Dongfang Xu
Communication-Efficient Multi-Modal Edge Inference via Uncertainty-Aware Distributed Learning
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Semantic communication is emerging as a key enabler for distributed edge intelligence due to its capability to convey task-relevant meaning. However, achieving communication-efficient training and robust inference over wireless links remains challenging. This challenge is further exacerbated for multi-modal edge inference (MMEI) by two factors: 1) prohibitive communication overhead for distributed learning over bandwidth-limited wireless links, due to the \emph{multi-modal} nature of the system; and 2) limited robustness under varying channels and noisy multi-modal inputs. In this paper, we propose a three-stage communication-aware distributed learning framework to improve training and inference efficiency while maintaining robustness over wireless channels. In Stage~I, devices perform local multi-modal self-supervised learning to obtain shared and modality-specific encoders without device--server exchange, thereby reducing the communication cost. In Stage~II, distributed fine-tuning with centralized evidential fusion calibrates per-modality uncertainty and reliably aggregates features distorted by noise or channel fading. In Stage~III, an uncertainty-guided feedback mechanism selectively requests additional features for uncertain samples, optimizing the communication--accuracy tradeoff in the distributed setting. Experiments on RGB--depth indoor scene classification show that the proposed framework attains higher accuracy with far fewer training communication rounds and remains robust to modality degradation or channel variation, outperforming existing self-supervised and fully supervised baselines.
Joint Radiation Power, Antenna Position, and Beamforming Optimization for Pinching-Antenna Systems with Motion Power Consumption
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Pinching-antenna systems (PASS) have been recently proposed to improve the performance of wireless networks by reconfiguring both the large-scale and small-scale channel conditions. However, existing studies ignore the physical constraints of antenna placement and assume fixed antenna radiation power. To fill this research gap, this paper investigates the design of PASS taking into account the motion power consumption of pinching-antennas (PAs) and the impact of adjustable antenna radiation power. To that end, we minimize the average power consumption for a given quality-of-service (QoS) requirement, by jointly optimizing the antenna positions, antenna radiation power ratios, and transmit beamforming. To the best of the authors' knowledge, this is the first work to consider radiation power optimization in PASS, which provides an additional degree of freedom (DoF) for system design. The cases with both continuous and discrete antenna placement are considered, where the main challenge lies in the fact that the antenna positions affect both the magnitude and phase of the channel coefficients of PASS, making system optimization very challenging. To tackle the resulting unique obstacles, an alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM)-based framework is proposed to solve the problem for continuous antenna movement, while its discrete counterpart is formulated as a mixed integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) problem and solved by the block coordinate descent (BCD) method. Simulation results validate the performance enhancement achieved by incorporating PA movement power assumption and adjustable radiation power into PASS design, while also demonstrating the efficiency of the proposed optimization framework. The benefits of PASS over conventional multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems in mitigating the large-scale path loss and inter-user interference is also revealed.
Multi-Modal Self-Supervised Semantic Communication
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Semantic communication is emerging as a promising paradigm that focuses on the extraction and transmission of semantic meanings using deep learning techniques. While current research primarily addresses the reduction of semantic communication overhead, it often overlooks the training phase, which can incur significant communication costs in dynamic wireless environments. To address this challenge, we propose a multi-modal semantic communication system that leverages multi-modal self-supervised learning to enhance task-agnostic feature extraction. The proposed approach employs self-supervised learning during the pre-training phase to extract task-agnostic semantic features, followed by supervised fine-tuning for downstream tasks. This dual-phase strategy effectively captures both modality-invariant and modality-specific features while minimizing training-related communication overhead. Experimental results on the NYU Depth V2 dataset demonstrate that the proposed method significantly reduces training-related communication overhead while maintaining or exceeding the performance of existing supervised learning approaches. The findings underscore the advantages of multi-modal self-supervised learning in semantic communication, paving the way for more efficient and scalable edge inference systems.
Globally Optimal Movable Antenna-Enhanced multi-user Communication: Discrete Antenna Positioning, Motion Power Consumption, and Imperfect CSI
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:Movable antennas (MAs) represent a promising paradigm to enhance the spatial degrees of freedom of conventional multi-antenna systems by dynamically adapting the positions of antenna elements within a designated transmit area. In particular, by employing electro-mechanical MA drivers, the positions of the MA elements can be adjusted to shape a favorable spatial correlation for improving system performance. Although preliminary research has explored beamforming designs for MA systems, the intricacies of the power consumption and the precise positioning of MA elements are not well understood. Moreover, the assumption of perfect CSI adopted in the literature is impractical due to the significant pilot overhead and the extensive time to acquire perfect CSI. To address these challenges, we model the motion of MA elements through discrete steps and quantify the associated power consumption as a function of these movements. Furthermore, by leveraging the properties of the MA channel model, we introduce a novel CSI error model tailored for MA systems that facilitates robust resource allocation design. In particular, we optimize the beamforming and the MA positions at the BS to minimize the total BS power consumption, encompassing both radiated and MA motion power while guaranteeing a minimum required SINR for each user. To this end, novel algorithms exploiting the branch and bound (BnB) method are developed to obtain the optimal solution for perfect and imperfect CSI. Moreover, to support practical implementation, we propose low-complexity algorithms with guaranteed convergence by leveraging successive convex approximation (SCA). Our numerical results validate the optimality of the proposed BnB-based algorithms. Furthermore, we unveil that both proposed SCA-based algorithms approach the optimal performance within a few iterations, thus highlighting their practical advantages.
Sensing-aided Near-Field Secure Communications with Mobile Eavesdroppers
Aug 25, 2024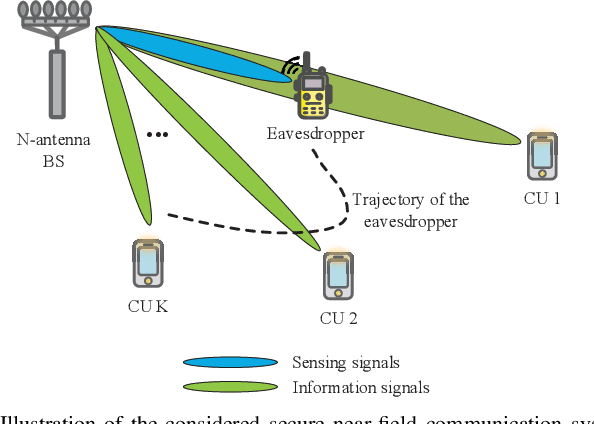
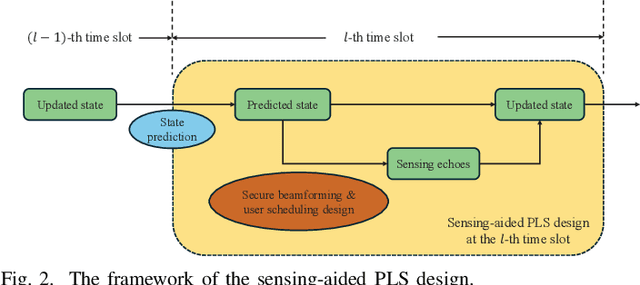
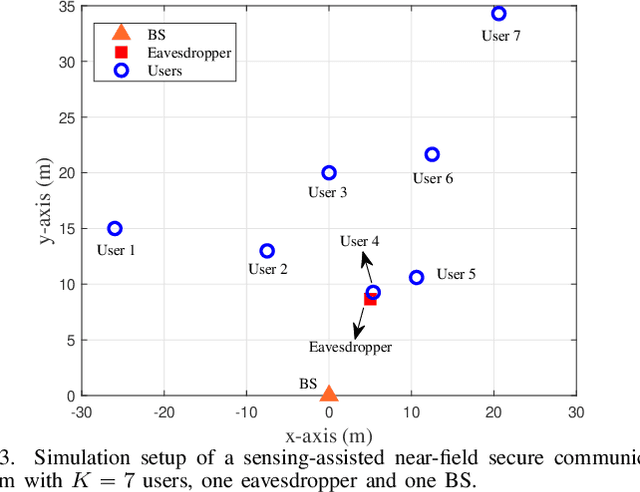
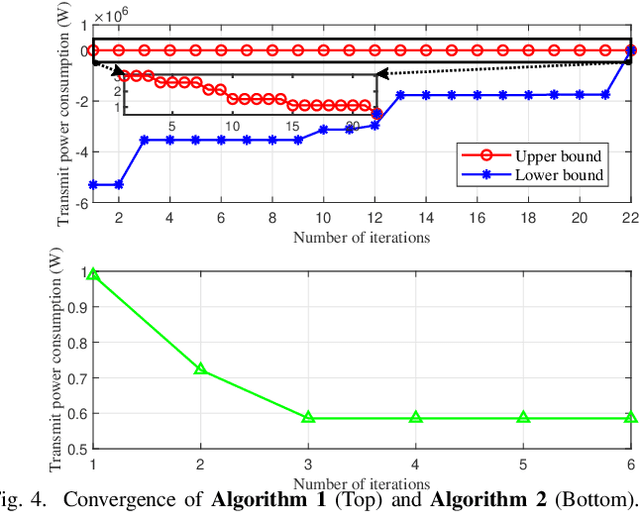
Abstract:The additional degree of freedom (DoF) in the distance domain of near-field communication offers new opportunities for physical layer security (PLS) design. However, existing works mainly consider static eavesdroppers, and the related study with mobile eavesdroppers is still in its infancy due to the difficulty in obtaining the channel state information (CSI) of the eavesdropper. To this end, we propose to leverage the sensing capability of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems to assist PLS design. To comprehensively study the dynamic behaviors of the system, we propose a Pareto optimization framework, where a multi-objective optimization problem (MOOP) is formulated to simultaneously optimize three key performance metrics: power consumption, number of securely served users, and tracking performance, while guaranteeing the achievable rate of the users with a given leakage rate constraint. A globally optimal design based on the generalized Benders decomposition (GBD) method is proposed to achieve the Pareto optimal solutions. To reduce the computational complexity, we further design a low-complexity algorithm based on zero-forcing (ZF) beamforming and successive convex approximation (SCA). Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms and reveal the intrinsic trade-offs between the three performance metrics. It is observed that near-field communication offers a favorable beam diffraction effect for PLS, where the energy of the information signal is nulled around the eavesdropper and focused on the users.
Resource Allocation Design for Next-Generation Multiple Access: A Tutorial Overview
Jul 03, 2024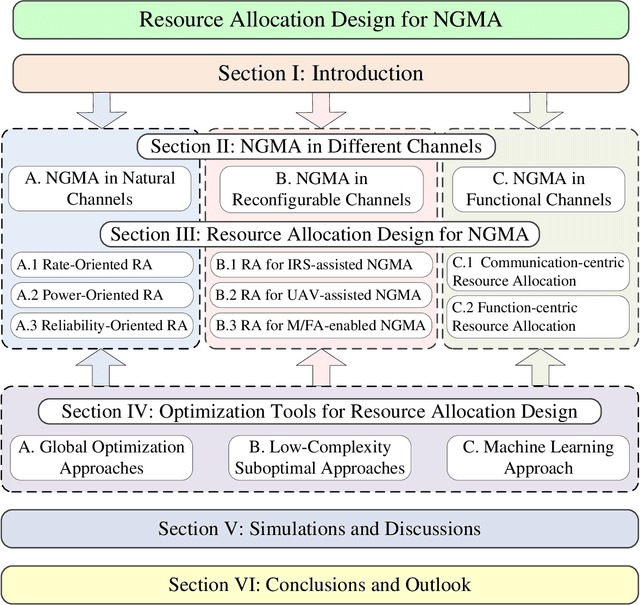
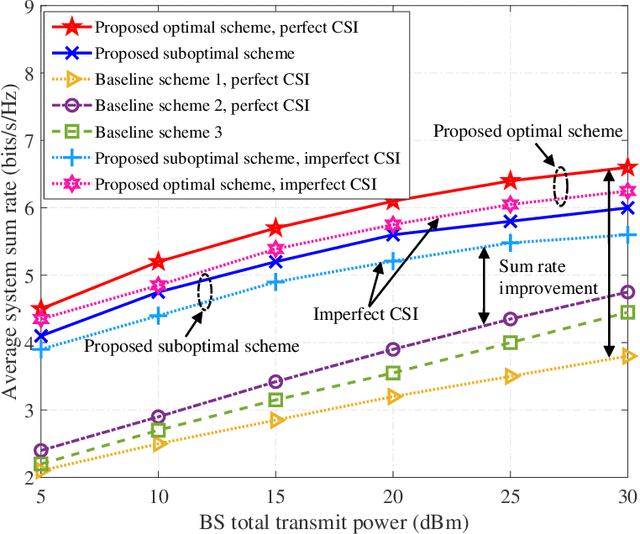
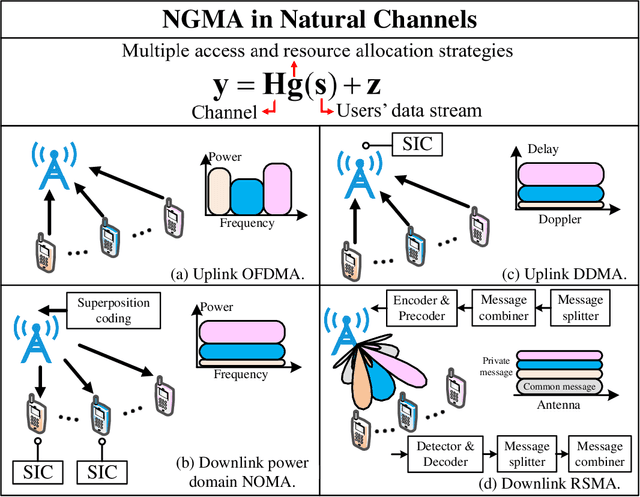
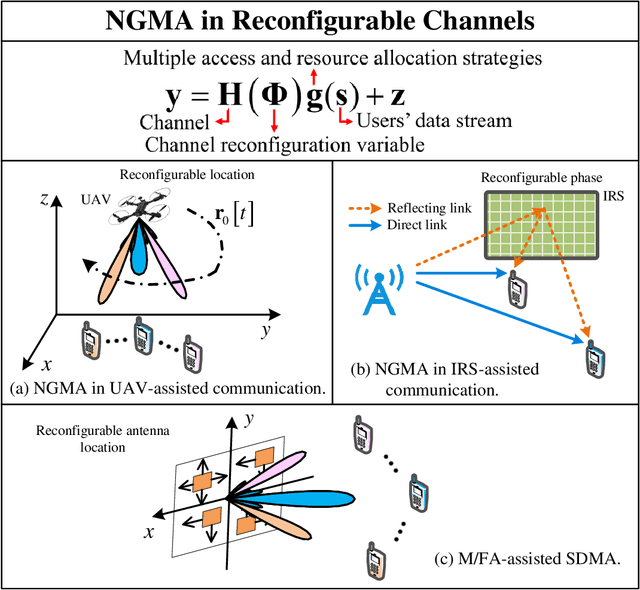
Abstract:Multiple access is the cornerstone technology for each generation of wireless cellular networks and resource allocation design plays a crucial role in multiple access. In this paper, we present a comprehensive tutorial overview for junior researchers in this field, aiming to offer a foundational guide for resource allocation design in the context of next-generation multiple access (NGMA). Initially, we identify three types of channels in future wireless cellular networks over which NGMA will be implemented, namely: natural channels, reconfigurable channels, and functional channels. Natural channels are traditional uplink and downlink communication channels; reconfigurable channels are defined as channels that can be proactively reshaped via emerging platforms or techniques, such as intelligent reflecting surface (IRS), unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), and movable/fluid antenna (M/FA); and functional channels support not only communication but also other functionalities simultaneously, with typical examples including integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) and joint computing and communication (JCAC) channels. Then, we introduce NGMA models applicable to these three types of channels that cover most of the practical communication scenarios of future wireless communications. Subsequently, we articulate the key optimization technical challenges inherent in the resource allocation design for NGMA, categorizing them into rate-oriented, power-oriented, and reliability-oriented resource allocation designs. The corresponding optimization approaches for solving the formulated resource allocation design problems are then presented. Finally, simulation results are presented and discussed to elucidate the practical implications and insights derived from resource allocation designs in NGMA.
Wireless Information and Energy Transfer in the Era of 6G Communications
Apr 29, 2024
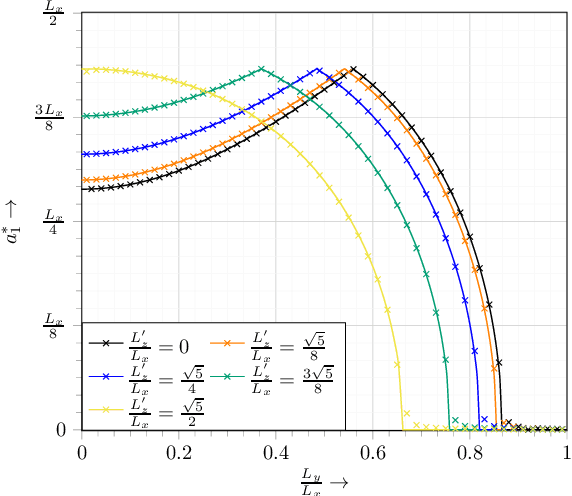
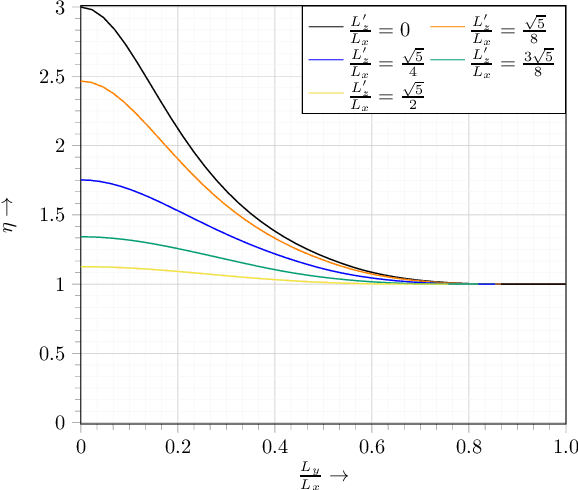

Abstract:Wireless information and energy transfer (WIET) represents an emerging paradigm which employs controllable transmission of radio-frequency signals for the dual purpose of data communication and wireless charging. As such, WIET is widely regarded as an enabler of envisioned 6G use cases that rely on energy-sustainable Internet-of-Things (IoT) networks, such as smart cities and smart grids. Meeting the quality-of-service demands of WIET, in terms of both data transfer and power delivery, requires effective co-design of the information and energy signals. In this article, we present the main principles and design aspects of WIET, focusing on its integration in 6G networks. First, we discuss how conventional communication notions such as resource allocation and waveform design need to be revisited in the context of WIET. Next, we consider various candidate 6G technologies that can boost WIET efficiency, namely, holographic multiple-input multiple-output, near-field beamforming, terahertz communication, intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs), and reconfigurable (fluid) antenna arrays. We introduce respective WIET design methods, analyze the promising performance gains of these WIET systems, and discuss challenges, open issues, and future research directions. Finally, a near-field energy beamforming scheme and a power-based IRS beamforming algorithm are experimentally validated using a wireless energy transfer testbed. The vision of WIET in communication systems has been gaining momentum in recent years, with constant progress with respect to theoretical but also practical aspects. The comprehensive overview of the state of the art of WIET presented in this paper highlights the potentials of WIET systems as well as their overall benefits in 6G networks.
Sensing-assisted Robust SWIPT for Mobile Energy Harvesting Receivers
Feb 15, 2024



Abstract:Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) has been proposed to offer communication services and transfer power to the energy harvesting receiver (EHR) concurrently. However, existing works mainly focused on static EHRs, without considering the location uncertainty caused by the movement of EHRs and location estimation errors. To tackle this issue, this paper considers the sensing-assisted SWIPT design in a networked integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system in the presence of location uncertainty. A two-phase robust design is proposed to reduce the location uncertainty and improve the power transfer efficiency. In particular, each time frame is divided into two phases, i.e., sensing and WPT phases, via time-splitting. The sensing phase performs collaborative sensing to localize the EHR, whose results are then utilized in the WPT phase for efficient WPT. To minimize the power consumption with given communication and power transfer requirements, a two-layer optimization framework is proposed to jointly optimize the time-splitting ratio, coordinated beamforming policy, and sensing node selection. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed design and demonstrate the existence of an optimal time-splitting ratio for given location uncertainty.
Interference Mitigation for Network-Level ISAC: An Optimization Perspective
Feb 15, 2024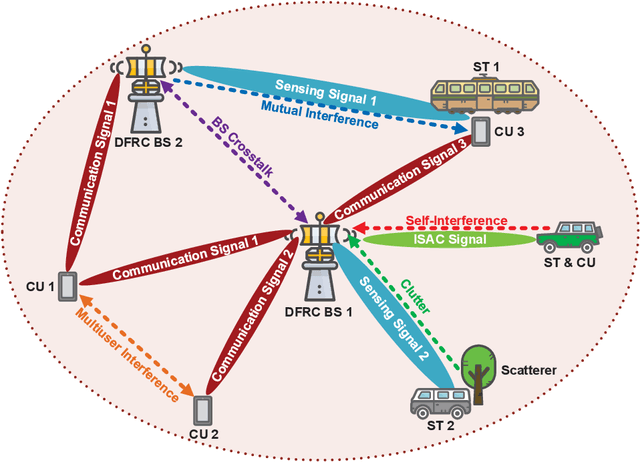
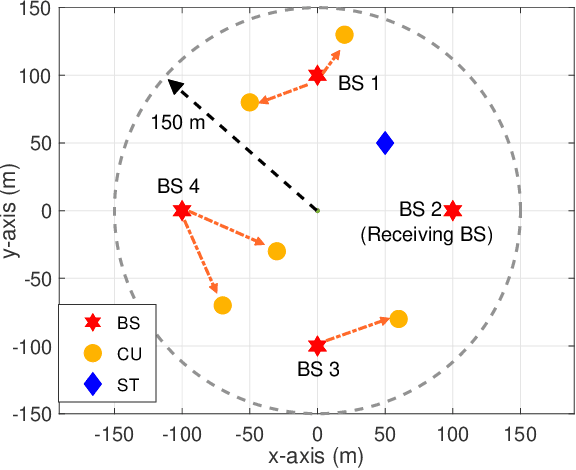
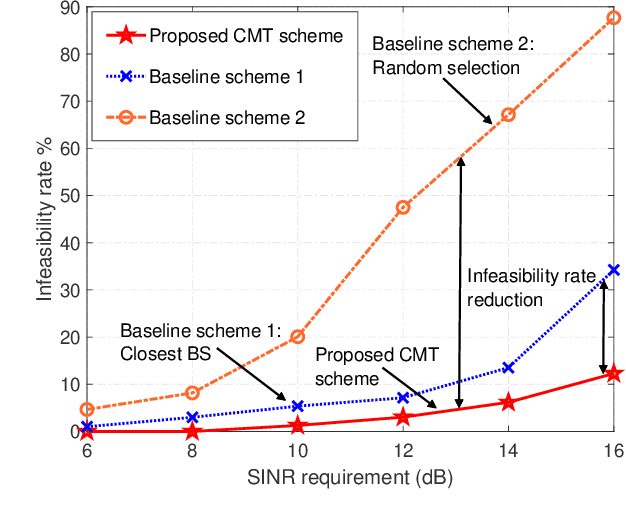
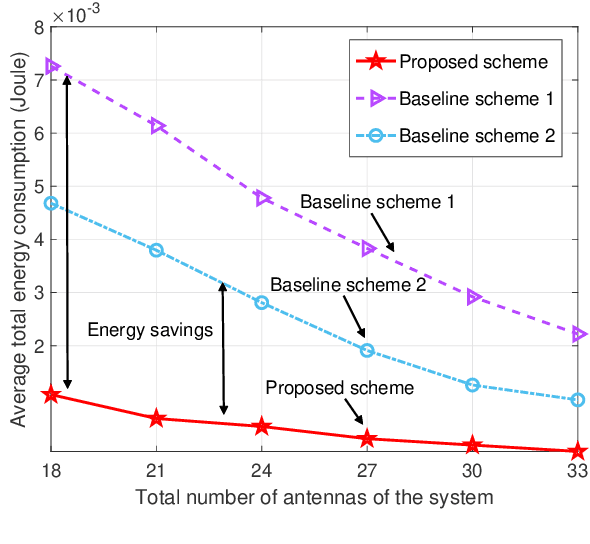
Abstract:Future wireless networks are envisioned to simultaneously provide high data-rate communication and ubiquitous environment-aware services for numerous users. One promising approach to meet this demand is to employ network-level integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) by jointly designing the signal processing and resource allocation over the entire network. However, to unleash the full potential of network-level ISAC, some critical challenges must be tackled. Among them, interference management is one of the most significant ones. In this article, we build up a bridge between interference mitigation techniques and the corresponding optimization methods, which facilitates efficient interference mitigation in network-level ISAC systems. In particular, we first identify several types of interference in network-level ISAC systems, including self-interference, mutual interference, crosstalk, clutter, and multiuser interference. Then, we present several promising techniques that can be utilized to suppress specific types of interference. For each type of interference, we discuss the corresponding problem formulation and identify the associated optimization methods. Moreover, to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed interference mitigation techniques, two concrete network-level ISAC systems, namely coordinated cellular network-based and distributed antenna-based ISAC systems, are investigated from interference management perspective. Experiment results indicate that it is beneficial to collaboratively employ different interference mitigation techniques and leverage the network structure to achieve the full potential of network-level ISAC. Finally, we highlight several promising future research directions for the design of ISAC systems.
Movable Antenna-Enhanced Multiuser Communication: Optimal Discrete Antenna Positioning and Beamforming
Aug 04, 2023


Abstract:Movable antennas (MAs) are a promising paradigm to enhance the spatial degrees of freedom of conventional multi-antenna systems by flexibly adapting the positions of the antenna elements within a given transmit area. In this paper, we model the motion of the MA elements as discrete movements and study the corresponding resource allocation problem for MA-enabled multiuser multiple-input single-output (MISO) communication systems. Specifically, we jointly optimize the beamforming and the MA positions at the base station (BS) for the minimization of the total transmit power while guaranteeing the minimum required signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) of each individual user. To obtain the globally optimal solution to the formulated resource allocation problem, we develop an iterative algorithm capitalizing on the generalized Bender's decomposition with guaranteed convergence. Our numerical results demonstrate that the proposed MA-enabled communication system can significantly reduce the BS transmit power and the number of antenna elements needed to achieve a desired performance compared to state-of-the-art techniques, such as antenna selection. Furthermore, we observe that refining the step size of the MA motion driver improves performance at the expense of a higher computational complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge