Chuyang Zhao
MonoFormer: One Transformer for Both Diffusion and Autoregression
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:Most existing multimodality methods use separate backbones for autoregression-based discrete text generation and diffusion-based continuous visual generation, or the same backbone by discretizing the visual data to use autoregression for both text and visual generation. In this paper, we propose to study a simple idea: share one transformer for both autoregression and diffusion. The feasibility comes from two main aspects: (i) Transformer is successfully applied to diffusion for visual generation, and (ii) transformer training for autoregression and diffusion is very similar, and the difference merely lies in that diffusion uses bidirectional attention mask and autoregression uses causal attention mask. Experimental results show that our approach achieves comparable image generation performance to current state-of-the-art methods as well as maintains the text generation capability. The project is publicly available at https://monoformer.github.io/.
MS-DETR: Efficient DETR Training with Mixed Supervision
Jan 08, 2024



Abstract:DETR accomplishes end-to-end object detection through iteratively generating multiple object candidates based on image features and promoting one candidate for each ground-truth object. The traditional training procedure using one-to-one supervision in the original DETR lacks direct supervision for the object detection candidates. We aim at improving the DETR training efficiency by explicitly supervising the candidate generation procedure through mixing one-to-one supervision and one-to-many supervision. Our approach, namely MS-DETR, is simple, and places one-to-many supervision to the object queries of the primary decoder that is used for inference. In comparison to existing DETR variants with one-to-many supervision, such as Group DETR and Hybrid DETR, our approach does not need additional decoder branches or object queries. The object queries of the primary decoder in our approach directly benefit from one-to-many supervision and thus are superior in object candidate prediction. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms related DETR variants, such as DN-DETR, Hybrid DETR, and Group DETR, and the combination with related DETR variants further improves the performance.
Style Variable and Irrelevant Learning for Generalizable Person Re-identification
Sep 12, 2022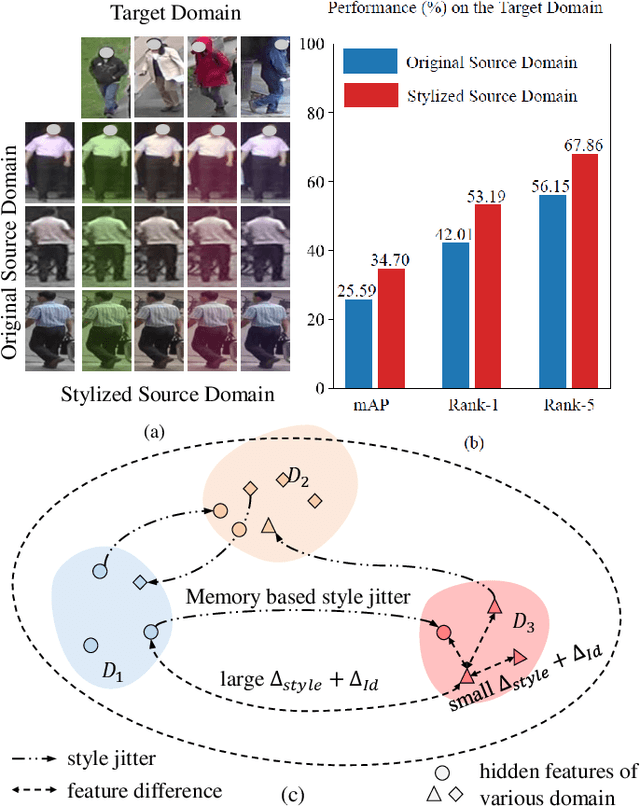
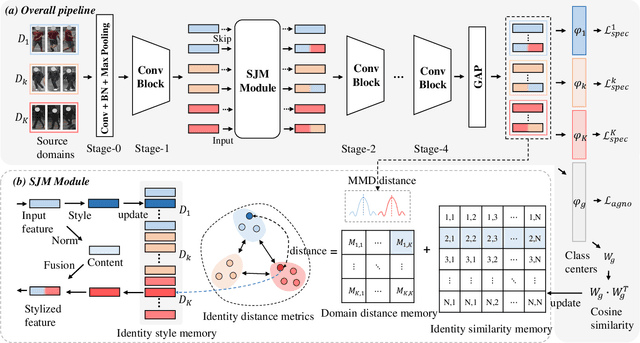
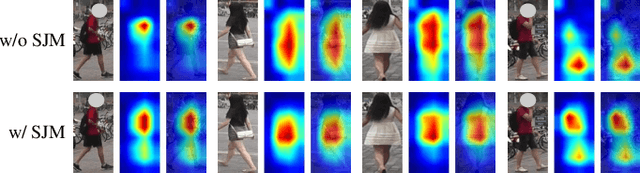
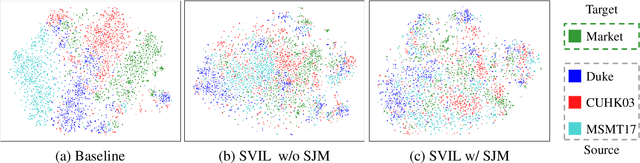
Abstract:Recently, due to the poor performance of supervised person re-identification (ReID) to an unseen domain, Domain Generalization (DG) person ReID has attracted a lot of attention which aims to learn a domain-insensitive model and can resist the influence of domain bias. In this paper, we first verify through an experiment that style factors are a vital part of domain bias. Base on this conclusion, we propose a Style Variable and Irrelevant Learning (SVIL) method to eliminate the effect of style factors on the model. Specifically, we design a Style Jitter Module (SJM) in SVIL. The SJM module can enrich the style diversity of the specific source domain and reduce the style differences of various source domains. This leads to the model focusing on identity-relevant information and being insensitive to the style changes. Besides, we organically combine the SJM module with a meta-learning algorithm, maximizing the benefits and further improving the generalization ability of the model. Note that our SJM module is plug-and-play and inference cost-free. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of our SVIL and our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on DG-ReID benchmarks by a large margin.
Symmetric Network with Spatial Relationship Modeling for Natural Language-based Vehicle Retrieval
Jun 22, 2022
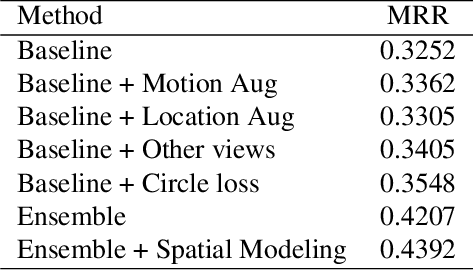

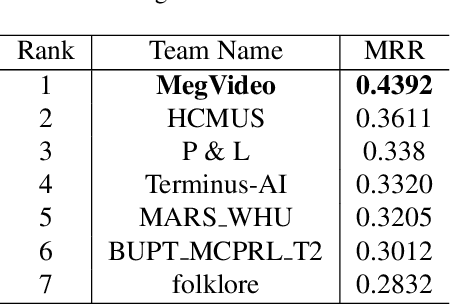
Abstract:Natural language (NL) based vehicle retrieval aims to search specific vehicle given text description. Different from the image-based vehicle retrieval, NL-based vehicle retrieval requires considering not only vehicle appearance, but also surrounding environment and temporal relations. In this paper, we propose a Symmetric Network with Spatial Relationship Modeling (SSM) method for NL-based vehicle retrieval. Specifically, we design a symmetric network to learn the unified cross-modal representations between text descriptions and vehicle images, where vehicle appearance details and vehicle trajectory global information are preserved. Besides, to make better use of location information, we propose a spatial relationship modeling methods to take surrounding environment and mutual relationship between vehicles into consideration. The qualitative and quantitative experiments verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. We achieve 43.92% MRR accuracy on the test set of the 6th AI City Challenge on natural language-based vehicle retrieval track, yielding the 1st place among all valid submissions on the public leaderboard. The code is available at https://github.com/hbchen121/AICITY2022_Track2_SSM.
* 8 pages, 3 figures, publised to CVPRW
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge