Conghui Hu
CLAIR: CLIP-Aided Weakly Supervised Zero-Shot Cross-Domain Image Retrieval
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:The recent growth of large foundation models that can easily generate pseudo-labels for huge quantity of unlabeled data makes unsupervised Zero-Shot Cross-Domain Image Retrieval (UZS-CDIR) less relevant. In this paper, we therefore turn our attention to weakly supervised ZS-CDIR (WSZS-CDIR) with noisy pseudo labels generated by large foundation models such as CLIP. To this end, we propose CLAIR to refine the noisy pseudo-labels with a confidence score from the similarity between the CLIP text and image features. Furthermore, we design inter-instance and inter-cluster contrastive losses to encode images into a class-aware latent space, and an inter-domain contrastive loss to alleviate domain discrepancies. We also learn a novel cross-domain mapping function in closed-form, using only CLIP text embeddings to project image features from one domain to another, thereby further aligning the image features for retrieval. Finally, we enhance the zero-shot generalization ability of our CLAIR to handle novel categories by introducing an extra set of learnable prompts. Extensive experiments are carried out using TUBerlin, Sketchy, Quickdraw, and DomainNet zero-shot datasets, where our CLAIR consistently shows superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
Rethink Cross-Modal Fusion in Weakly-Supervised Audio-Visual Video Parsing
Nov 14, 2023



Abstract:Existing works on weakly-supervised audio-visual video parsing adopt hybrid attention network (HAN) as the multi-modal embedding to capture the cross-modal context. It embeds the audio and visual modalities with a shared network, where the cross-attention is performed at the input. However, such an early fusion method highly entangles the two non-fully correlated modalities and leads to sub-optimal performance in detecting single-modality events. To deal with this problem, we propose the messenger-guided mid-fusion transformer to reduce the uncorrelated cross-modal context in the fusion. The messengers condense the full cross-modal context into a compact representation to only preserve useful cross-modal information. Furthermore, due to the fact that microphones capture audio events from all directions, while cameras only record visual events within a restricted field of view, there is a more frequent occurrence of unaligned cross-modal context from audio for visual event predictions. We thus propose cross-audio prediction consistency to suppress the impact of irrelevant audio information on visual event prediction. Experiments consistently illustrate the superior performance of our framework compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
Sketch-based Video Object Segmentation: Benchmark and Analysis
Nov 13, 2023
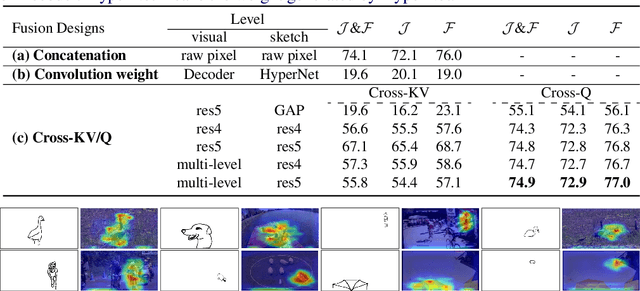
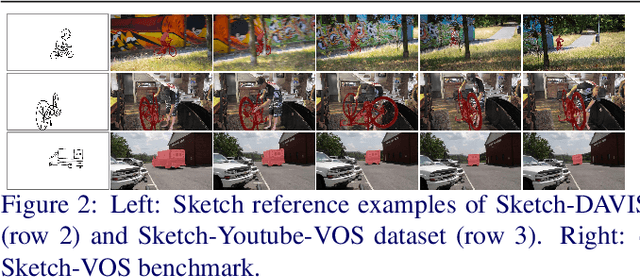
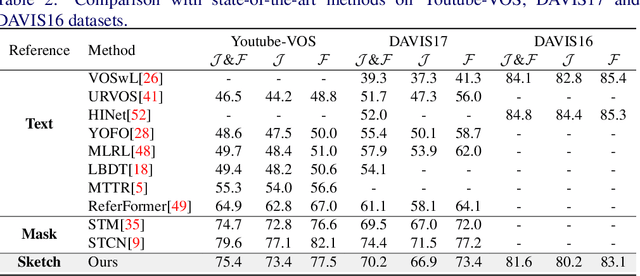
Abstract:Reference-based video object segmentation is an emerging topic which aims to segment the corresponding target object in each video frame referred by a given reference, such as a language expression or a photo mask. However, language expressions can sometimes be vague in conveying an intended concept and ambiguous when similar objects in one frame are hard to distinguish by language. Meanwhile, photo masks are costly to annotate and less practical to provide in a real application. This paper introduces a new task of sketch-based video object segmentation, an associated benchmark, and a strong baseline. Our benchmark includes three datasets, Sketch-DAVIS16, Sketch-DAVIS17 and Sketch-YouTube-VOS, which exploit human-drawn sketches as an informative yet low-cost reference for video object segmentation. We take advantage of STCN, a popular baseline of semi-supervised VOS task, and evaluate what the most effective design for incorporating a sketch reference is. Experimental results show sketch is more effective yet annotation-efficient than other references, such as photo masks, language and scribble.
Generalized Few-Shot Point Cloud Segmentation Via Geometric Words
Sep 20, 2023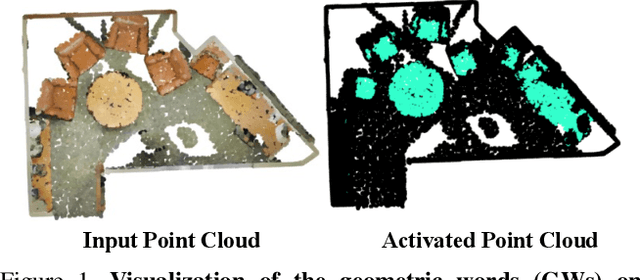

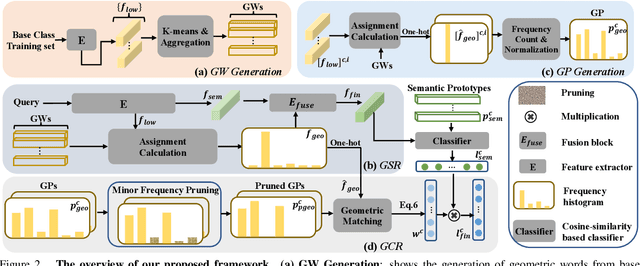

Abstract:Existing fully-supervised point cloud segmentation methods suffer in the dynamic testing environment with emerging new classes. Few-shot point cloud segmentation algorithms address this problem by learning to adapt to new classes at the sacrifice of segmentation accuracy for the base classes, which severely impedes its practicality. This largely motivates us to present the first attempt at a more practical paradigm of generalized few-shot point cloud segmentation, which requires the model to generalize to new categories with only a few support point clouds and simultaneously retain the capability to segment base classes. We propose the geometric words to represent geometric components shared between the base and novel classes, and incorporate them into a novel geometric-aware semantic representation to facilitate better generalization to the new classes without forgetting the old ones. Moreover, we introduce geometric prototypes to guide the segmentation with geometric prior knowledge. Extensive experiments on S3DIS and ScanNet consistently illustrate the superior performance of our method over baseline methods. Our code is available at: https://github.com/Pixie8888/GFS-3DSeg_GWs.
Feature Representation Learning for Unsupervised Cross-domain Image Retrieval
Jul 20, 2022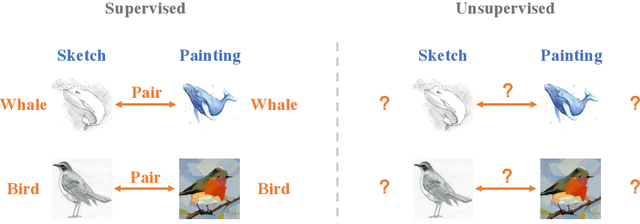

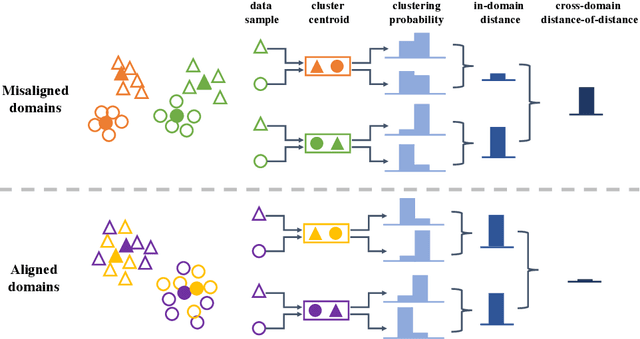

Abstract:Current supervised cross-domain image retrieval methods can achieve excellent performance. However, the cost of data collection and labeling imposes an intractable barrier to practical deployment in real applications. In this paper, we investigate the unsupervised cross-domain image retrieval task, where class labels and pairing annotations are no longer a prerequisite for training. This is an extremely challenging task because there is no supervision for both in-domain feature representation learning and cross-domain alignment. We address both challenges by introducing: 1) a new cluster-wise contrastive learning mechanism to help extract class semantic-aware features, and 2) a novel distance-of-distance loss to effectively measure and minimize the domain discrepancy without any external supervision. Experiments on the Office-Home and DomainNet datasets consistently show the superior image retrieval accuracies of our framework over state-of-the-art approaches. Our source code can be found at https://github.com/conghuihu/UCDIR.
Towards Unsupervised Sketch-based Image Retrieval
May 18, 2021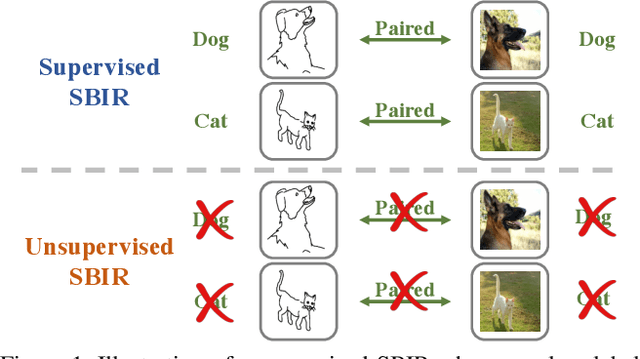
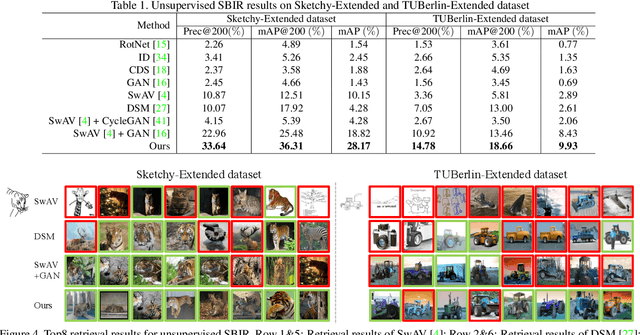
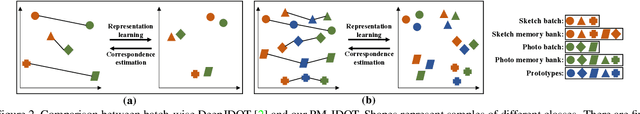
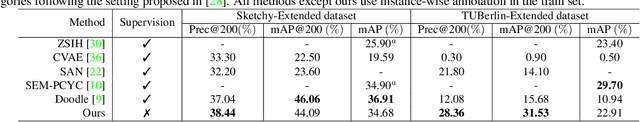
Abstract:Current supervised sketch-based image retrieval (SBIR) methods achieve excellent performance. However, the cost of data collection and labeling imposes an intractable barrier to practical deployment of real applications. In this paper, we present the first attempt at unsupervised SBIR to remove the labeling cost (category annotations and sketch-photo pairings) that is conventionally needed for training. Existing single-domain unsupervised representation learning methods perform poorly in this application, due to the unique cross-domain (sketch and photo) nature of the problem. We therefore introduce a novel framework that simultaneously performs unsupervised representation learning and sketch-photo domain alignment. Technically this is underpinned by exploiting joint distribution optimal transport (JDOT) to align data from different domains during representation learning, which we extend with trainable cluster prototypes and feature memory banks to further improve scalability and efficacy. Extensive experiments show that our framework achieves excellent performance in the new unsupervised setting, and performs comparably or better than state-of-the-art in the zero-shot setting.
End-To-End Semi-supervised Learning for Differentiable Particle Filters
Nov 11, 2020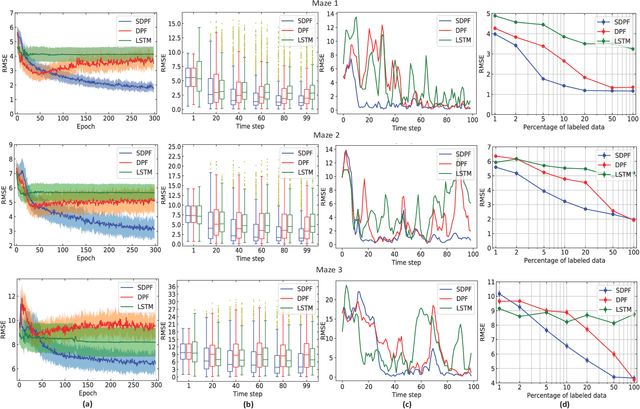
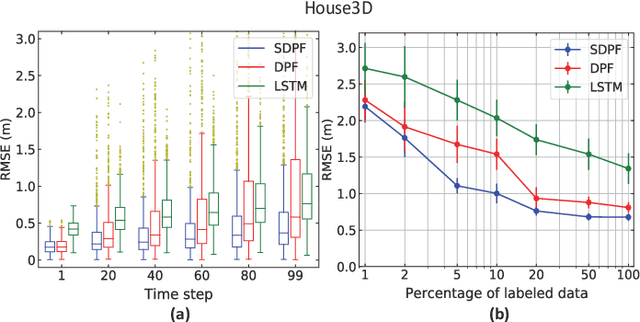

Abstract:Recent advances in incorporating neural networks into particle filters provide the desired flexibility to apply particle filters in large-scale real-world applications. The dynamic and measurement models in this framework are learnable through the differentiable implementation of particle filters. Past efforts in optimising such models often require the knowledge of true states which can be expensive to obtain or even unavailable in practice. In this paper, in order to reduce the demand for annotated data, we present an end-to-end learning objective based upon the maximisation of a pseudo-likelihood function which can improve the estimation of states when large portion of true states are unknown. We assess performance of the proposed method in state estimation tasks in robotics with simulated and real-world datasets.
Sketch-a-Classifier: Sketch-based Photo Classifier Generation
Apr 30, 2018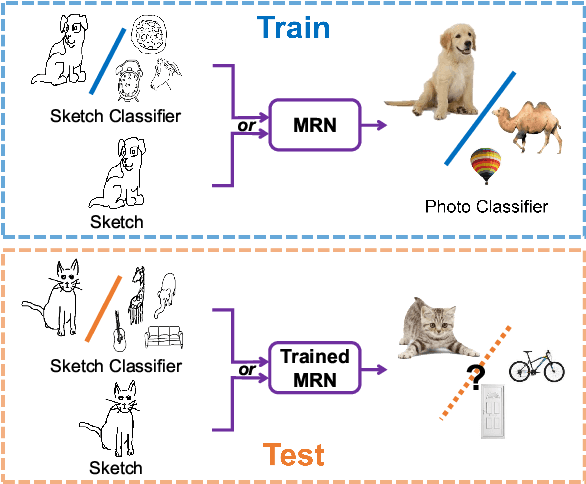
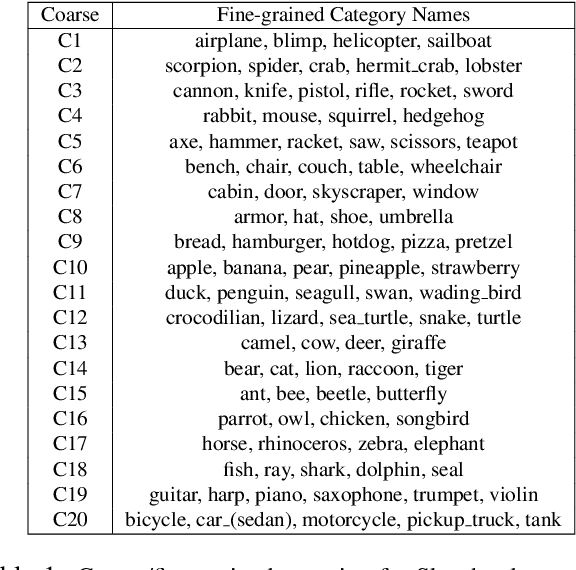
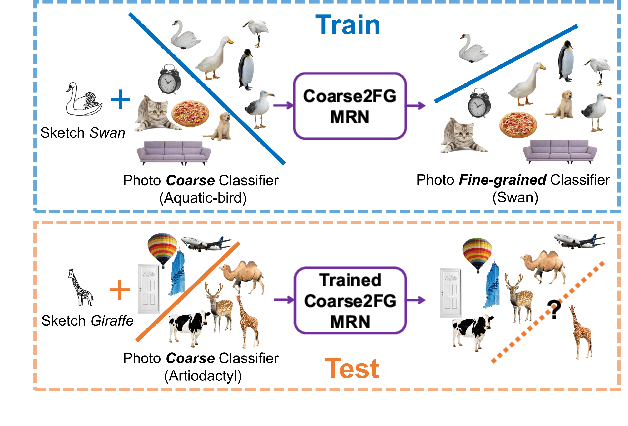
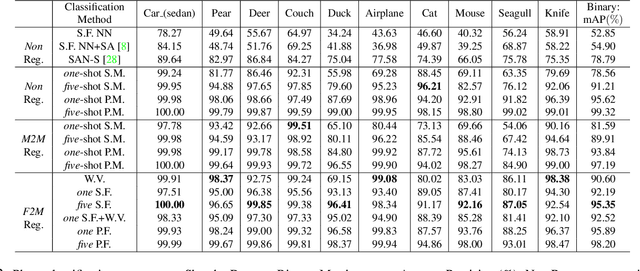
Abstract:Contemporary deep learning techniques have made image recognition a reasonably reliable technology. However training effective photo classifiers typically takes numerous examples which limits image recognition's scalability and applicability to scenarios where images may not be available. This has motivated investigation into zero-shot learning, which addresses the issue via knowledge transfer from other modalities such as text. In this paper we investigate an alternative approach of synthesizing image classifiers: almost directly from a user's imagination, via free-hand sketch. This approach doesn't require the category to be nameable or describable via attributes as per zero-shot learning. We achieve this via training a {model regression} network to map from {free-hand sketch} space to the space of photo classifiers. It turns out that this mapping can be learned in a category-agnostic way, allowing photo classifiers for new categories to be synthesized by user with no need for annotated training photos. {We also demonstrate that this modality of classifier generation can also be used to enhance the granularity of an existing photo classifier, or as a complement to name-based zero-shot learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge