Chuyuan Wang
Baltimore Atlas: FreqWeaver Adapter for Semi-supervised Ultra-high Spatial Resolution Land Cover Classification
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Ultra-high Spatial Resolution Land Cover Classification is essential for fine-grained land cover analysis, yet it remains challenging due to the high cost of pixel-level annotations, significant scale variation, and the limited adaptability of large-scale vision models. Existing methods typically focus on 1-meter spatial resolution imagery and rely heavily on annotated data, whereas practical applications often require processing higher-resolution imagery under weak supervision. To address this, we propose a parameter-efficient semi-supervised segmentation framework for 0.3 m spatial resolution imagery, which leverages the knowledge of SAM2 and introduces a remote sensing-specific FreqWeaver Adapter to enhance fine-grained detail modeling while maintaining a lightweight design at only 5.96% of the total model parameters. By effectively leveraging unlabeled data and maintaining minimal parameter overhead, the proposed method delivers robust segmentation results with superior structural consistency, achieving a 1.78% improvement over existing parameter-efficient tuning strategies and a 3.44% gain compared to state-of-the-art high-resolution remote sensing segmentation approaches.
Stratified Expert Cloning with Adaptive Selection for User Retention in Large-Scale Recommender Systems
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:User retention has emerged as a critical challenge in large-scale recommender systems, significantly impacting the long-term success of online platforms. Existing methods often focus on short-term engagement metrics, failing to capture the complex dynamics of user preferences and behaviors over extended periods. While reinforcement learning (RL) approaches have shown promise in optimizing long-term rewards, they face difficulties in credit assignment, sample efficiency, and exploration when applied to the user retention problem. In this work, we propose Stratified Expert Cloning (SEC), a novel imitation learning framework that effectively leverages abundant logged data from high-retention users to learn robust recommendation policies. SEC introduces three key innovations: 1) a multi-level expert stratification strategy that captures the nuances in expert user behaviors at different retention levels; 2) an adaptive expert selection mechanism that dynamically assigns users to the most suitable policy based on their current state and historical retention level; and 3) an action entropy regularization technique that promotes recommendation diversity and mitigates the risk of policy collapse. Through extensive offline experiments and online A/B tests on two major video platforms, Kuaishou and Kuaishou Lite, with hundreds of millions of daily active users, we demonstrate SEC's significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods in user retention. The results demonstrate significant improvements in user retention, with cumulative lifts of 0.098\% and 0.122\% in active days on Kuaishou and Kuaishou Lite respectively, additionally bringing tens of thousands of daily active users to each platform.
AlignPxtr: Aligning Predicted Behavior Distributions for Bias-Free Video Recommendations
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:In video recommendation systems, user behaviors such as watch time, likes, and follows are commonly used to infer user interest. However, these behaviors are influenced by various biases, including duration bias, demographic biases, and content category biases, which obscure true user preferences. In this paper, we hypothesize that biases and user interest are independent of each other. Based on this assumption, we propose a novel method that aligns predicted behavior distributions across different bias conditions using quantile mapping, theoretically guaranteeing zero mutual information between bias variables and the true user interest. By explicitly modeling the conditional distributions of user behaviors under different biases and mapping these behaviors to quantiles, we effectively decouple user interest from the confounding effects of various biases. Our approach uniquely handles both continuous signals (e.g., watch time) and discrete signals (e.g., likes, comments), while simultaneously addressing multiple bias dimensions. Additionally, we introduce a computationally efficient mean alignment alternative technique for practical real-time inference in large-scale systems. We validate our method through online A/B testing on two major video platforms: Kuaishou Lite and Kuaishou. The results demonstrate significant improvements in user engagement and retention, with \textbf{cumulative lifts of 0.267\% and 0.115\% in active days, and 1.102\% and 0.131\% in average app usage time}, respectively. The results demonstrate that our approach consistently achieves significant improvements in long-term user retention and substantial gains in average app usage time across different platforms. Our core code will be publised at https://github.com/justopit/CQE.
Conditional Quantile Estimation for Uncertain Watch Time in Short-Video Recommendation
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:Within the domain of short video recommendation, predicting users' watch time is a critical but challenging task. Prevailing deterministic solutions obtain accurate debiased statistical models, yet they neglect the intrinsic uncertainty inherent in user environments. In our observation, we found that this uncertainty could potentially limit these methods' accuracy in watch-time prediction on our online platform, despite that we have employed numerous features and complex network architectures. Consequently, we believe that a better solution is to model the conditional distribution of this uncertain watch time. In this paper, we introduce a novel estimation technique -- Conditional Quantile Estimation (CQE), which utilizes quantile regression to capture the nuanced distribution of watch time. The learned distribution accounts for the stochastic nature of users, thereby it provides a more accurate and robust estimation. In addition, we also design several strategies to enhance the quantile prediction including conditional expectation, conservative estimation, and dynamic quantile combination. We verify the effectiveness of our method through extensive offline evaluations using public datasets as well as deployment in a real-world video application with over 300 million daily active users.
What Makes for Good Visual Instructions? Synthesizing Complex Visual Reasoning Instructions for Visual Instruction Tuning
Nov 02, 2023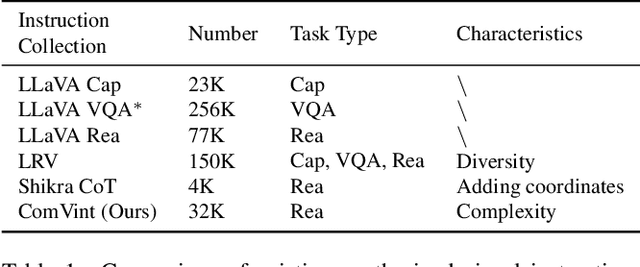
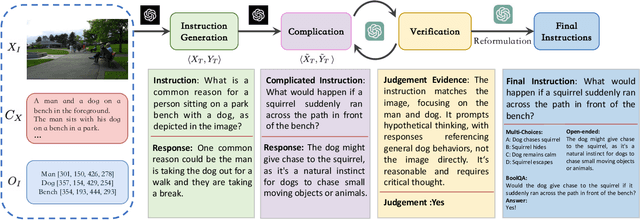
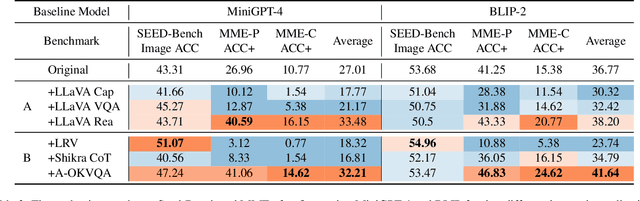
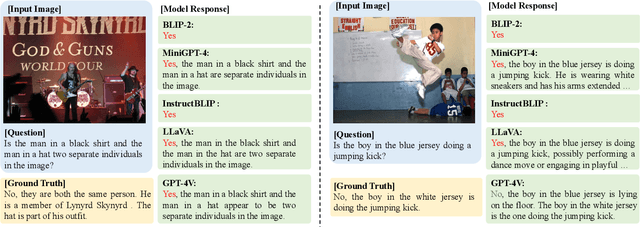
Abstract:Visual instruction tuning is an essential approach to improving the zero-shot generalization capability of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs). A surge of visual instruction datasets with various focuses and characteristics have been proposed recently, enabling MLLMs to achieve surprising results on evaluation benchmarks. To develop more capable MLLMs, in this paper, we aim to investigate a more fundamental question: ``what makes for good visual instructions?''. By conducting a comprehensive empirical study, we find that instructions focused on complex visual reasoning tasks are particularly effective in improving the performance of MLLMs on evaluation benchmarks. Building upon this finding, we design a systematic approach to automatically creating high-quality complex visual reasoning instructions. Our approach employs a synthesis-complication-reformulation paradigm, leveraging multiple stages to gradually increase the complexity of the instructions while guaranteeing quality. Based on this approach, we create the synthetic visual reasoning instruction dataset consisting of 32K examples, namely ComVint, and fine-tune four MLLMs on it. Experimental results demonstrate that our dataset consistently enhances the performance of all the compared MLLMs, e.g., improving the performance of MiniGPT-4 and BLIP-2 on MME-Cognition by 32.6% and 28.8%, respectively. Our code and data are publicly available at the link: https://github.com/RUCAIBox/ComVint.
PREFER: Prompt Ensemble Learning via Feedback-Reflect-Refine
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:As an effective tool for eliciting the power of Large Language Models (LLMs), prompting has recently demonstrated unprecedented abilities across a variety of complex tasks. To further improve the performance, prompt ensemble has attracted substantial interest for tackling the hallucination and instability of LLMs. However, existing methods usually adopt a two-stage paradigm, which requires a pre-prepared set of prompts with substantial manual effort, and is unable to perform directed optimization for different weak learners. In this paper, we propose a simple, universal, and automatic method named PREFER (Pompt Ensemble learning via Feedback-Reflect-Refine) to address the stated limitations. Specifically, given the fact that weak learners are supposed to focus on hard examples during boosting, PREFER builds a feedback mechanism for reflecting on the inadequacies of existing weak learners. Based on this, the LLM is required to automatically synthesize new prompts for iterative refinement. Moreover, to enhance stability of the prompt effect evaluation, we propose a novel prompt bagging method involving forward and backward thinking, which is superior to majority voting and is beneficial for both feedback and weight calculation in boosting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our PREFER achieves state-of-the-art performance in multiple types of tasks by a significant margin. We have made our code publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge