Chengmeng Li
ActiveUMI: Robotic Manipulation with Active Perception from Robot-Free Human Demonstrations
Oct 02, 2025


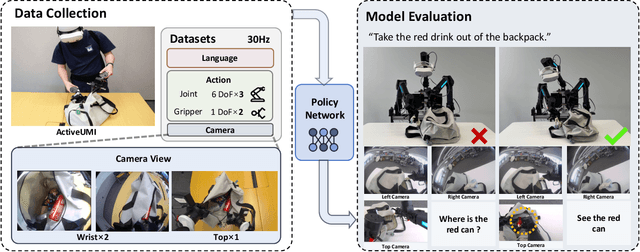
Abstract:We present ActiveUMI, a framework for a data collection system that transfers in-the-wild human demonstrations to robots capable of complex bimanual manipulation. ActiveUMI couples a portable VR teleoperation kit with sensorized controllers that mirror the robot's end-effectors, bridging human-robot kinematics via precise pose alignment. To ensure mobility and data quality, we introduce several key techniques, including immersive 3D model rendering, a self-contained wearable computer, and efficient calibration methods. ActiveUMI's defining feature is its capture of active, egocentric perception. By recording an operator's deliberate head movements via a head-mounted display, our system learns the crucial link between visual attention and manipulation. We evaluate ActiveUMI on six challenging bimanual tasks. Policies trained exclusively on ActiveUMI data achieve an average success rate of 70\% on in-distribution tasks and demonstrate strong generalization, retaining a 56\% success rate when tested on novel objects and in new environments. Our results demonstrate that portable data collection systems, when coupled with learned active perception, provide an effective and scalable pathway toward creating generalizable and highly capable real-world robot policies.
PointVLA: Injecting the 3D World into Vision-Language-Action Models
Mar 10, 2025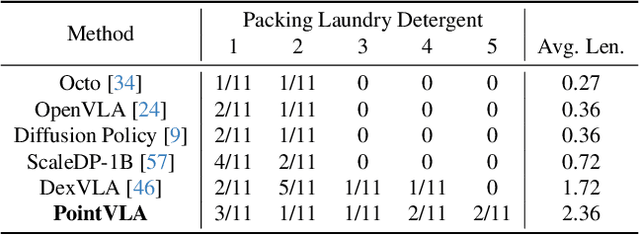
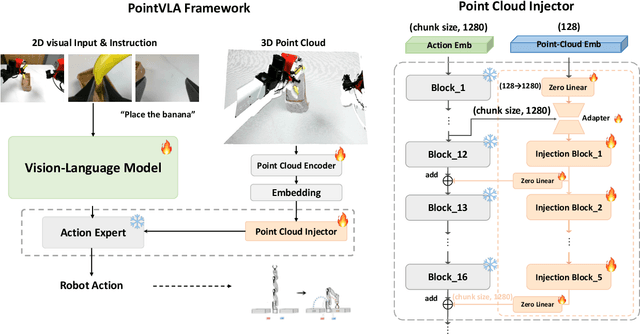
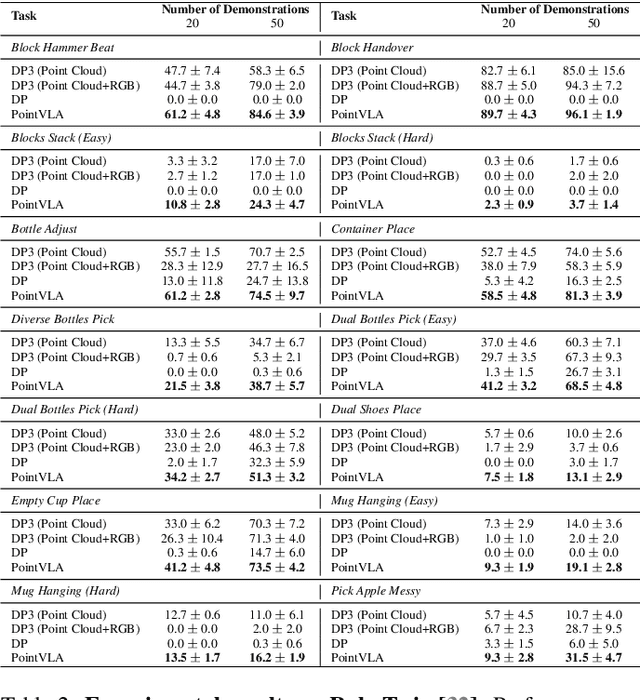
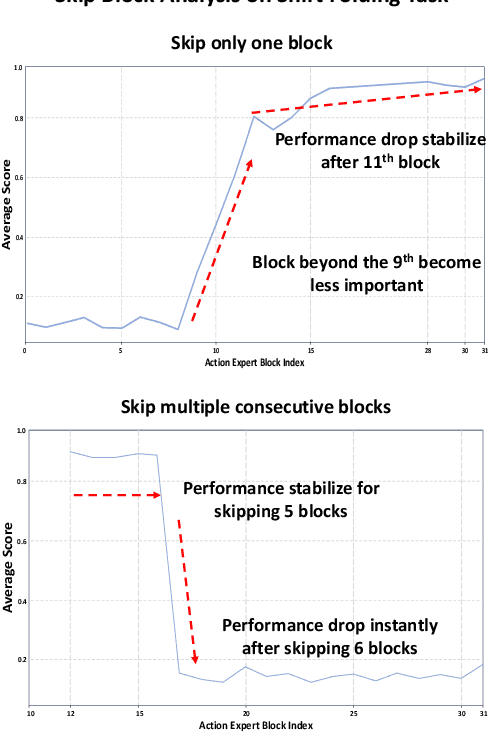
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models excel at robotic tasks by leveraging large-scale 2D vision-language pretraining, but their reliance on RGB images limits spatial reasoning critical for real-world interaction. Retraining these models with 3D data is computationally prohibitive, while discarding existing 2D datasets wastes valuable resources. To bridge this gap, we propose PointVLA, a framework that enhances pre-trained VLAs with point cloud inputs without requiring retraining. Our method freezes the vanilla action expert and injects 3D features via a lightweight modular block. To identify the most effective way of integrating point cloud representations, we conduct a skip-block analysis to pinpoint less useful blocks in the vanilla action expert, ensuring that 3D features are injected only into these blocks--minimizing disruption to pre-trained representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PointVLA outperforms state-of-the-art 2D imitation learning methods, such as OpenVLA, Diffusion Policy and DexVLA, across both simulated and real-world robotic tasks. Specifically, we highlight several key advantages of PointVLA enabled by point cloud integration: (1) Few-shot multi-tasking, where PointVLA successfully performs four different tasks using only 20 demonstrations each; (2) Real-vs-photo discrimination, where PointVLA distinguishes real objects from their images, leveraging 3D world knowledge to improve safety and reliability; (3) Height adaptability, Unlike conventional 2D imitation learning methods, PointVLA enables robots to adapt to objects at varying table height that unseen in train data. Furthermore, PointVLA achieves strong performance in long-horizon tasks, such as picking and packing objects from a moving conveyor belt, showcasing its ability to generalize across complex, dynamic environments.
Improving Vision-Language-Action Models via Chain-of-Affordance
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:Robot foundation models, particularly Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, have garnered significant attention for their ability to enhance robot policy learning, greatly improving robot generalization and robustness. OpenAI recent model, o1, showcased impressive capabilities in solving complex problems by utilizing extensive reasoning chains. This prompts an important question: can robot models achieve better performance in multi-task, complex environments by reviewing prior observations and then providing task-specific reasoning to guide action prediction? In this paper, we introduce \textbf{Chain-of-Affordance (CoA)}, a novel approach to scaling robot models by incorporating reasoning in the format of sequential robot affordances to facilitate task completion. Specifically, we prompt the model to consider the following four types of affordances before taking action: a) object affordance - what object to manipulate and where it is; b) grasp affordance - the specific object part to grasp; c) spatial affordance - the optimal space to place the object; and d) movement affordance - the collision-free path for movement. By integrating this knowledge into the policy model, the robot gains essential context, allowing it to act with increased precision and robustness during inference. Our experiments demonstrate that CoA achieves superior performance than state-of-the-art robot foundation models, such as OpenVLA and Octo. Additionally, CoA shows strong generalization to unseen object poses, identifies free space, and avoids obstacles in novel environments.
Diffusion-VLA: Scaling Robot Foundation Models via Unified Diffusion and Autoregression
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present DiffusionVLA, a novel framework that seamlessly combines the autoregression model with the diffusion model for learning visuomotor policy. Central to our approach is a next-token prediction objective, enabling the model to reason effectively over the user's query in the context of current observations. Subsequently, a diffusion model is attached to generate robust action outputs. To enhance policy learning through self-reasoning, we introduce a novel reasoning injection module that integrates reasoning phrases directly into the policy learning process. The whole framework is simple and flexible, making it easy to deploy and upgrade. We conduct extensive experiments using multiple real robots to validate the effectiveness of DiffusionVLA. Our tests include a challenging factory sorting task, where DiffusionVLA successfully categorizes objects, including those not seen during training. We observe that the reasoning module makes the model interpretable. It allows observers to understand the model thought process and identify potential causes of policy failures. Additionally, we test DiffusionVLA on a zero-shot bin-picking task, achieving 63.7\% accuracy on 102 previously unseen objects. Our method demonstrates robustness to visual changes, such as distractors and new backgrounds, and easily adapts to new embodiments. Furthermore, DiffusionVLA can follow novel instructions and retain conversational ability. Notably, DiffusionVLA is data-efficient and fast at inference; our smallest DiffusionVLA-2B runs 82Hz on a single A6000 GPU and can train from scratch on less than 50 demonstrations for a complex task. Finally, we scale the model from 2B to 72B parameters, showcasing improved generalization capabilities with increased model size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge