Dayu Yang
DocAgent: A Multi-Agent System for Automated Code Documentation Generation
Apr 11, 2025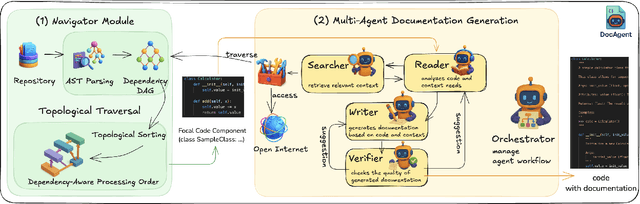
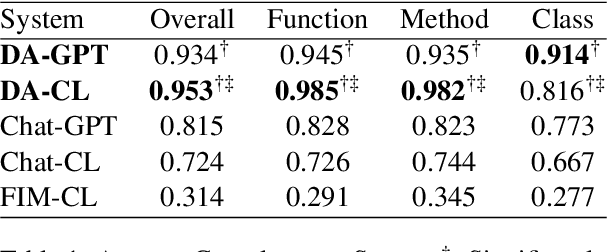
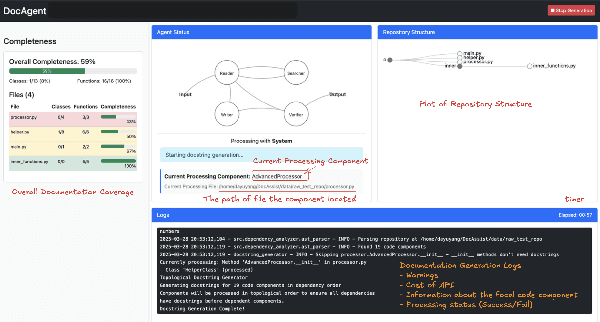

Abstract:High-quality code documentation is crucial for software development especially in the era of AI. However, generating it automatically using Large Language Models (LLMs) remains challenging, as existing approaches often produce incomplete, unhelpful, or factually incorrect outputs. We introduce DocAgent, a novel multi-agent collaborative system using topological code processing for incremental context building. Specialized agents (Reader, Searcher, Writer, Verifier, Orchestrator) then collaboratively generate documentation. We also propose a multi-faceted evaluation framework assessing Completeness, Helpfulness, and Truthfulness. Comprehensive experiments show DocAgent significantly outperforms baselines consistently. Our ablation study confirms the vital role of the topological processing order. DocAgent offers a robust approach for reliable code documentation generation in complex and proprietary repositories.
Code to Think, Think to Code: A Survey on Code-Enhanced Reasoning and Reasoning-Driven Code Intelligence in LLMs
Feb 26, 2025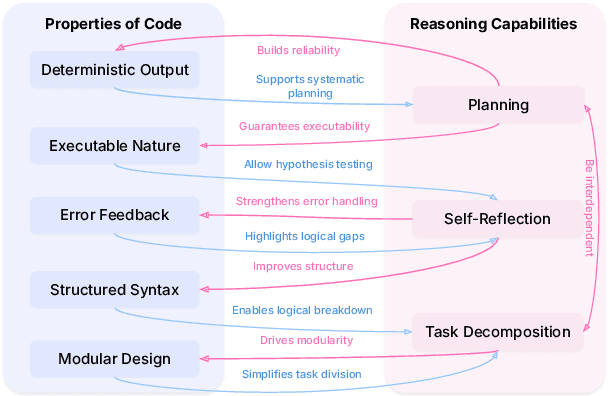
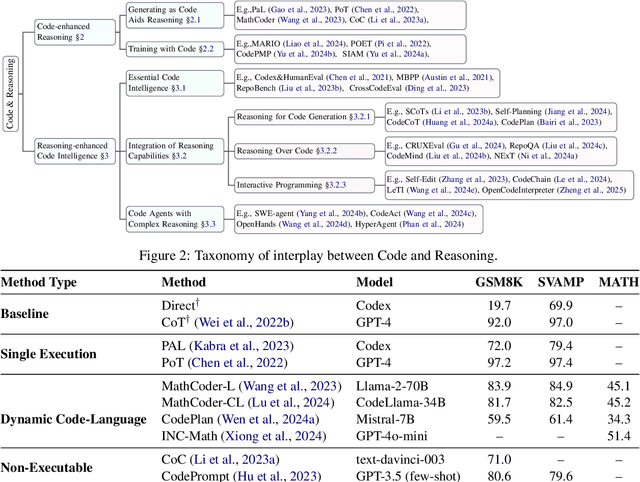


Abstract:In large language models (LLMs), code and reasoning reinforce each other: code offers an abstract, modular, and logic-driven structure that supports reasoning, while reasoning translates high-level goals into smaller, executable steps that drive more advanced code intelligence. In this study, we examine how code serves as a structured medium for enhancing reasoning: it provides verifiable execution paths, enforces logical decomposition, and enables runtime validation. We also explore how improvements in reasoning have transformed code intelligence from basic completion to advanced capabilities, enabling models to address complex software engineering tasks through planning and debugging. Finally, we identify key challenges and propose future research directions to strengthen this synergy, ultimately improving LLM's performance in both areas.
Enhancing Table Representations with LLM-powered Synthetic Data Generation
Nov 04, 2024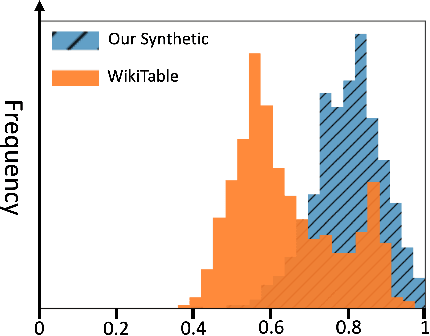
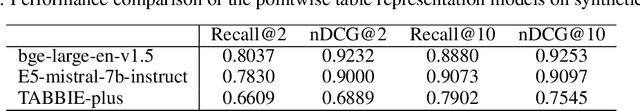
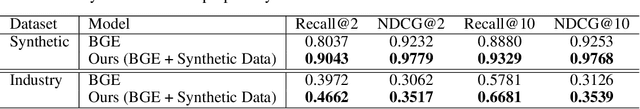

Abstract:In the era of data-driven decision-making, accurate table-level representations and efficient table recommendation systems are becoming increasingly crucial for improving table management, discovery, and analysis. However, existing approaches to tabular data representation often face limitations, primarily due to their focus on cell-level tasks and the lack of high-quality training data. To address these challenges, we first formulate a clear definition of table similarity in the context of data transformation activities within data-driven enterprises. This definition serves as the foundation for synthetic data generation, which require a well-defined data generation process. Building on this, we propose a novel synthetic data generation pipeline that harnesses the code generation and data manipulation capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to create a large-scale synthetic dataset tailored for table-level representation learning. Through manual validation and performance comparisons on the table recommendation task, we demonstrate that the synthetic data generated by our pipeline aligns with our proposed definition of table similarity and significantly enhances table representations, leading to improved recommendation performance.
Toward Automatic Group Membership Annotation for Group Fairness Evaluation
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:With the increasing research attention on fairness in information retrieval systems, more and more fairness-aware algorithms have been proposed to ensure fairness for a sustainable and healthy retrieval ecosystem. However, as the most adopted measurement of fairness-aware algorithms, group fairness evaluation metrics, require group membership information that needs massive human annotations and is barely available for general information retrieval datasets. This data sparsity significantly impedes the development of fairness-aware information retrieval studies. Hence, a practical, scalable, low-cost group membership annotation method is needed to assist or replace human annotations. This study explored how to leverage language models to automatically annotate group membership for group fairness evaluations, focusing on annotation accuracy and its impact. Our experimental results show that BERT-based models outperformed state-of-the-art large language models, including GPT and Mistral, achieving promising annotation accuracy with minimal supervision in recent fair-ranking datasets. Our impact-oriented evaluations reveal that minimal annotation error will not degrade the effectiveness and robustness of group fairness evaluation. The proposed annotation method reduces tremendous human efforts and expands the frontier of fairness-aware studies to more datasets.
Behavior Alignment: A New Perspective of Evaluating LLM-based Conversational Recommendation Systems
Apr 17, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated great potential in Conversational Recommender Systems (CRS). However, the application of LLMs to CRS has exposed a notable discrepancy in behavior between LLM-based CRS and human recommenders: LLMs often appear inflexible and passive, frequently rushing to complete the recommendation task without sufficient inquiry.This behavior discrepancy can lead to decreased accuracy in recommendations and lower user satisfaction. Despite its importance, existing studies in CRS lack a study about how to measure such behavior discrepancy. To fill this gap, we propose Behavior Alignment, a new evaluation metric to measure how well the recommendation strategies made by a LLM-based CRS are consistent with human recommenders'. Our experiment results show that the new metric is better aligned with human preferences and can better differentiate how systems perform than existing evaluation metrics. As Behavior Alignment requires explicit and costly human annotations on the recommendation strategies, we also propose a classification-based method to implicitly measure the Behavior Alignment based on the responses. The evaluation results confirm the robustness of the method.
Predicting Mergers and Acquisitions: Temporal Dynamic Industry Networks
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:M&A activities are pivotal for market consolidation, enabling firms to augment market power through strategic complementarities. Existing research often overlooks the peer effect, the mutual influence of M&A behaviors among firms, and fails to capture complex interdependencies within industry networks. Common approaches suffer from reliance on ad-hoc feature engineering, data truncation leading to significant information loss, reduced predictive accuracy, and challenges in real-world application. Additionally, the rarity of M&A events necessitates data rebalancing in conventional models, introducing bias and undermining prediction reliability. We propose an innovative M&A predictive model utilizing the Temporal Dynamic Industry Network (TDIN), leveraging temporal point processes and deep learning to adeptly capture industry-wide M&A dynamics. This model facilitates accurate, detailed deal-level predictions without arbitrary data manipulation or rebalancing, demonstrated through superior evaluation results from M&A cases between January 1997 and December 2020. Our approach marks a significant improvement over traditional models by providing detailed insights into M&A activities and strategic recommendations for specific firms.
Zero-shot Query Reformulation for Conversational Search
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:As the popularity of voice assistants continues to surge, conversational search has gained increased attention in Information Retrieval. However, data sparsity issues in conversational search significantly hinder the progress of supervised conversational search methods. Consequently, researchers are focusing more on zero-shot conversational search approaches. Nevertheless, existing zero-shot methods face three primary limitations: they are not universally applicable to all retrievers, their effectiveness lacks sufficient explainability, and they struggle to resolve common conversational ambiguities caused by omission. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel Zero-shot Query Reformulation (ZeQR) framework that reformulates queries based on previous dialogue contexts without requiring supervision from conversational search data. Specifically, our framework utilizes language models designed for machine reading comprehension tasks to explicitly resolve two common ambiguities: coreference and omission, in raw queries. In comparison to existing zero-shot methods, our approach is universally applicable to any retriever without additional adaptation or indexing. It also provides greater explainability and effectively enhances query intent understanding because ambiguities are explicitly and proactively resolved. Through extensive experiments on four TREC conversational datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
An Exploration Study of Mixed-initiative Query Reformulation in Conversational Passage Retrieval
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we report our methods and experiments for the TREC Conversational Assistance Track (CAsT) 2022. In this work, we aim to reproduce multi-stage retrieval pipelines and explore one of the potential benefits of involving mixed-initiative interaction in conversational passage retrieval scenarios: reformulating raw queries. Before the first ranking stage of a multi-stage retrieval pipeline, we propose a mixed-initiative query reformulation module, which achieves query reformulation based on the mixed-initiative interaction between the users and the system, as the replacement for the neural reformulation method. Specifically, we design an algorithm to generate appropriate questions related to the ambiguities in raw queries, and another algorithm to reformulate raw queries by parsing users' feedback and incorporating it into the raw query. For the first ranking stage of our multi-stage pipelines, we adopt a sparse ranking function: BM25, and a dense retrieval method: TCT-ColBERT. For the second-ranking step, we adopt a pointwise reranker: MonoT5, and a pairwise reranker: DuoT5. Experiments on both TREC CAsT 2021 and TREC CAsT 2022 datasets show the effectiveness of our mixed-initiative-based query reformulation method on improving retrieval performance compared with two popular reformulators: a neural reformulator: CANARD-T5 and a rule-based reformulator: historical query reformulator(HQE).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge