oct 23, 2020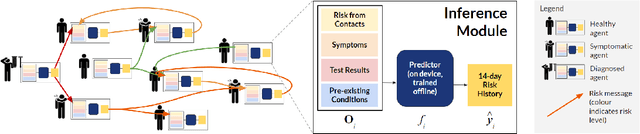
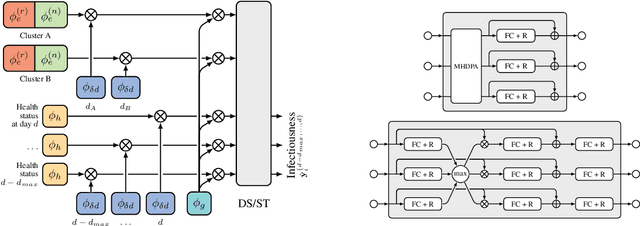
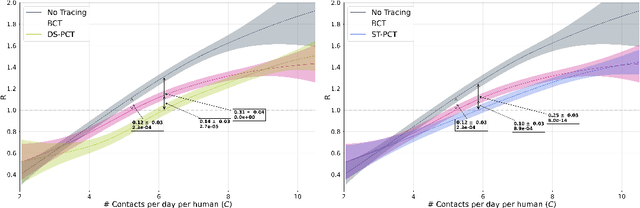
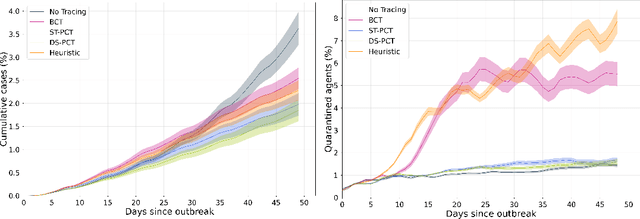
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has spread rapidly worldwide, overwhelming manual contact tracing in many countries and resulting in widespread lockdowns for emergency containment. Large-scale digital contact tracing (DCT) has emerged as a potential solution to resume economic and social activity while minimizing spread of the virus. Various DCT methods have been proposed, each making trade-offs between privacy, mobility restrictions, and public health. The most common approach, binary contact tracing (BCT), models infection as a binary event, informed only by an individual's test results, with corresponding binary recommendations that either all or none of the individual's contacts quarantine. BCT ignores the inherent uncertainty in contacts and the infection process, which could be used to tailor messaging to high-risk individuals, and prompt proactive testing or earlier warnings. It also does not make use of observations such as symptoms or pre-existing medical conditions, which could be used to make more accurate infectiousness predictions. In this paper, we use a recently-proposed COVID-19 epidemiological simulator to develop and test methods that can be deployed to a smartphone to locally and proactively predict an individual's infectiousness (risk of infecting others) based on their contact history and other information, while respecting strong privacy constraints. Predictions are used to provide personalized recommendations to the individual via an app, as well as to send anonymized messages to the individual's contacts, who use this information to better predict their own infectiousness, an approach we call proactive contact tracing (PCT). We find a deep-learning based PCT method which improves over BCT for equivalent average mobility, suggesting PCT could help in safe re-opening and second-wave prevention.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge