Kai Tu
Hermes: Unlocking Security Analysis of Cellular Network Protocols by Synthesizing Finite State Machines from Natural Language Specifications
Oct 11, 2023
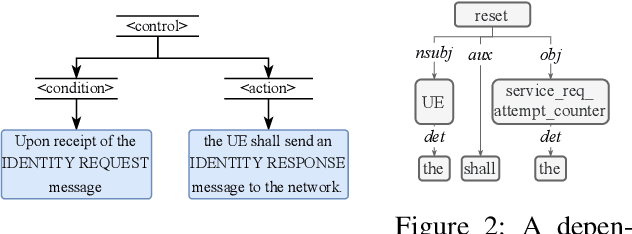

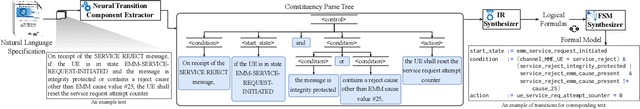
Abstract:In this paper, we present Hermes, an end-to-end framework to automatically generate formal representations from natural language cellular specifications. We first develop a neural constituency parser, NEUTREX, to process transition-relevant texts and extract transition components (i.e., states, conditions, and actions). We also design a domain-specific language to translate these transition components to logical formulas by leveraging dependency parse trees. Finally, we compile these logical formulas to generate transitions and create the formal model as finite state machines. To demonstrate the effectiveness of Hermes, we evaluate it on 4G NAS, 5G NAS, and 5G RRC specifications and obtain an overall accuracy of 81-87%, which is a substantial improvement over the state-of-the-art. Our security analysis of the extracted models uncovers 3 new vulnerabilities and identifies 19 previous attacks in 4G and 5G specifications, and 7 deviations in commercial 4G basebands.
Style Variable and Irrelevant Learning for Generalizable Person Re-identification
Sep 12, 2022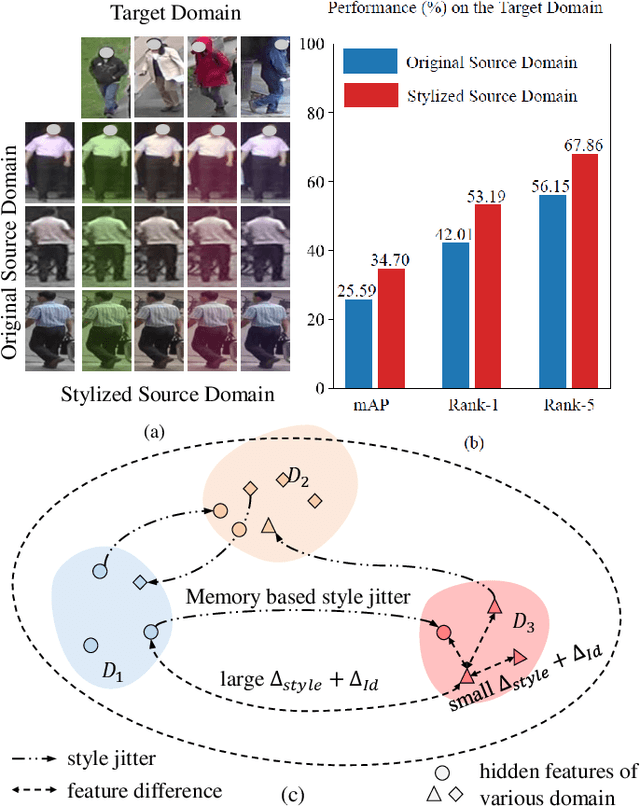
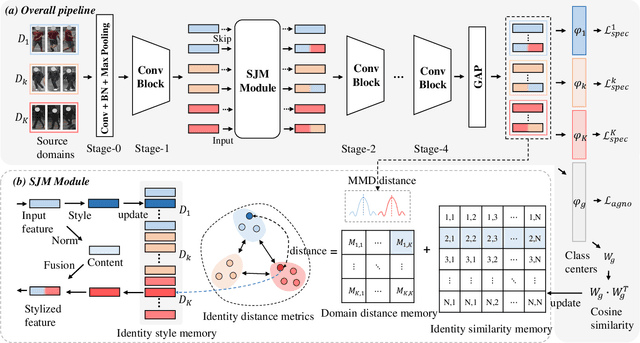
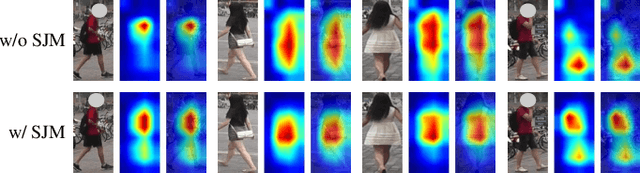
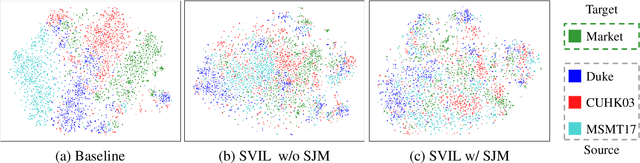
Abstract:Recently, due to the poor performance of supervised person re-identification (ReID) to an unseen domain, Domain Generalization (DG) person ReID has attracted a lot of attention which aims to learn a domain-insensitive model and can resist the influence of domain bias. In this paper, we first verify through an experiment that style factors are a vital part of domain bias. Base on this conclusion, we propose a Style Variable and Irrelevant Learning (SVIL) method to eliminate the effect of style factors on the model. Specifically, we design a Style Jitter Module (SJM) in SVIL. The SJM module can enrich the style diversity of the specific source domain and reduce the style differences of various source domains. This leads to the model focusing on identity-relevant information and being insensitive to the style changes. Besides, we organically combine the SJM module with a meta-learning algorithm, maximizing the benefits and further improving the generalization ability of the model. Note that our SJM module is plug-and-play and inference cost-free. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of our SVIL and our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on DG-ReID benchmarks by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge