Dhavan Shah
Optimizing Social Media Annotation of HPV Vaccine Skepticism and Misinformation Using Large Language Models: An Experimental Evaluation of In-Context Learning and Fine-Tuning Stance Detection Across Multiple Models
Nov 22, 2024


Abstract:This paper leverages large-language models (LLMs) to experimentally determine optimal strategies for scaling up social media content annotation for stance detection on HPV vaccine-related tweets. We examine both conventional fine-tuning and emergent in-context learning methods, systematically varying strategies of prompt engineering across widely used LLMs and their variants (e.g., GPT4, Mistral, and Llama3, etc.). Specifically, we varied prompt template design, shot sampling methods, and shot quantity to detect stance on HPV vaccination. Our findings reveal that 1) in general, in-context learning outperforms fine-tuning in stance detection for HPV vaccine social media content; 2) increasing shot quantity does not necessarily enhance performance across models; and 3) different LLMs and their variants present differing sensitivity to in-context learning conditions. We uncovered that the optimal in-context learning configuration for stance detection on HPV vaccine tweets involves six stratified shots paired with detailed contextual prompts. This study highlights the potential and provides an applicable approach for applying LLMs to research on social media stance and skepticism detection.
Purrfessor: A Fine-tuned Multimodal LLaVA Diet Health Chatbot
Nov 22, 2024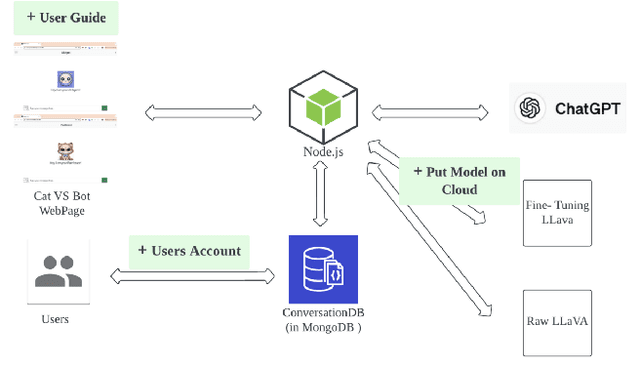
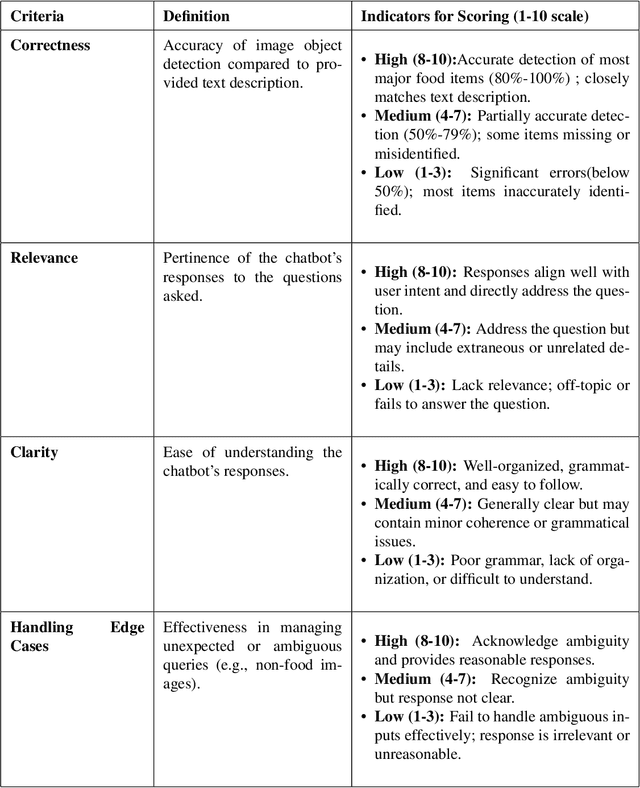
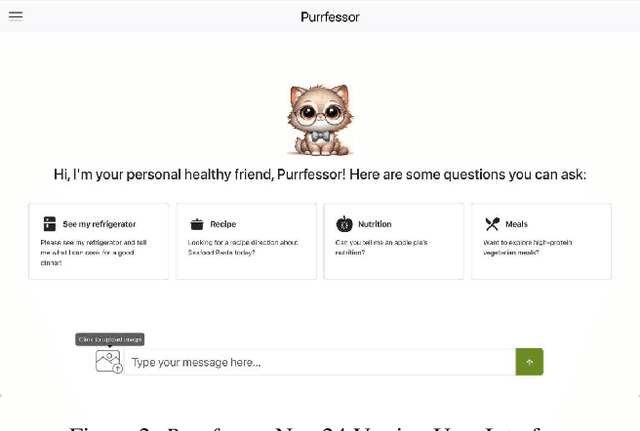
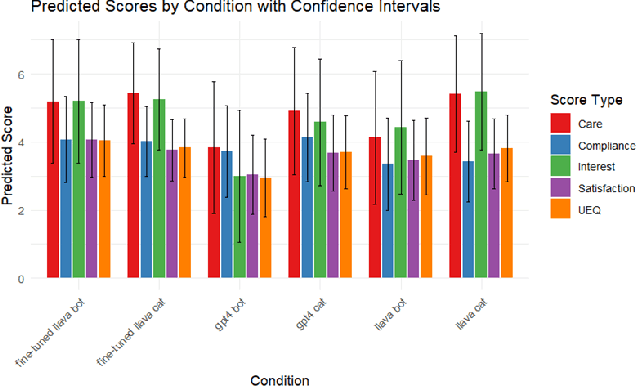
Abstract:This study introduces Purrfessor, an innovative AI chatbot designed to provide personalized dietary guidance through interactive, multimodal engagement. Leveraging the Large Language-and-Vision Assistant (LLaVA) model fine-tuned with food and nutrition data and a human-in-the-loop approach, Purrfessor integrates visual meal analysis with contextual advice to enhance user experience and engagement. We conducted two studies to evaluate the chatbot's performance and user experience: (a) simulation assessments and human validation were conducted to examine the performance of the fine-tuned model; (b) a 2 (Profile: Bot vs. Pet) by 3 (Model: GPT-4 vs. LLaVA vs. Fine-tuned LLaVA) experiment revealed that Purrfessor significantly enhanced users' perceptions of care ($\beta = 1.59$, $p = 0.04$) and interest ($\beta = 2.26$, $p = 0.01$) compared to the GPT-4 bot. Additionally, user interviews highlighted the importance of interaction design details, emphasizing the need for responsiveness, personalization, and guidance to improve user engagement.
Beyond Demographics: Aligning Role-playing LLM-based Agents Using Human Belief Networks
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Creating human-like large language model (LLM) agents is crucial for faithful social simulation. Having LLMs role-play based on demographic information sometimes improves human likeness but often does not. This study assessed whether LLM alignment with human behavior can be improved by integrating information from empirically-derived human belief networks. Using data from a human survey, we estimated a belief network encompassing 18 topics loading on two non-overlapping latent factors. We then seeded LLM-based agents with an opinion on one topic, and assessed the alignment of its expressed opinions on remaining test topics with corresponding human data. Role-playing based on demographic information alone did not align LLM and human opinions, but seeding the agent with a single belief greatly improved alignment for topics related in the belief network, and not for topics outside the network. These results suggest a novel path for human-LLM belief alignment in work seeking to simulate and understand patterns of belief distributions in society.
Evaluating LLM Agent Group Dynamics against Human Group Dynamics: A Case Study on Wisdom of Partisan Crowds
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:This study investigates the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) to simulate human group dynamics, particularly within politically charged contexts. We replicate the Wisdom of Partisan Crowds phenomenon using LLMs to role-play as Democrat and Republican personas, engaging in a structured interaction akin to human group study. Our approach evaluates how agents' responses evolve through social influence. Our key findings indicate that LLM agents role-playing detailed personas and without Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning closely align with human behaviors, while having CoT reasoning hurts the alignment. However, incorporating explicit biases into agent prompts does not necessarily enhance the wisdom of partisan crowds. Moreover, fine-tuning LLMs with human data shows promise in achieving human-like behavior but poses a risk of overfitting certain behaviors. These findings show the potential and limitations of using LLM agents in modeling human group phenomena.
Simulating Opinion Dynamics with Networks of LLM-based Agents
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Accurately simulating human opinion dynamics is crucial for understanding a variety of societal phenomena, including polarization and the spread of misinformation. However, the agent-based models (ABMs) commonly used for such simulations lack fidelity to human behavior. We propose a new approach to simulating opinion dynamics based on populations of Large Language Models (LLMs). Our findings reveal a strong inherent bias in LLM agents towards accurate information, leading to consensus in line with scientific reality. However, this bias limits the simulation of individuals with resistant views on issues like climate change. After inducing confirmation bias through prompt engineering, we observed opinion fragmentation in line with existing agent-based research. These insights highlight the promise and limitations of LLM agents in this domain and suggest a path forward: refining LLMs with real-world discourse to better simulate the evolution of human beliefs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge