Dmitry Ustalov
Challenge on Optimization of Context Collection for Code Completion
Oct 05, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of workflows and methods for software engineering using AI emphasizes the need for a systematic evaluation and analysis of their ability to leverage information from entire projects, particularly in large code bases. In this challenge on optimization of context collection for code completion, organized by JetBrains in collaboration with Mistral AI as part of the ASE 2025 conference, participants developed efficient mechanisms for collecting context from source code repositories to improve fill-in-the-middle code completions for Python and Kotlin. We constructed a large dataset of real-world code in these two programming languages using permissively licensed open-source projects. The submissions were evaluated based on their ability to maximize completion quality for multiple state-of-the-art neural models using the chrF metric. During the public phase of the competition, nineteen teams submitted solutions to the Python track and eight teams submitted solutions to the Kotlin track. In the private phase, six teams competed, of which five submitted papers to the workshop.
Confidence and Stability of Global and Pairwise Scores in NLP Evaluation
Jul 02, 2025
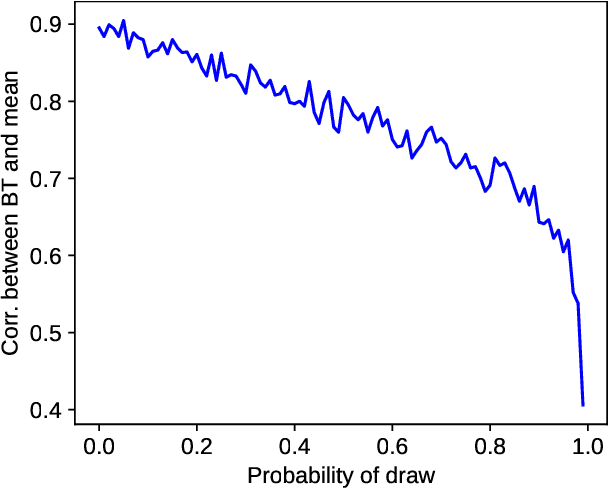

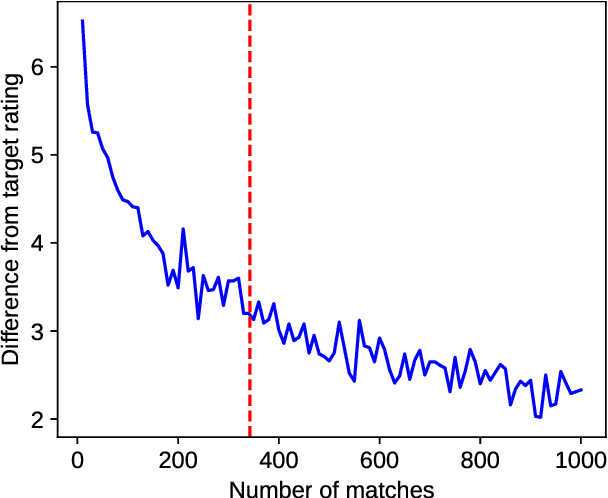
Abstract:With the advent of highly capable instruction-tuned neural language models, benchmarking in natural language processing (NLP) is increasingly shifting towards pairwise comparison leaderboards, such as LMSYS Arena, from traditional global pointwise scores (e.g., GLUE, BIG-bench, SWE-bench). This paper empirically investigates the strengths and weaknesses of both global scores and pairwise comparisons to aid decision-making in selecting appropriate model evaluation strategies. Through computational experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets using standard global metrics and the popular Bradley-Terry model for pairwise comparisons, we found that while global scores provide more reliable overall rankings, they can underestimate strong models with rare, significant errors or low confidence. Conversely, pairwise comparisons are particularly effective for identifying strong contenders among models with lower global scores, especially where quality metrics are hard to define (e.g., text generation), though they require more comparisons to converge if ties are frequent. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/HSPyroblast/srw-ranking under a permissive license.
Reliable, Reproducible, and Really Fast Leaderboards with Evalica
Dec 15, 2024Abstract:The rapid advancement of natural language processing (NLP) technologies, such as instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs), urges the development of modern evaluation protocols with human and machine feedback. We introduce Evalica, an open-source toolkit that facilitates the creation of reliable and reproducible model leaderboards. This paper presents its design, evaluates its performance, and demonstrates its usability through its Web interface, command-line interface, and Python API.
Toloka Visual Question Answering Benchmark
Sep 28, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present Toloka Visual Question Answering, a new crowdsourced dataset allowing comparing performance of machine learning systems against human level of expertise in the grounding visual question answering task. In this task, given an image and a textual question, one has to draw the bounding box around the object correctly responding to that question. Every image-question pair contains the response, with only one correct response per image. Our dataset contains 45,199 pairs of images and questions in English, provided with ground truth bounding boxes, split into train and two test subsets. Besides describing the dataset and releasing it under a CC BY license, we conducted a series of experiments on open source zero-shot baseline models and organized a multi-phase competition at WSDM Cup that attracted 48 participants worldwide. However, by the time of paper submission, no machine learning model outperformed the non-expert crowdsourcing baseline according to the intersection over union evaluation score.
Best Prompts for Text-to-Image Models and How to Find Them
Sep 23, 2022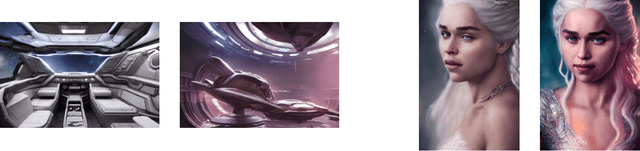


Abstract:Recent progress in generative models, especially in text-guided diffusion models, has enabled the production of aesthetically-pleasing imagery resembling the works of professional human artists. However, one has to carefully compose the textual description, called the prompt, and augment it with a set of clarifying keywords. Since aesthetics are challenging to evaluate computationally, human feedback is needed to determine the optimal prompt formulation and keyword combination. In this paper, we present a human-in-the-loop approach to learning the most useful combination of prompt keywords using a genetic algorithm. We also show how such an approach can improve the aesthetic appeal of images depicting the same descriptions.
Clustering Without Knowing How To: Application and Evaluation
Sep 21, 2022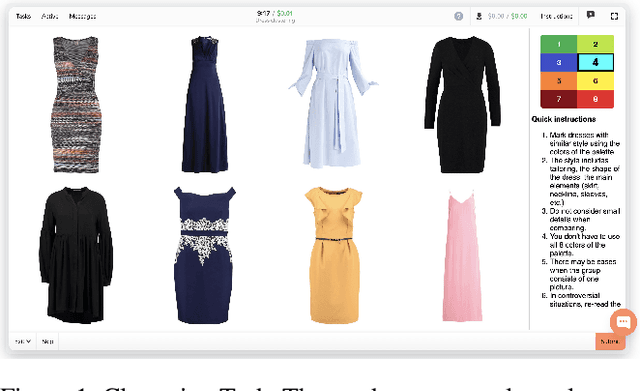
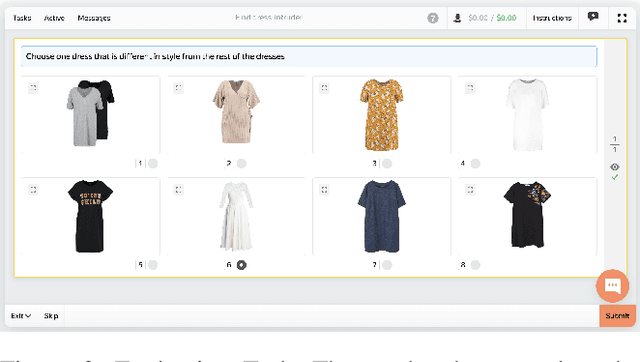
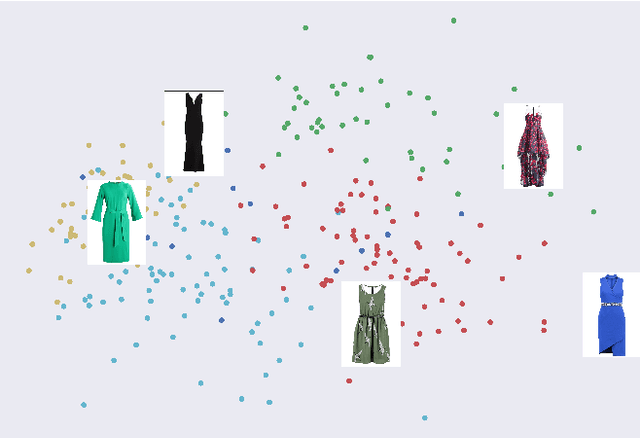
Abstract:Crowdsourcing allows running simple human intelligence tasks on a large crowd of workers, enabling solving problems for which it is difficult to formulate an algorithm or train a machine learning model in reasonable time. One of such problems is data clustering by an under-specified criterion that is simple for humans, but difficult for machines. In this demonstration paper, we build a crowdsourced system for image clustering and release its code under a free license at https://github.com/Toloka/crowdclustering. Our experiments on two different image datasets, dresses from Zalando's FEIDEGGER and shoes from the Toloka Shoes Dataset, confirm that one can yield meaningful clusters with no machine learning algorithms purely with crowdsourcing.
Vox Populi, Vox DIY: Benchmark Dataset for Crowdsourced Audio Transcription
Jul 02, 2021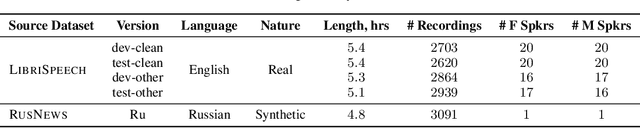
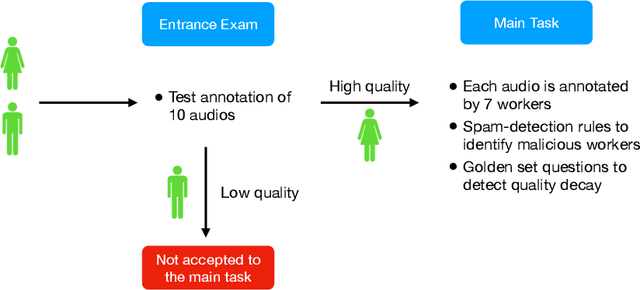
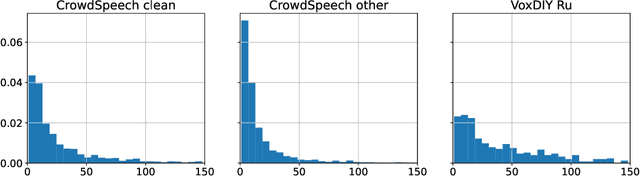
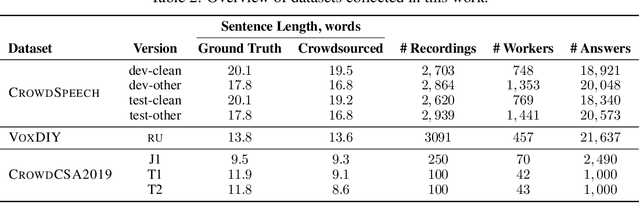
Abstract:Domain-specific data is the crux of the successful transfer of machine learning systems from benchmarks to real life. Crowdsourcing has become one of the standard tools for cheap and time-efficient data collection for simple problems such as image classification: thanks in large part to advances in research on aggregation methods. However, the applicability of crowdsourcing to more complex tasks (e.g., speech recognition) remains limited due to the lack of principled aggregation methods for these modalities. The main obstacle towards designing advanced aggregation methods is the absence of training data, and in this work, we focus on bridging this gap in speech recognition. For this, we collect and release CrowdSpeech -- the first publicly available large-scale dataset of crowdsourced audio transcriptions. Evaluation of existing aggregation methods on our data shows room for improvement, suggesting that our work may entail the design of better algorithms. At a higher level, we also contribute to the more general challenge of collecting high-quality datasets using crowdsourcing: we develop a principled pipeline for constructing datasets of crowdsourced audio transcriptions in any novel domain. We show its applicability on an under-resourced language by constructing VoxDIY -- a counterpart of CrowdSpeech for the Russian language. We also release the code that allows a full replication of our data collection pipeline and share various insights on best practices of data collection via crowdsourcing.
Word Sense Disambiguation for 158 Languages using Word Embeddings Only
Mar 14, 2020
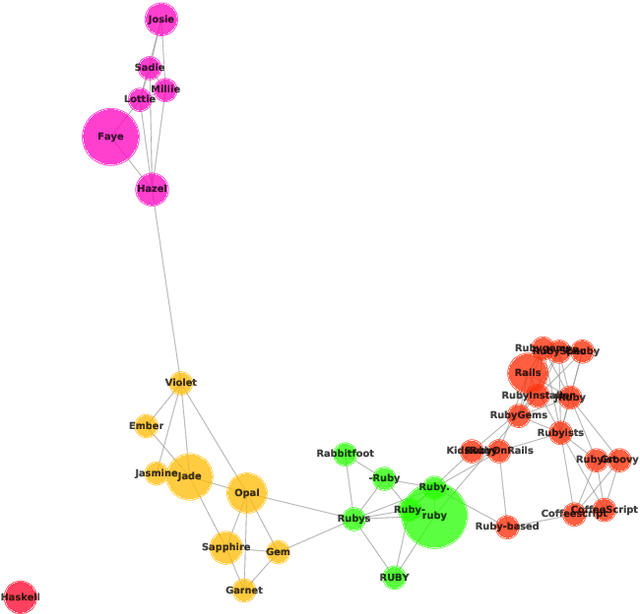

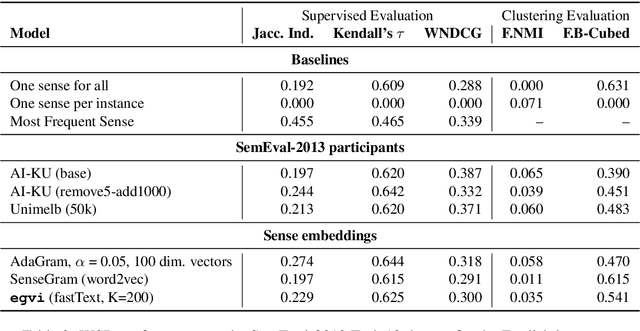
Abstract:Disambiguation of word senses in context is easy for humans, but is a major challenge for automatic approaches. Sophisticated supervised and knowledge-based models were developed to solve this task. However, (i) the inherent Zipfian distribution of supervised training instances for a given word and/or (ii) the quality of linguistic knowledge representations motivate the development of completely unsupervised and knowledge-free approaches to word sense disambiguation (WSD). They are particularly useful for under-resourced languages which do not have any resources for building either supervised and/or knowledge-based models. In this paper, we present a method that takes as input a standard pre-trained word embedding model and induces a fully-fledged word sense inventory, which can be used for disambiguation in context. We use this method to induce a collection of sense inventories for 158 languages on the basis of the original pre-trained fastText word embeddings by Grave et al. (2018), enabling WSD in these languages. Models and system are available online.
HHMM at SemEval-2019 Task 2: Unsupervised Frame Induction using Contextualized Word Embeddings
May 05, 2019
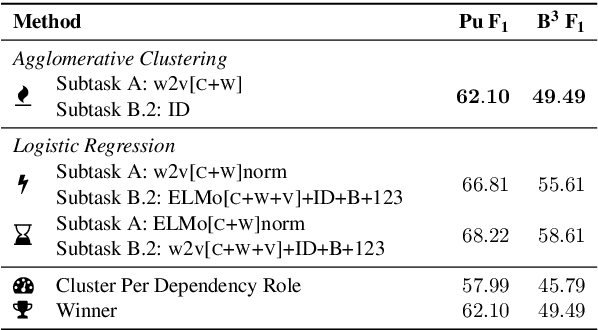
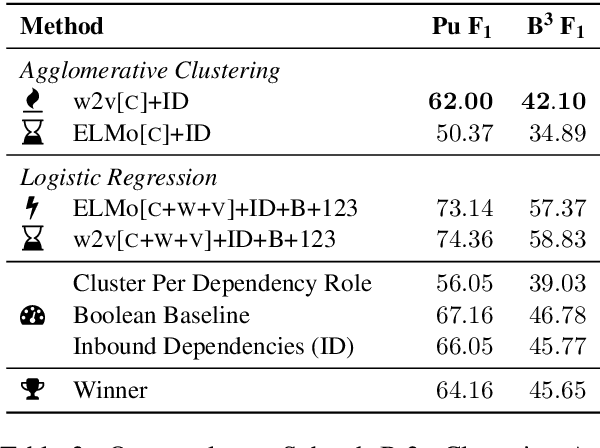
Abstract:We present our system for semantic frame induction that showed the best performance in Subtask B.1 and finished as the runner-up in Subtask A of the SemEval 2019 Task 2 on unsupervised semantic frame induction (QasemiZadeh et al., 2019). Our approach separates this task into two independent steps: verb clustering using word and their context embeddings and role labeling by combining these embeddings with syntactical features. A simple combination of these steps shows very competitive results and can be extended to process other datasets and languages.
Unsupervised Sense-Aware Hypernymy Extraction
Sep 17, 2018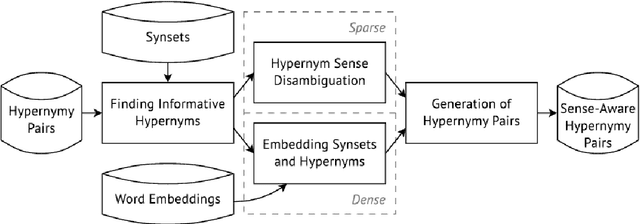
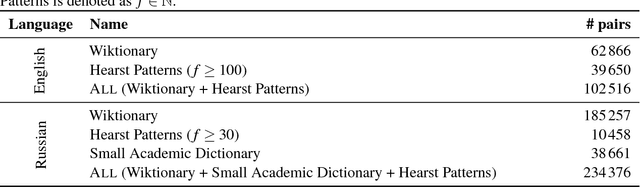
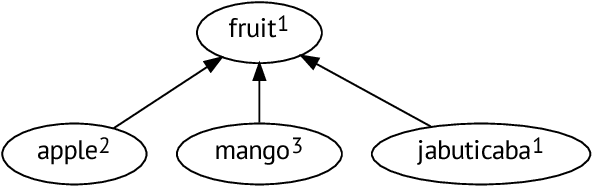

Abstract:In this paper, we show how unsupervised sense representations can be used to improve hypernymy extraction. We present a method for extracting disambiguated hypernymy relationships that propagates hypernyms to sets of synonyms (synsets), constructs embeddings for these sets, and establishes sense-aware relationships between matching synsets. Evaluation on two gold standard datasets for English and Russian shows that the method successfully recognizes hypernymy relationships that cannot be found with standard Hearst patterns and Wiktionary datasets for the respective languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge