Ricardo Santos
Counterfactual Fairness with Graph Uncertainty
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Evaluating machine learning (ML) model bias is key to building trustworthy and robust ML systems. Counterfactual Fairness (CF) audits allow the measurement of bias of ML models with a causal framework, yet their conclusions rely on a single causal graph that is rarely known with certainty in real-world scenarios. We propose CF with Graph Uncertainty (CF-GU), a bias evaluation procedure that incorporates the uncertainty of specifying a causal graph into CF. CF-GU (i) bootstraps a Causal Discovery algorithm under domain knowledge constraints to produce a bag of plausible Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), (ii) quantifies graph uncertainty with the normalized Shannon entropy, and (iii) provides confidence bounds on CF metrics. Experiments on synthetic data show how contrasting domain knowledge assumptions support or refute audits of CF, while experiments on real-world data (COMPAS and Adult datasets) pinpoint well-known biases with high confidence, even when supplied with minimal domain knowledge constraints.
Improving Representation Learning of Complex Critical Care Data with ICU-BERT
Feb 26, 2025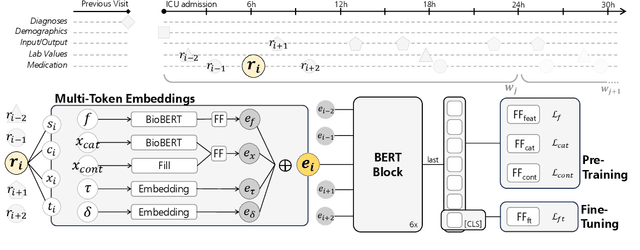
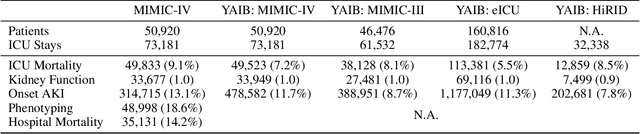
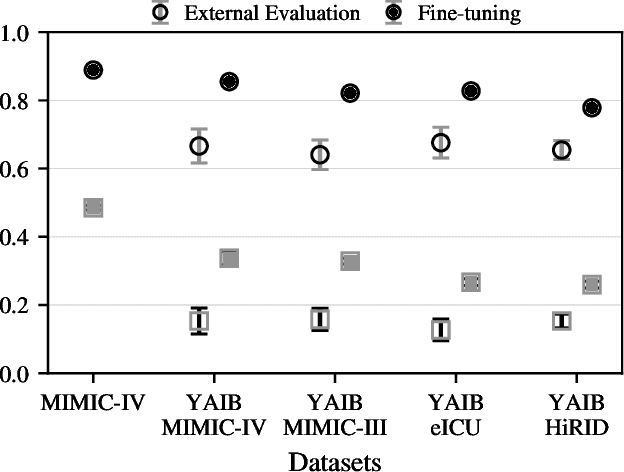
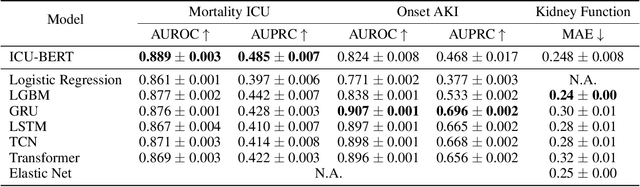
Abstract:The multivariate, asynchronous nature of real-world clinical data, such as that generated in Intensive Care Units (ICUs), challenges traditional AI-based decision-support systems. These often assume data regularity and feature independence and frequently rely on limited data scopes and manual feature engineering. The potential of generative AI technologies has not yet been fully exploited to analyze clinical data. We introduce ICU-BERT, a transformer-based model pre-trained on the MIMIC-IV database using a multi-task scheme to learn robust representations of complex ICU data with minimal preprocessing. ICU-BERT employs a multi-token input strategy, incorporating dense embeddings from a biomedical Large Language Model to learn a generalizable representation of complex and multivariate ICU data. With an initial evaluation of five tasks and four additional ICU datasets, ICU-BERT results indicate that ICU-BERT either compares to or surpasses current performance benchmarks by leveraging fine-tuning. By integrating structured and unstructured data, ICU-BERT advances the use of foundational models in medical informatics, offering an adaptable solution for clinical decision support across diverse applications.
Enhancing Power Grid Inspections with Machine Learning
Feb 18, 2025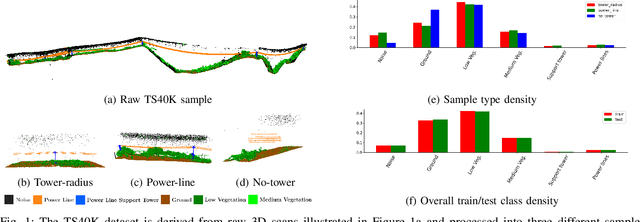
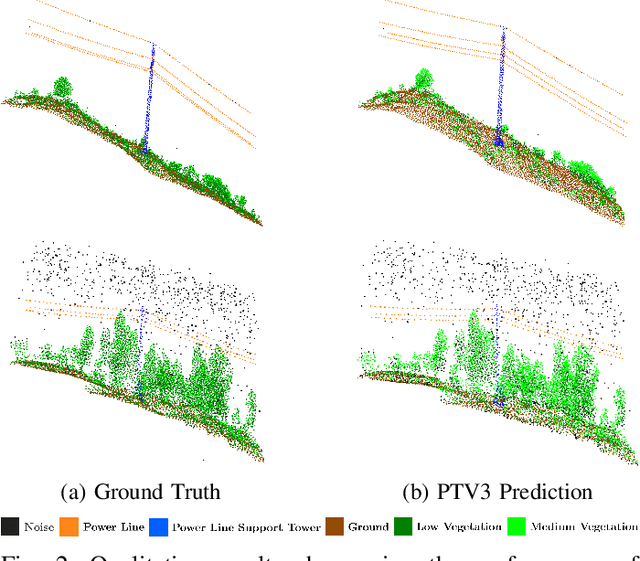


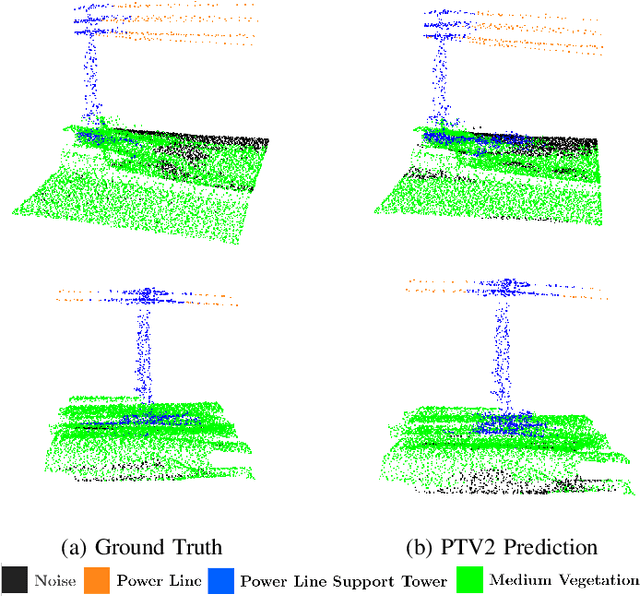
Abstract:Ensuring the safety and reliability of power grids is critical as global energy demands continue to rise. Traditional inspection methods, such as manual observations or helicopter surveys, are resource-intensive and lack scalability. This paper explores the use of 3D computer vision to automate power grid inspections, utilizing the TS40K dataset -- a high-density, annotated collection of 3D LiDAR point clouds. By concentrating on 3D semantic segmentation, our approach addresses challenges like class imbalance and noisy data to enhance the detection of critical grid components such as power lines and towers. The benchmark results indicate significant performance improvements, with IoU scores reaching 95.53% for the detection of power lines using transformer-based models. Our findings illustrate the potential for integrating ML into grid maintenance workflows, increasing efficiency and enabling proactive risk management strategies.
MERGE -- A Bimodal Dataset for Static Music Emotion Recognition
Jul 08, 2024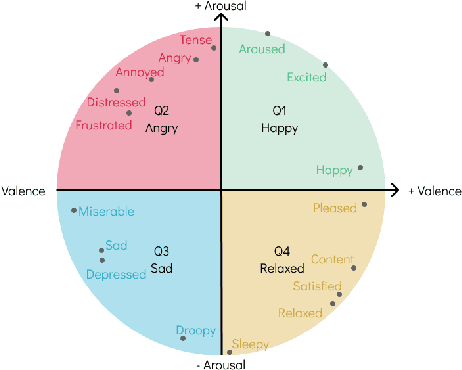
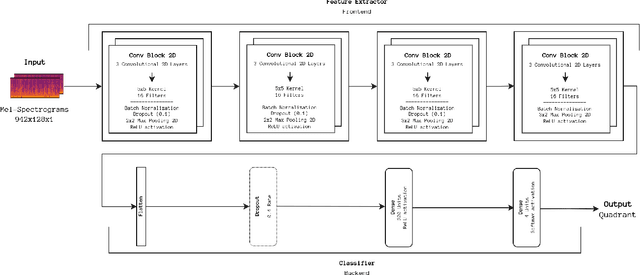
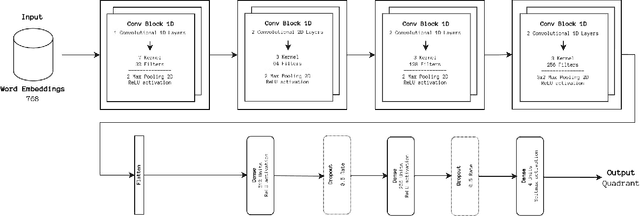
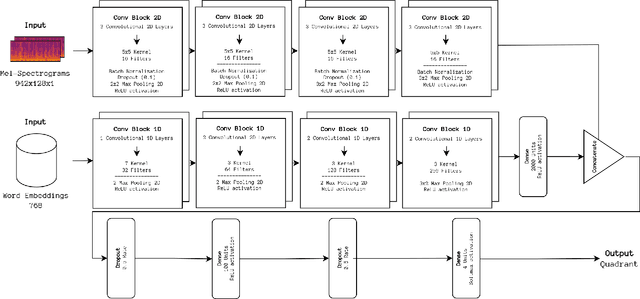
Abstract:The Music Emotion Recognition (MER) field has seen steady developments in recent years, with contributions from feature engineering, machine learning, and deep learning. The landscape has also shifted from audio-centric systems to bimodal ensembles that combine audio and lyrics. However, a severe lack of public and sizeable bimodal databases has hampered the development and improvement of bimodal audio-lyrics systems. This article proposes three new audio, lyrics, and bimodal MER research datasets, collectively called MERGE, created using a semi-automatic approach. To comprehensively assess the proposed datasets and establish a baseline for benchmarking, we conducted several experiments for each modality, using feature engineering, machine learning, and deep learning methodologies. In addition, we propose and validate fixed train-validate-test splits. The obtained results confirm the viability of the proposed datasets, achieving the best overall result of 79.21% F1-score for bimodal classification using a deep neural network.
TS40K: a 3D Point Cloud Dataset of Rural Terrain and Electrical Transmission System
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Research on supervised learning algorithms in 3D scene understanding has risen in prominence and witness great increases in performance across several datasets. The leading force of this research is the problem of autonomous driving followed by indoor scene segmentation. However, openly available 3D data on these tasks mainly focuses on urban scenarios. In this paper, we propose TS40K, a 3D point cloud dataset that encompasses more than 40,000 Km on electrical transmission systems situated in European rural terrain. This is not only a novel problem for the research community that can aid in the high-risk mission of power-grid inspection, but it also offers 3D point clouds with distinct characteristics from those in self-driving and indoor 3D data, such as high point-density and no occlusion. In our dataset, each 3D point is labeled with 1 out of 22 annotated classes. We evaluate the performance of state-of-the-art methods on our dataset concerning 3D semantic segmentation and 3D object detection. Finally, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the results along with key challenges such as using labels that were not originally intended for learning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge