Edoardo Nemni
Conditional Progressive Generative Adversarial Network for satellite image generation
Nov 28, 2022


Abstract:Image generation and image completion are rapidly evolving fields, thanks to machine learning algorithms that are able to realistically replace missing pixels. However, generating large high resolution images, with a large level of details, presents important computational challenges. In this work, we formulate the image generation task as completion of an image where one out of three corners is missing. We then extend this approach to iteratively build larger images with the same level of detail. Our goal is to obtain a scalable methodology to generate high resolution samples typically found in satellite imagery data sets. We introduce a conditional progressive Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), that generates the missing tile in an image, using as input three initial adjacent tiles encoded in a latent vector by a Wasserstein auto-encoder. We focus on a set of images used by the United Nations Satellite Centre (UNOSAT) to train flood detection tools, and validate the quality of synthetic images in a realistic setup.
Deep learning based landslide density estimation on SAR data for rapid response
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:This work aims to produce landslide density estimates using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite imageries to prioritise emergency resources for rapid response. We use the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Landslide Inventory data annotated by experts after Hurricane Mar\'ia in Puerto Rico on Sept 20, 2017, and their subsequent susceptibility study which uses extensive additional information such as precipitation, soil moisture, geological terrain features, closeness to waterways and roads, etc. Since such data might not be available during other events or regions, we aimed to produce a landslide density map using only elevation and SAR data to be useful to decision-makers in rapid response scenarios. The USGS Landslide Inventory contains the coordinates of 71,431 landslide heads (not their full extent) and was obtained by manual inspection of aerial and satellite imagery. It is estimated that around 45\% of the landslides are smaller than a Sentinel-1 typical pixel which is 10m $\times$ 10m, although many are long and thin, probably leaving traces across several pixels. Our method obtains 0.814 AUC in predicting the correct density estimation class at the chip level (128$\times$128 pixels, at Sentinel-1 resolution) using only elevation data and up to three SAR acquisitions pre- and post-hurricane, thus enabling rapid assessment after a disaster. The USGS Susceptibility Study reports a 0.87 AUC, but it is measured at the landslide level and uses additional information sources (such as proximity to fluvial channels, roads, precipitation, etc.) which might not regularly be available in an rapid response emergency scenario.
SAR-based landslide classification pretraining leads to better segmentation
Nov 17, 2022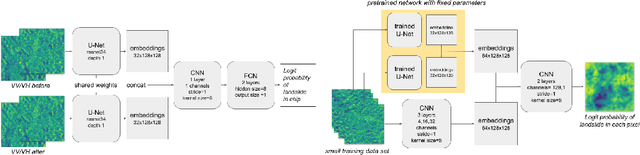
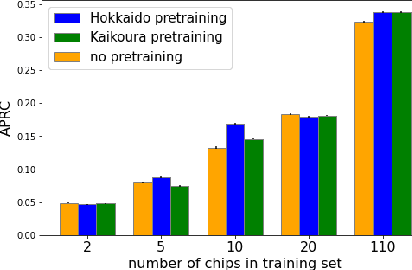
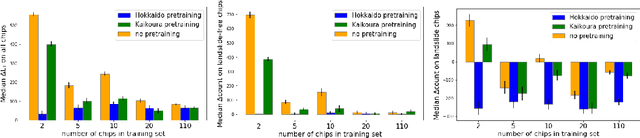
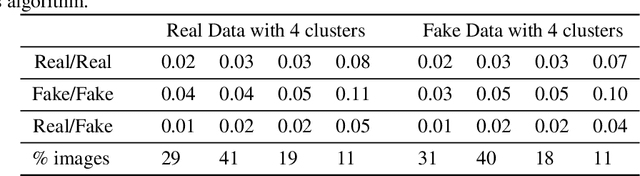
Abstract:Rapid assessment after a natural disaster is key for prioritizing emergency resources. In the case of landslides, rapid assessment involves determining the extent of the area affected and measuring the size and location of individual landslides. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is an active remote sensing technique that is unaffected by weather conditions. Deep Learning algorithms can be applied to SAR data, but training them requires large labeled datasets. In the case of landslides, these datasets are laborious to produce for segmentation, and often they are not available for the specific region in which the event occurred. Here, we study how deep learning algorithms for landslide segmentation on SAR products can benefit from pretraining on a simpler task and from data from different regions. The method we explore consists of two training stages. First, we learn the task of identifying whether a SAR image contains any landslides or not. Then, we learn to segment in a sparsely labeled scenario where half of the data do not contain landslides. We test whether the inclusion of feature embeddings derived from stage-1 helps with landslide detection in stage-2. We find that it leads to minor improvements in the Area Under the Precision-Recall Curve, but also to a significantly lower false positive rate in areas without landslides and an improved estimate of the average number of landslide pixels in a chip. A more accurate pixel count allows to identify the most affected areas with higher confidence. This could be valuable in rapid response scenarios where prioritization of resources at a global scale is important. We make our code publicly available at https://github.com/VMBoehm/SAR-landslide-detection-pretraining.
Deep Learning for Rapid Landslide Detection using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Datacubes
Nov 05, 2022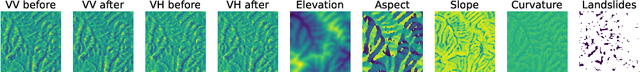
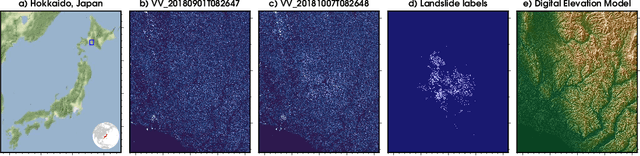
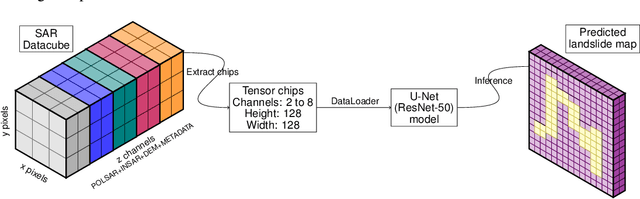
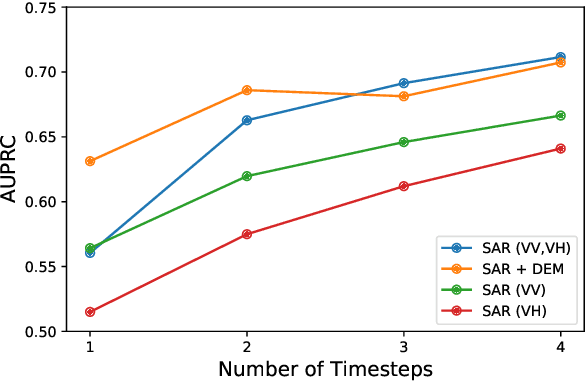
Abstract:With climate change predicted to increase the likelihood of landslide events, there is a growing need for rapid landslide detection technologies that help inform emergency responses. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is a remote sensing technique that can provide measurements of affected areas independent of weather or lighting conditions. Usage of SAR, however, is hindered by domain knowledge that is necessary for the pre-processing steps and its interpretation requires expert knowledge. We provide simplified, pre-processed, machine-learning ready SAR datacubes for four globally located landslide events obtained from several Sentinel-1 satellite passes before and after a landslide triggering event together with segmentation maps of the landslides. From this dataset, using the Hokkaido, Japan datacube, we study the feasibility of SAR-based landslide detection with supervised deep learning (DL). Our results demonstrate that DL models can be used to detect landslides from SAR data, achieving an Area under the Precision-Recall curve exceeding 0.7. We find that additional satellite visits enhance detection performance, but that early detection is possible when SAR data is combined with terrain information from a digital elevation model. This can be especially useful for time-critical emergency interventions. Code is made publicly available at https://github.com/iprapas/landslide-sar-unet.
Dual-Tasks Siamese Transformer Framework for Building Damage Assessment
Jan 26, 2022


Abstract:Accurate and fine-grained information about the extent of damage to buildings is essential for humanitarian relief and disaster response. However, as the most commonly used architecture in remote sensing interpretation tasks, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have limited ability to model the non-local relationship between pixels. Recently, Transformer architecture first proposed for modeling long-range dependency in natural language processing has shown promising results in computer vision tasks. Considering the frontier advances of Transformer architecture in the computer vision field, in this paper, we present the first attempt at designing a Transformer-based damage assessment architecture (DamFormer). In DamFormer, a siamese Transformer encoder is first constructed to extract non-local and representative deep features from input multitemporal image-pairs. Then, a multitemporal fusion module is designed to fuse information for downstream tasks. Finally, a lightweight dual-tasks decoder aggregates multi-level features for final prediction. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time that such a deep Transformer-based network is proposed for multitemporal remote sensing interpretation tasks. The experimental results on the large-scale damage assessment dataset xBD demonstrate the potential of the Transformer-based architecture.
Proceedings of NeurIPS 2020 Workshop on Artificial Intelligence for Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Response
Dec 08, 2020Abstract:These are the "proceedings" of the 2nd AI + HADR workshop which was held virtually on December 12, 2020 as part of the Neural Information Processing Systems conference. These are non-archival and merely serve as a way to collate all the papers accepted to the workshop.
PulseSatellite: A tool using human-AI feedback loops for satellite image analysis in humanitarian contexts
Jan 29, 2020

Abstract:Humanitarian response to natural disasters and conflicts can be assisted by satellite image analysis. In a humanitarian context, very specific satellite image analysis tasks must be done accurately and in a timely manner to provide operational support. We present PulseSatellite, a collaborative satellite image analysis tool which leverages neural network models that can be retrained on-the fly and adapted to specific humanitarian contexts and geographies. We present two case studies, in mapping shelters and floods respectively, that illustrate the capabilities of PulseSatellite.
* 2 pages, 2 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge