Curtis Lisle
MHub.ai: A Simple, Standardized, and Reproducible Platform for AI Models in Medical Imaging
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform medical imaging by automating image analysis and accelerating clinical research. However, research and clinical use are limited by the wide variety of AI implementations and architectures, inconsistent documentation, and reproducibility issues. Here, we introduce MHub.ai, an open-source, container-based platform that standardizes access to AI models with minimal configuration, promoting accessibility and reproducibility in medical imaging. MHub.ai packages models from peer-reviewed publications into standardized containers that support direct processing of DICOM and other formats, provide a unified application interface, and embed structured metadata. Each model is accompanied by publicly available reference data that can be used to confirm model operation. MHub.ai includes an initial set of state-of-the-art segmentation, prediction, and feature extraction models for different modalities. The modular framework enables adaptation of any model and supports community contributions. We demonstrate the utility of the platform in a clinical use case through comparative evaluation of lung segmentation models. To further strengthen transparency and reproducibility, we publicly release the generated segmentations and evaluation metrics and provide interactive dashboards that allow readers to inspect individual cases and reproduce or extend our analysis. By simplifying model use, MHub.ai enables side-by-side benchmarking with identical execution commands and standardized outputs, and lowers the barrier to clinical translation.
Uncertainty-Guided Coarse-to-Fine Tumor Segmentation with Anatomy-Aware Post-Processing
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Reliable tumor segmentation in thoracic computed tomography (CT) remains challenging due to boundary ambiguity, class imbalance, and anatomical variability. We propose an uncertainty-guided, coarse-to-fine segmentation framework that combines full-volume tumor localization with refined region-of-interest (ROI) segmentation, enhanced by anatomically aware post-processing. The first-stage model generates a coarse prediction, followed by anatomically informed filtering based on lung overlap, proximity to lung surfaces, and component size. The resulting ROIs are segmented by a second-stage model trained with uncertainty-aware loss functions to improve accuracy and boundary calibration in ambiguous regions. Experiments on private and public datasets demonstrate improvements in Dice and Hausdorff scores, with fewer false positives and enhanced spatial interpretability. These results highlight the value of combining uncertainty modeling and anatomical priors in cascaded segmentation pipelines for robust and clinically meaningful tumor delineation. On the Orlando dataset, our framework improved Swin UNETR Dice from 0.4690 to 0.6447. Reduction in spurious components was strongly correlated with segmentation gains, underscoring the value of anatomically informed post-processing.
Self-Supervised Learning for Organs At Risk and Tumor Segmentation with Uncertainty Quantification
May 04, 2023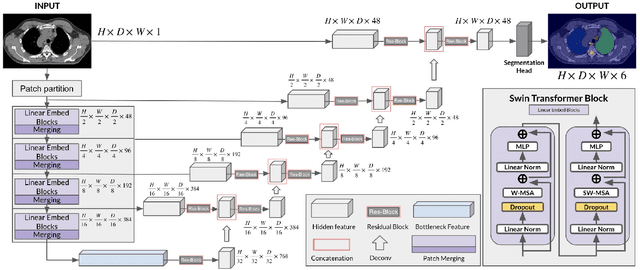
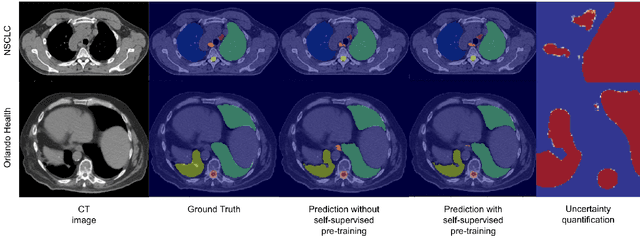
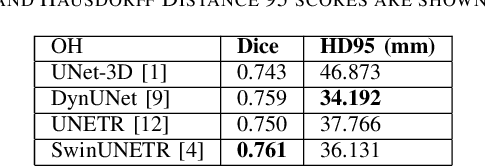
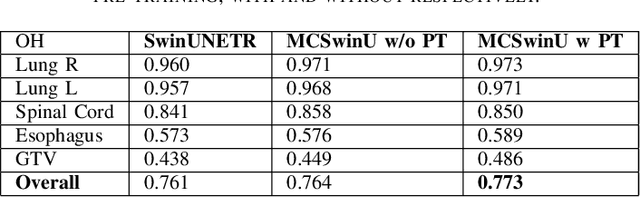
Abstract:In this study, our goal is to show the impact of self-supervised pre-training of transformers for organ at risk (OAR) and tumor segmentation as compared to costly fully-supervised learning. The proposed algorithm is called Monte Carlo Transformer based U-Net (MC-Swin-U). Unlike many other available models, our approach presents uncertainty quantification with Monte Carlo dropout strategy while generating its voxel-wise prediction. We test and validate the proposed model on both public and one private datasets and evaluate the gross tumor volume (GTV) as well as nearby risky organs' boundaries. We show that self-supervised pre-training approach improves the segmentation scores significantly while providing additional benefits for avoiding large-scale annotation costs.
Enhancing Organ at Risk Segmentation with Improved Deep Neural Networks
Feb 03, 2022



Abstract:Organ at risk (OAR) segmentation is a crucial step for treatment planning and outcome determination in radiotherapy treatments of cancer patients. Several deep learning based segmentation algorithms have been developed in recent years, however, U-Net remains the de facto algorithm designed specifically for biomedical image segmentation and has spawned many variants with known weaknesses. In this study, our goal is to present simple architectural changes in U-Net to improve its accuracy and generalization properties. Unlike many other available studies evaluating their algorithms on single center data, we thoroughly evaluate several variations of U-Net as well as our proposed enhanced architecture on multiple data sets for an extensive and reliable study of the OAR segmentation problem. Our enhanced segmentation model includes (a)architectural changes in the loss function, (b)optimization framework, and (c)convolution type. Testing on three publicly available multi-object segmentation data sets, we achieved an average of 80% dice score compared to the baseline U-Net performance of 63%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge