Diogo Lavado
Enhancing Power Grid Inspections with Machine Learning
Feb 18, 2025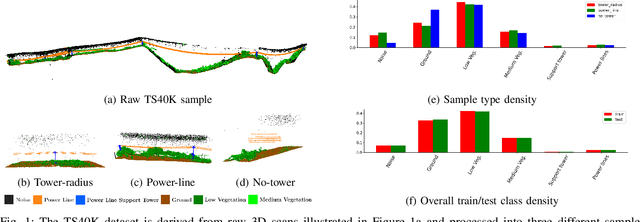
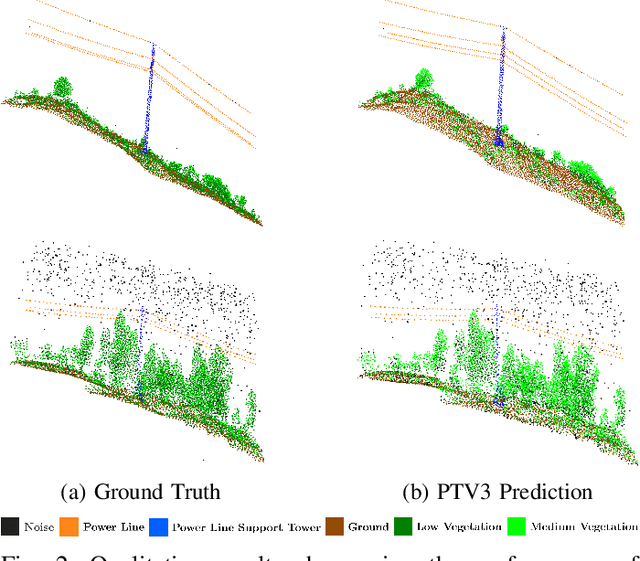


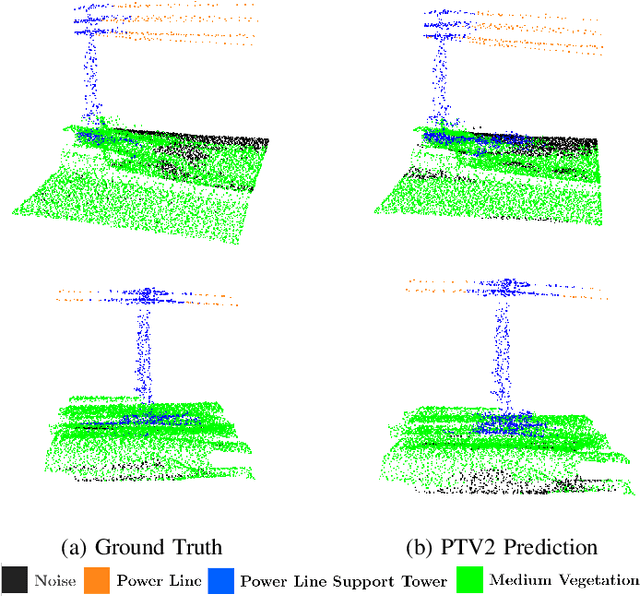
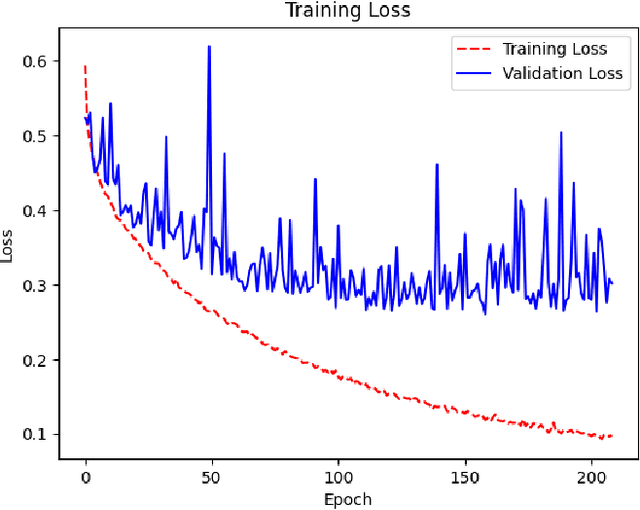
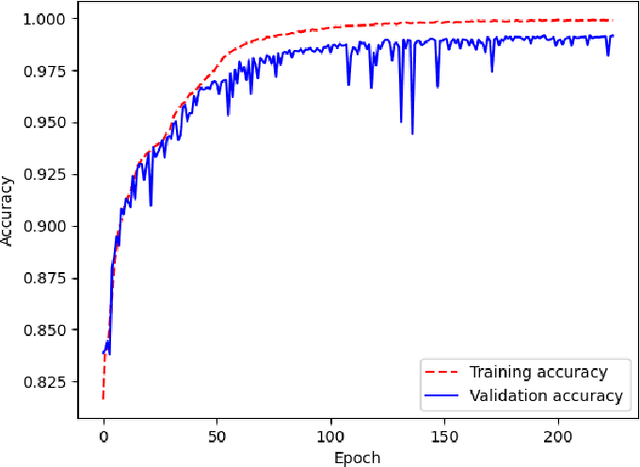
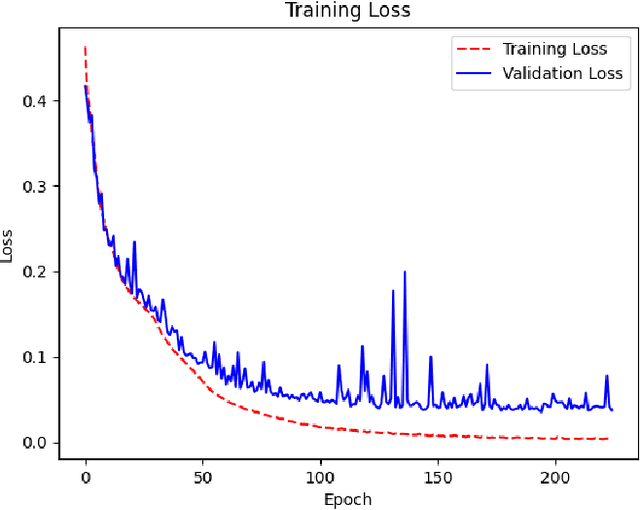
Abstract:Ensuring the safety and reliability of power grids is critical as global energy demands continue to rise. Traditional inspection methods, such as manual observations or helicopter surveys, are resource-intensive and lack scalability. This paper explores the use of 3D computer vision to automate power grid inspections, utilizing the TS40K dataset -- a high-density, annotated collection of 3D LiDAR point clouds. By concentrating on 3D semantic segmentation, our approach addresses challenges like class imbalance and noisy data to enhance the detection of critical grid components such as power lines and towers. The benchmark results indicate significant performance improvements, with IoU scores reaching 95.53% for the detection of power lines using transformer-based models. Our findings illustrate the potential for integrating ML into grid maintenance workflows, increasing efficiency and enabling proactive risk management strategies.
TS40K: a 3D Point Cloud Dataset of Rural Terrain and Electrical Transmission System
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Research on supervised learning algorithms in 3D scene understanding has risen in prominence and witness great increases in performance across several datasets. The leading force of this research is the problem of autonomous driving followed by indoor scene segmentation. However, openly available 3D data on these tasks mainly focuses on urban scenarios. In this paper, we propose TS40K, a 3D point cloud dataset that encompasses more than 40,000 Km on electrical transmission systems situated in European rural terrain. This is not only a novel problem for the research community that can aid in the high-risk mission of power-grid inspection, but it also offers 3D point clouds with distinct characteristics from those in self-driving and indoor 3D data, such as high point-density and no occlusion. In our dataset, each 3D point is labeled with 1 out of 22 annotated classes. We evaluate the performance of state-of-the-art methods on our dataset concerning 3D semantic segmentation and 3D object detection. Finally, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the results along with key challenges such as using labels that were not originally intended for learning tasks.
Achieving Constraints in Neural Networks: A Stochastic Augmented Lagrangian Approach
Oct 25, 2023


Abstract:Regularizing Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) is essential for improving generalizability and preventing overfitting. Fixed penalty methods, though common, lack adaptability and suffer from hyperparameter sensitivity. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to DNN regularization by framing the training process as a constrained optimization problem. Where the data fidelity term is the minimization objective and the regularization terms serve as constraints. Then, we employ the Stochastic Augmented Lagrangian (SAL) method to achieve a more flexible and efficient regularization mechanism. Our approach extends beyond black-box regularization, demonstrating significant improvements in white-box models, where weights are often subject to hard constraints to ensure interpretability. Experimental results on image-based classification on MNIST, CIFAR10, and CIFAR100 datasets validate the effectiveness of our approach. SAL consistently achieves higher Accuracy while also achieving better constraint satisfaction, thus showcasing its potential for optimizing DNNs under constrained settings.
Low-Resource White-Box Semantic Segmentation of Supporting Towers on 3D Point Clouds via Signature Shape Identification
Jun 13, 2023



Abstract:Research in 3D semantic segmentation has been increasing performance metrics, like the IoU, by scaling model complexity and computational resources, leaving behind researchers and practitioners that (1) cannot access the necessary resources and (2) do need transparency on the model decision mechanisms. In this paper, we propose SCENE-Net, a low-resource white-box model for 3D point cloud semantic segmentation. SCENE-Net identifies signature shapes on the point cloud via group equivariant non-expansive operators (GENEOs), providing intrinsic geometric interpretability. Our training time on a laptop is 85~min, and our inference time is 20~ms. SCENE-Net has 11 trainable geometrical parameters and requires fewer data than black-box models. SCENE--Net offers robustness to noisy labeling and data imbalance and has comparable IoU to state-of-the-art methods. With this paper, we release a 40~000 Km labeled dataset of rural terrain point clouds and our code implementation.
Faster than LASER -- Towards Stream Reasoning with Deep Neural Networks
Jun 15, 2021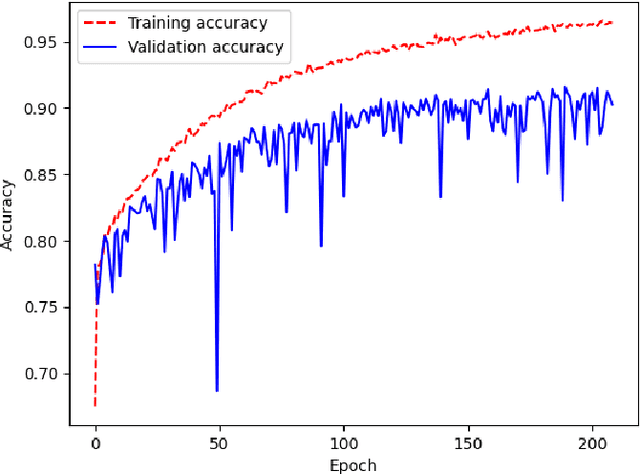
Abstract:With the constant increase of available data in various domains, such as the Internet of Things, Social Networks or Smart Cities, it has become fundamental that agents are able to process and reason with such data in real time. Whereas reasoning over time-annotated data with background knowledge may be challenging, due to the volume and velocity in which such data is being produced, such complex reasoning is necessary in scenarios where agents need to discover potential problems and this cannot be done with simple stream processing techniques. Stream Reasoners aim at bridging this gap between reasoning and stream processing and LASER is such a stream reasoner designed to analyse and perform complex reasoning over streams of data. It is based on LARS, a rule-based logical language extending Answer Set Programming, and it has shown better runtime results than other state-of-the-art stream reasoning systems. Nevertheless, for high levels of data throughput even LASER may be unable to compute answers in a timely fashion. In this paper, we study whether Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks, which have shown to be particularly well-suited for time series forecasting and classification, can be trained to approximate reasoning with LASER, so that agents can benefit from their high processing speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge