Clare D. Thiem
Design Principles for Lifelong Learning AI Accelerators
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Lifelong learning - an agent's ability to learn throughout its lifetime - is a hallmark of biological learning systems and a central challenge for artificial intelligence (AI). The development of lifelong learning algorithms could lead to a range of novel AI applications, but this will also require the development of appropriate hardware accelerators, particularly if the models are to be deployed on edge platforms, which have strict size, weight, and power constraints. Here, we explore the design of lifelong learning AI accelerators that are intended for deployment in untethered environments. We identify key desirable capabilities for lifelong learning accelerators and highlight metrics to evaluate such accelerators. We then discuss current edge AI accelerators and explore the future design of lifelong learning accelerators, considering the role that different emerging technologies could play.
Frustrated Arrays of Nanomagnets for Efficient Reservoir Computing
Mar 16, 2021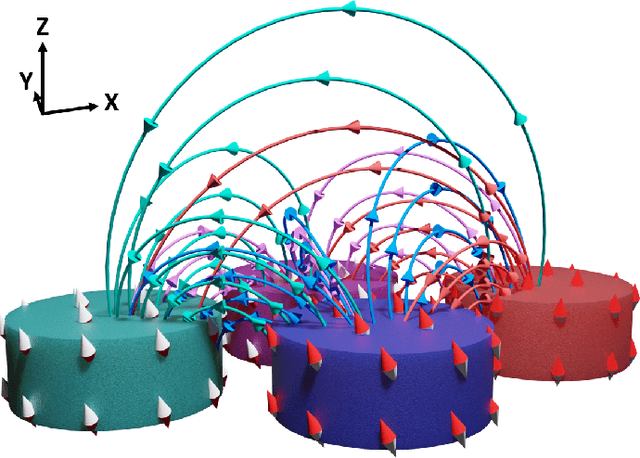


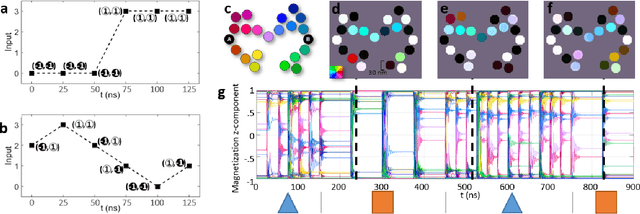
Abstract:We simulated our nanomagnet reservoir computer (NMRC) design on benchmark tasks, demonstrating NMRC's high memory content and expressibility. In support of the feasibility of this method, we fabricated a frustrated nanomagnet reservoir layer. Using this structure, we describe a low-power, low-area system with an area-energy-delay product $10^7$ lower than conventional RC systems, that is therefore promising for size, weight, and power (SWaP) constrained applications.
Reservoir Computing with Planar Nanomagnet Arrays
Mar 24, 2020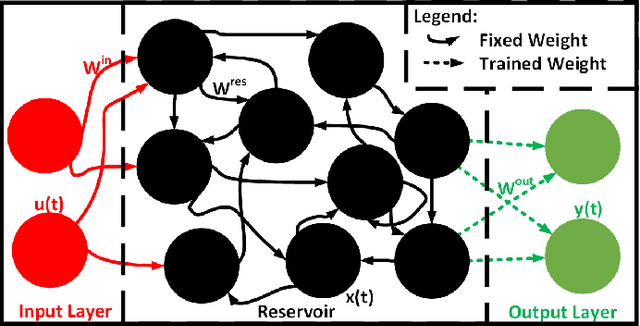
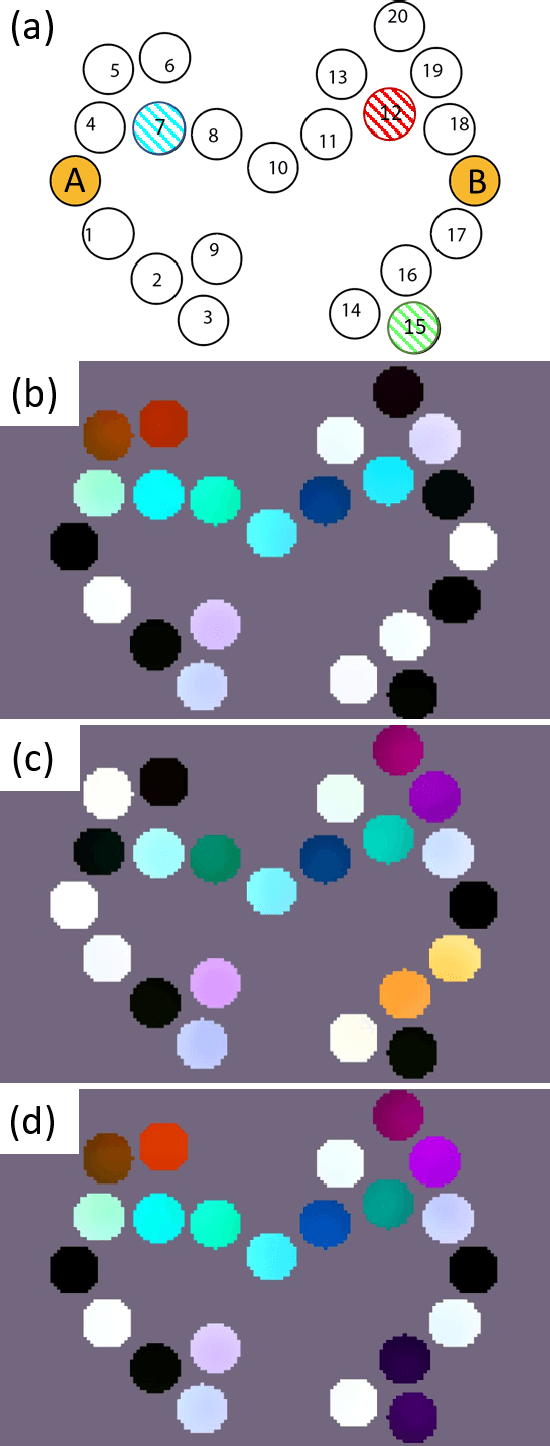
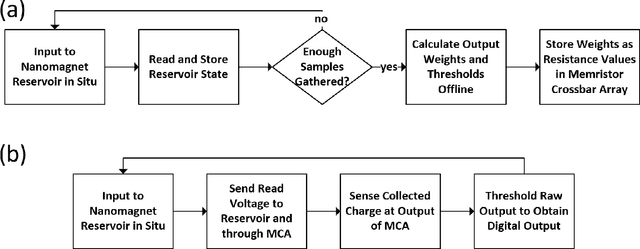
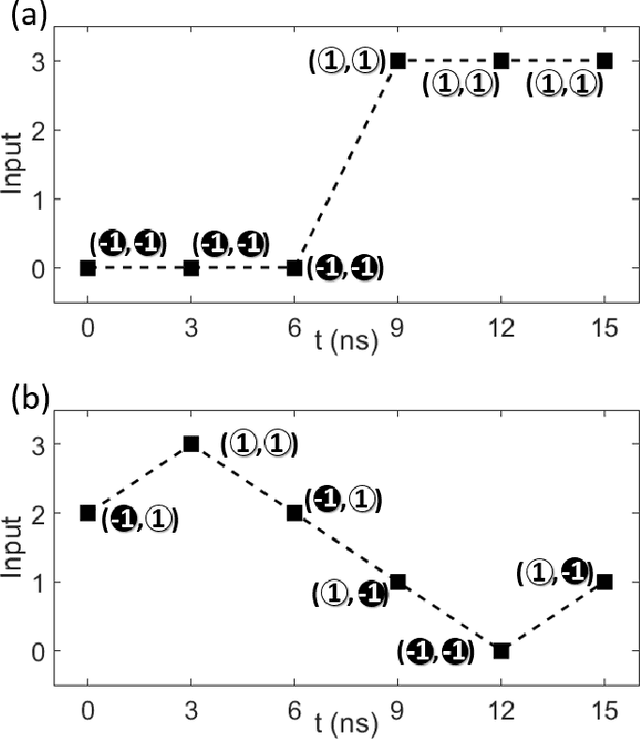
Abstract:Reservoir computing is an emerging methodology for neuromorphic computing that is especially well-suited for hardware implementations in size, weight, and power (SWaP) constrained environments. This work proposes a novel hardware implementation of a reservoir computer using a planar nanomagnet array. A small nanomagnet reservoir is demonstrated via micromagnetic simulations to be able to identify simple waveforms with 100% accuracy. Planar nanomagnet reservoirs are a promising new solution to the growing need for dedicated neuromorphic hardware.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge