Chengbo Wang
DisorientLiDAR: Physical Attacks on LiDAR-based Localization
Sep 16, 2025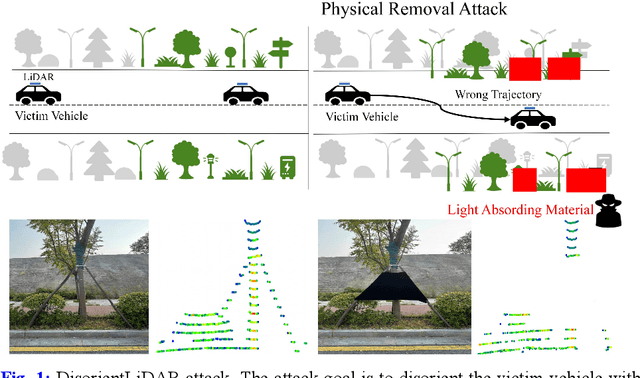
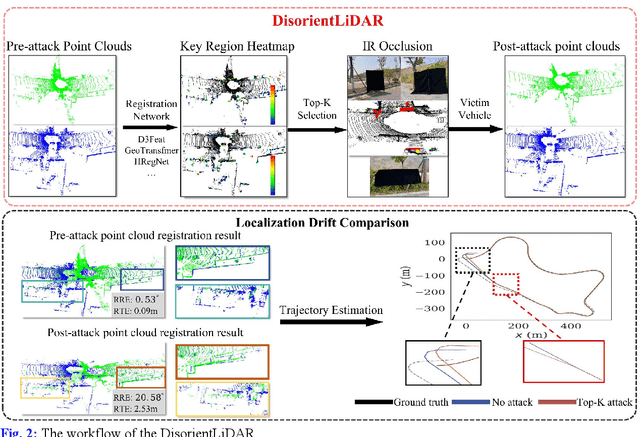
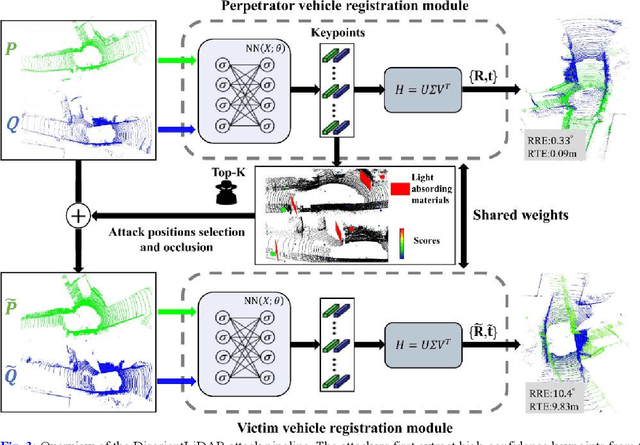
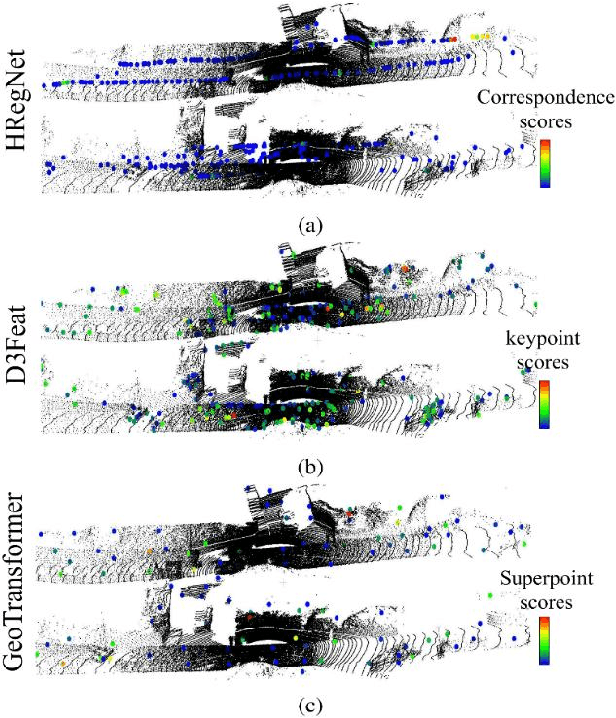
Abstract:Deep learning models have been shown to be susceptible to adversarial attacks with visually imperceptible perturbations. Even this poses a serious security challenge for the localization of self-driving cars, there has been very little exploration of attack on it, as most of adversarial attacks have been applied to 3D perception. In this work, we propose a novel adversarial attack framework called DisorientLiDAR targeting LiDAR-based localization. By reverse-engineering localization models (e.g., feature extraction networks), adversaries can identify critical keypoints and strategically remove them, thereby disrupting LiDAR-based localization. Our proposal is first evaluated on three state-of-the-art point-cloud registration models (HRegNet, D3Feat, and GeoTransformer) using the KITTI dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that removing regions containing Top-K keypoints significantly degrades their registration accuracy. We further validate the attack's impact on the Autoware autonomous driving platform, where hiding merely a few critical regions induces noticeable localization drift. Finally, we extended our attacks to the physical world by hiding critical regions with near-infrared absorptive materials, thereby successfully replicate the attack effects observed in KITTI data. This step has been closer toward the realistic physical-world attack that demonstrate the veracity and generality of our proposal.
PIS3R: Very Large Parallax Image Stitching via Deep 3D Reconstruction
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Image stitching aim to align two images taken from different viewpoints into one seamless, wider image. However, when the 3D scene contains depth variations and the camera baseline is significant, noticeable parallax occurs-meaning the relative positions of scene elements differ substantially between views. Most existing stitching methods struggle to handle such images with large parallax effectively. To address this challenge, in this paper, we propose an image stitching solution called PIS3R that is robust to very large parallax based on the novel concept of deep 3D reconstruction. First, we apply visual geometry grounded transformer to two input images with very large parallax to obtain both intrinsic and extrinsic parameters, as well as the dense 3D scene reconstruction. Subsequently, we reproject reconstructed dense point cloud onto a designated reference view using the recovered camera parameters, achieving pixel-wise alignment and generating an initial stitched image. Finally, to further address potential artifacts such as holes or noise in the initial stitching, we propose a point-conditioned image diffusion module to obtain the refined result.Compared with existing methods, our solution is very large parallax tolerant and also provides results that fully preserve the geometric integrity of all pixels in the 3D photogrammetric context, enabling direct applicability to downstream 3D vision tasks such as SfM. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm provides accurate stitching results for images with very large parallax, and outperforms the existing methods qualitatively and quantitatively.
DUN-SRE: Deep Unrolling Network with Spatiotemporal Rotation Equivariance for Dynamic MRI Reconstruction
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) exhibits transformation symmetries, including spatial rotation symmetry within individual frames and temporal symmetry along the time dimension. Explicit incorporation of these symmetry priors in the reconstruction model can significantly improve image quality, especially under aggressive undersampling scenarios. Recently, Equivariant convolutional neural network (ECNN) has shown great promise in exploiting spatial symmetry priors. However, existing ECNNs critically fail to model temporal symmetry, arguably the most universal and informative structural prior in dynamic MRI reconstruction. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel Deep Unrolling Network with Spatiotemporal Rotation Equivariance (DUN-SRE) for Dynamic MRI Reconstruction. The DUN-SRE establishes spatiotemporal equivariance through a (2+1)D equivariant convolutional architecture. In particular, it integrates both the data consistency and proximal mapping module into a unified deep unrolling framework. This architecture ensures rigorous propagation of spatiotemporal rotation symmetry constraints throughout the reconstruction process, enabling more physically accurate modeling of cardiac motion dynamics in cine MRI. In addition, a high-fidelity group filter parameterization mechanism is developed to maintain representation precision while enforcing symmetry constraints. Comprehensive experiments on Cardiac CINE MRI datasets demonstrate that DUN-SRE achieves state-of-the-art performance, particularly in preserving rotation-symmetric structures, offering strong generalization capability to a broad range of dynamic MRI reconstruction tasks.
Faster and Better 3D Splatting via Group Training
Dec 10, 2024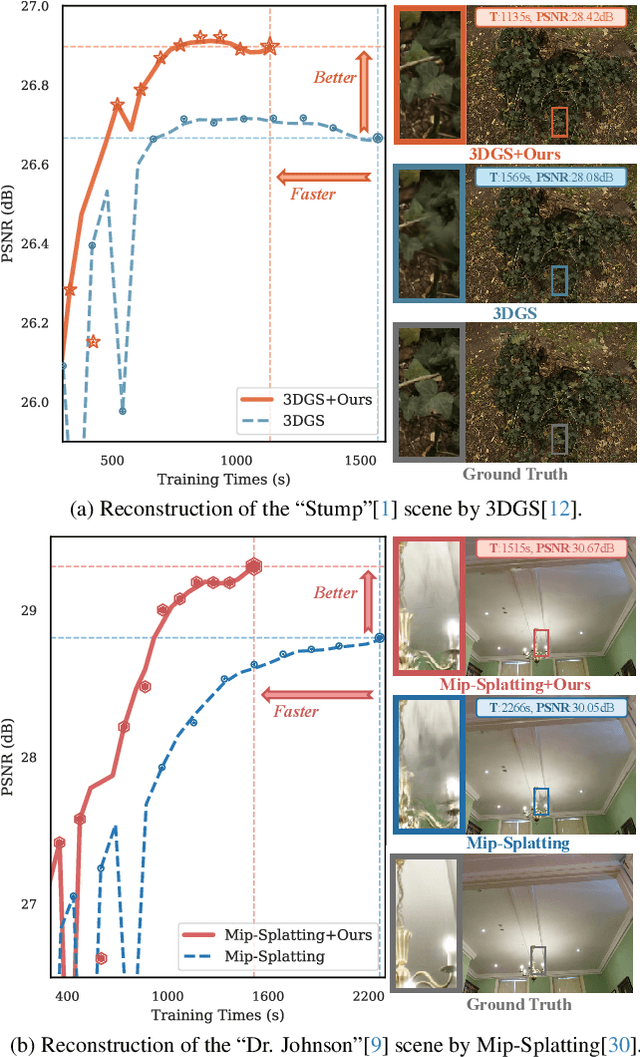
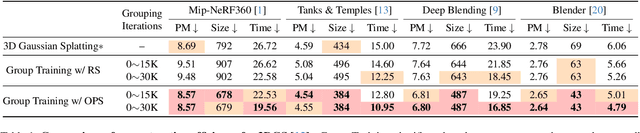
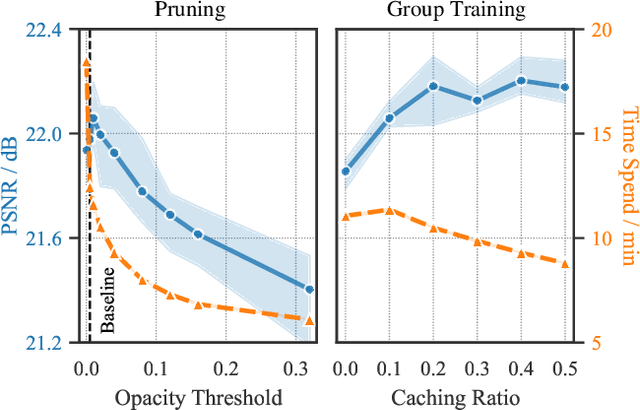
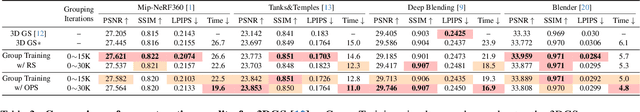
Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful technique for novel view synthesis, demonstrating remarkable capability in high-fidelity scene reconstruction through its Gaussian primitive representations. However, the computational overhead induced by the massive number of primitives poses a significant bottleneck to training efficiency. To overcome this challenge, we propose Group Training, a simple yet effective strategy that organizes Gaussian primitives into manageable groups, optimizing training efficiency and improving rendering quality. This approach shows universal compatibility with existing 3DGS frameworks, including vanilla 3DGS and Mip-Splatting, consistently achieving accelerated training while maintaining superior synthesis quality. Extensive experiments reveal that our straightforward Group Training strategy achieves up to 30% faster convergence and improved rendering quality across diverse scenarios.
SRE-CNN: A Spatiotemporal Rotation-Equivariant CNN for Cardiac Cine MR Imaging
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Dynamic MR images possess various transformation symmetries,including the rotation symmetry of local features within the image and along the temporal dimension. Utilizing these symmetries as prior knowledge can facilitate dynamic MR imaging with high spatiotemporal resolution. Equivariant CNN is an effective tool to leverage the symmetry priors. However, current equivariant CNN methods fail to fully exploit these symmetry priors in dynamic MR imaging. In this work, we propose a novel framework of Spatiotemporal Rotation-Equivariant CNN (SRE-CNN), spanning from the underlying high-precision filter design to the construction of the temporal-equivariant convolutional module and imaging model, to fully harness the rotation symmetries inherent in dynamic MR images. The temporal-equivariant convolutional module enables exploitation the rotation symmetries in both spatial and temporal dimensions, while the high-precision convolutional filter, based on parametrization strategy, enhances the utilization of rotation symmetry of local features to improve the reconstruction of detailed anatomical structures. Experiments conducted on highly undersampled dynamic cardiac cine data (up to 20X) have demonstrated the superior performance of our proposed approach, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Deep Residual Shrinkage Networks for EMG-based Gesture Identification
Feb 08, 2022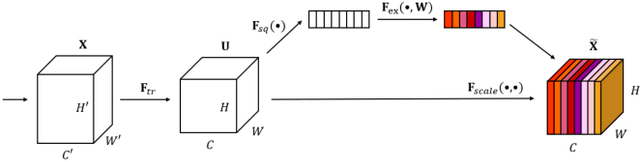
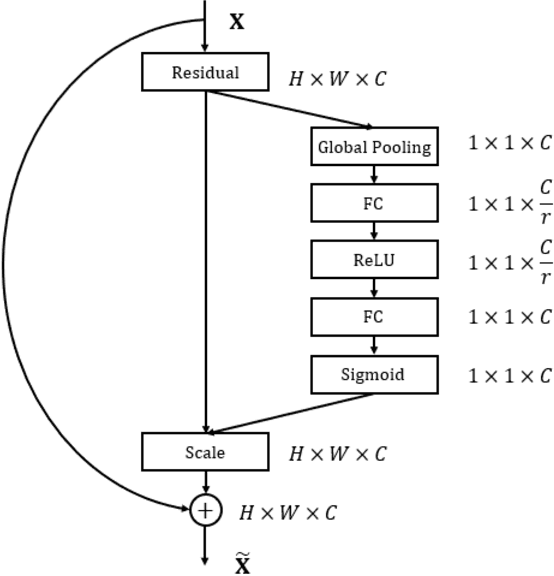
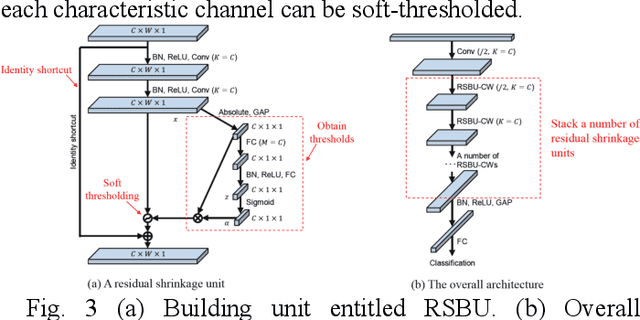
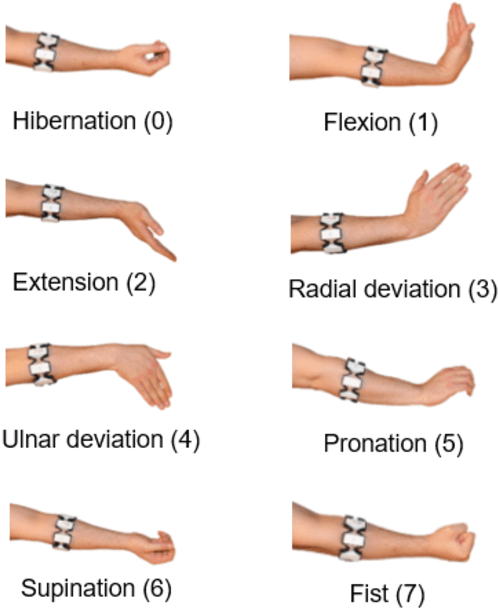
Abstract:This work introduces a method for high-accuracy EMG based gesture identification. A newly developed deep learning method, namely, deep residual shrinkage network is applied to perform gesture identification. Based on the feature of EMG signal resulting from gestures, optimizations are made to improve the identification accuracy. Finally, three different algorithms are applied to compare the accuracy of EMG signal recognition with that of DRSN. The result shows that DRSN excel traditional neural networks in terms of EMG recognition accuracy. This paper provides a reliable way to classify EMG signals, as well as exploring possible applications of DRSN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge