David J Hawkes
Towards a Computed-Aided Diagnosis System in Colonoscopy: Automatic Polyp Segmentation Using Convolution Neural Networks
Jan 15, 2021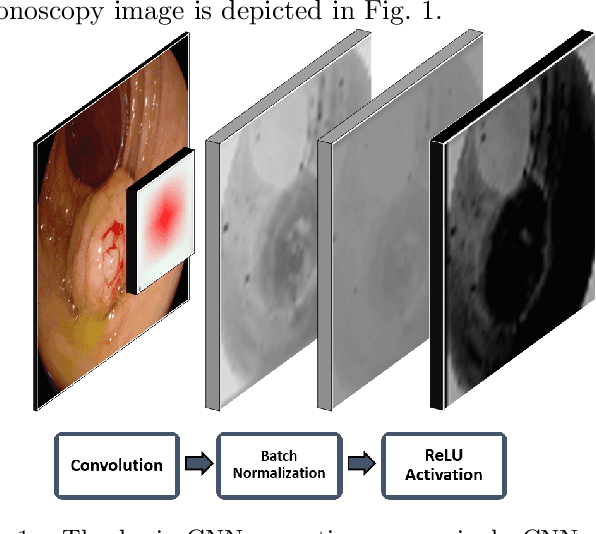
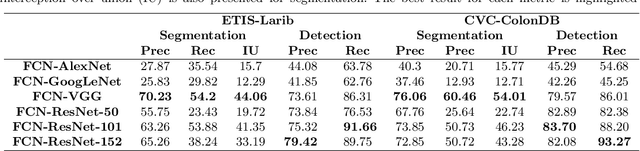
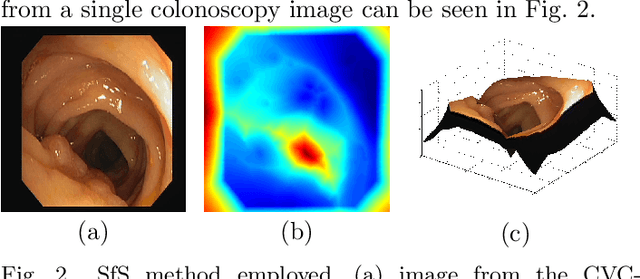
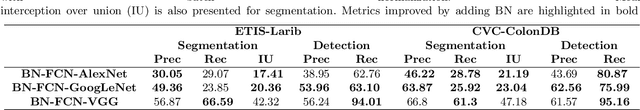
Abstract:Early diagnosis is essential for the successful treatment of bowel cancers including colorectal cancer (CRC) and capsule endoscopic imaging with robotic actuation can be a valuable diagnostic tool when combined with automated image analysis. We present a deep learning rooted detection and segmentation framework for recognizing lesions in colonoscopy and capsule endoscopy images. We restructure established convolution architectures, such as VGG and ResNets, by converting them into fully-connected convolution networks (FCNs), fine-tune them and study their capabilities for polyp segmentation and detection. We additionally use Shape from-Shading (SfS) to recover depth and provide a richer representation of the tissue's structure in colonoscopy images. Depth is incorporated into our network models as an additional input channel to the RGB information and we demonstrate that the resulting network yields improved performance. Our networks are tested on publicly available datasets and the most accurate segmentation model achieved a mean segmentation IU of 47.78% and 56.95% on the ETIS-Larib and CVC-Colon datasets, respectively. For polyp detection, the top performing models we propose surpass the current state of the art with detection recalls superior to 90% for all datasets tested. To our knowledge, we present the first work to use FCNs for polyp segmentation in addition to proposing a novel combination of SfS and RGB that boosts performance
* 10 pages, 6 figures
Image quality assessment for closed-loop computer-assisted lung ultrasound
Aug 20, 2020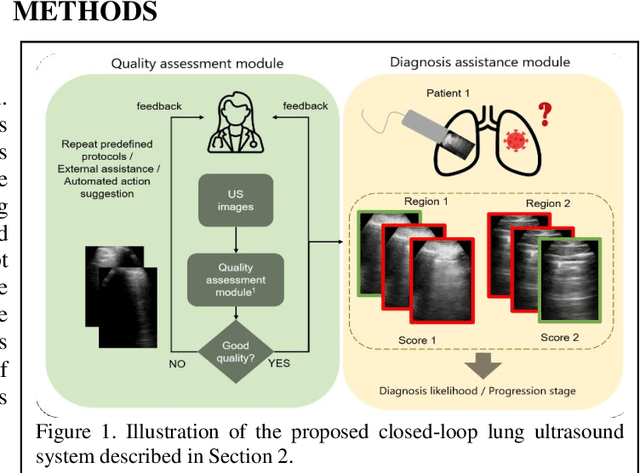
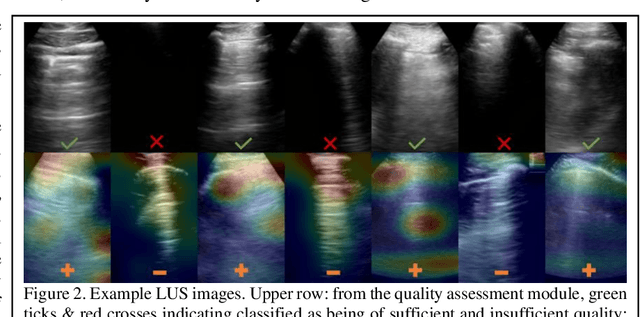
Abstract:We describe a novel, two-stage computer assistance system for lung anomaly detection using ultrasound imaging in the intensive care setting to improve operator performance and patient stratification during coronavirus pandemics. The proposed system consists of two deep-learning-based models. A quality assessment module automates predictions of image quality, and a diagnosis assistance module determines the likelihood-of-anomaly in ultrasound images of sufficient quality. Our two-stage strategy uses a novelty detection algorithm to address the lack of control cases available for training a quality assessment classifier. The diagnosis assistance module can then be trained with data that are deemed of sufficient quality, guaranteed by the closed-loop feedback mechanism from the quality assessment module. Integrating the two modules yields accurate, fast, and practical acquisition guidance and diagnostic assistance for patients with suspected respiratory conditions at the point-of-care. Using more than 25,000 ultrasound images from 37 COVID-19-positive patients scanned at two hospitals, plus 12 control cases, this study demonstrates the feasibility of using the proposed machine learning approach. We report an accuracy of 86% when classifying between sufficient and insufficient quality images by the quality assessment module. For data of sufficient quality, the mean classification accuracy in detecting COVID-19-positive cases was 95% on five holdout test data sets, unseen during the training of any networks within the proposed system.
The challenges of deploying artificial intelligence models in a rapidly evolving pandemic
May 19, 2020Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, emerged into a world being rapidly transformed by artificial intelligence (AI) based on big data, computational power and neural networks. The gaze of these networks has in recent years turned increasingly towards applications in healthcare. It was perhaps inevitable that COVID-19, a global disease propagating health and economic devastation, should capture the attention and resources of the world's computer scientists in academia and industry. The potential for AI to support the response to the pandemic has been proposed across a wide range of clinical and societal challenges, including disease forecasting, surveillance and antiviral drug discovery. This is likely to continue as the impact of the pandemic unfolds on the world's people, industries and economy but a surprising observation on the current pandemic has been the limited impact AI has had to date in the management of COVID-19. This correspondence focuses on exploring potential reasons behind the lack of successful adoption of AI models developed for COVID-19 diagnosis and prognosis, in front-line healthcare services. We highlight the moving clinical needs that models have had to address at different stages of the epidemic, and explain the importance of translating models to reflect local healthcare environments. We argue that both basic and applied research are essential to accelerate the potential of AI models, and this is particularly so during a rapidly evolving pandemic. This perspective on the response to COVID-19, may provide a glimpse into how the global scientific community should react to combat future disease outbreaks more effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge