Burak Kantarci
Proactive SFC Provisioning with Forecast-Driven DRL in Data Centers
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Service Function Chaining (SFC) requires efficient placement of Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) to satisfy diverse service requirements while maintaining high resource utilization in Data Centers (DCs). Conventional static resource allocation often leads to overprovisioning or underprovisioning due to the dynamic nature of traffic loads and application demands. To address this challenge, we propose a hybrid forecast-driven Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework that combines predictive intelligence with SFC provisioning. Specifically, we leverage DRL to generate datasets capturing DC resource utilization and service demands, which are then used to train deep learning forecasting models. Using Optuna-based hyperparameter optimization, the best-performing models, Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network, Temporal Graph Neural Network, and Long Short-Term Memory, are combined into an ensemble to enhance stability and accuracy. The ensemble predictions are integrated into the DC selection process, enabling proactive placement decisions that consider both current and future resource availability. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method not only sustains high acceptance ratios for resource-intensive services such as Cloud Gaming and VoIP but also significantly improves acceptance ratios for latency-critical categories such as Augmented Reality increases from 30% to 50%, while Industry 4.0 improves from 30% to 45%. Consequently, the prediction-based model achieves significantly lower E2E latencies of 20.5%, 23.8%, and 34.8% reductions for VoIP, Video Streaming, and Cloud Gaming, respectively. This strategy ensures more balanced resource allocation, and reduces contention.
Intent2QoS: Language Model-Driven Automation of Traffic Shaping Configurations
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Traffic shaping and Quality of Service (QoS) enforcement are critical for managing bandwidth, latency, and fairness in networks. These tasks often rely on low-level traffic control settings, which require manual setup and technical expertise. This paper presents an automated framework that converts high-level traffic shaping intents in natural or declarative language into valid and correct traffic control rules. To the best of our knowledge, we present the first end-to-end pipeline that ties intent translation in a queuing-theoretic semantic model and, with a rule-based critic, yields deployable Linux traffic control configuration sets. The framework has three steps: (1) a queuing simulation with priority scheduling and Active Queue Management (AQM) builds a semantic model; (2) a language model, using this semantic model and a traffic profile, generates sub-intents and configuration rules; and (3) a rule-based critic checks and adjusts the rules for correctness and policy compliance. We evaluate multiple language models by generating traffic control commands from business intents that comply with relevant standards for traffic control protocols. Experimental results on 100 intents show significant gains, with LLaMA3 reaching 0.88 semantic similarity and 0.87 semantic coverage, outperforming other models by over 30\. A thorough sensitivity study demonstrates that AQM-guided prompting reduces variability threefold compared to zero-shot baselines.
Structure-Aware NL-to-SQL for SFC Provisioning via AST-Masking Empowered Language Models
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Effective Service Function Chain (SFC) provisioning requires precise orchestration in dynamic and latency-sensitive networks. Reinforcement Learning (RL) improves adaptability but often ignores structured domain knowledge, which limits generalization and interpretability. Large Language Models (LLMs) address this gap by translating natural language (NL) specifications into executable Structured Query Language (SQL) commands for specification-driven SFC management. Conventional fine-tuning, however, can cause syntactic inconsistencies and produce inefficient queries. To overcome this, we introduce Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)-Masking, a structure-aware fine-tuning method that uses SQL ASTs to assign weights to key components and enforce syntax-aware learning without adding inference overhead. Experiments show that AST-Masking significantly improves SQL generation accuracy across multiple language models. FLAN-T5 reaches an Execution Accuracy (EA) of 99.6%, while Gemma achieves the largest absolute gain from 7.5% to 72.0%. These results confirm the effectiveness of structure-aware fine-tuning in ensuring syntactically correct and efficient SQL generation for interpretable SFC orchestration.
Spatiotemporal Semantic V2X Framework for Cooperative Collision Prediction
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) demand real-time collision prediction to ensure road safety and reduce accident severity. Conventional approaches rely on transmitting raw video or high-dimensional sensory data from roadside units (RSUs) to vehicles, which is impractical under vehicular communication bandwidth and latency constraints. In this work, we propose a semantic V2X framework in which RSU-mounted cameras generate spatiotemporal semantic embeddings of future frames using the Video Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture (V-JEPA). To evaluate the system, we construct a digital twin of an urban traffic environment enabling the generation of d verse traffic scenarios with both safe and collision events. These embeddings of the future frame, extracted from V-JEPA, capture task-relevant traffic dynamics and are transmitted via V2X links to vehicles, where a lightweight attentive probe and classifier decode them to predict imminent collisions. By transmitting only semantic embeddings instead of raw frames, the proposed system significantly reduces communication overhead while maintaining predictive accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that the framework with an appropriate processing method achieves a 10% F1-score improvement for collision prediction while reducing transmission requirements by four orders of magnitude compared to raw video. This validates the potential of semantic V2X communication to enable cooperative, real-time collision prediction in ITS.
A Digital Twin Framework for Metamorphic Testing of Autonomous Driving Systems Using Generative Model
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Ensuring the safety of self-driving cars remains a major challenge due to the complexity and unpredictability of real-world driving environments. Traditional testing methods face significant limitations, such as the oracle problem, which makes it difficult to determine whether a system's behavior is correct, and the inability to cover the full range of scenarios an autonomous vehicle may encounter. In this paper, we introduce a digital twin-driven metamorphic testing framework that addresses these challenges by creating a virtual replica of the self-driving system and its operating environment. By combining digital twin technology with AI-based image generative models such as Stable Diffusion, our approach enables the systematic generation of realistic and diverse driving scenes. This includes variations in weather, road topology, and environmental features, all while maintaining the core semantics of the original scenario. The digital twin provides a synchronized simulation environment where changes can be tested in a controlled and repeatable manner. Within this environment, we define three metamorphic relations inspired by real-world traffic rules and vehicle behavior. We validate our framework in the Udacity self-driving simulator and demonstrate that it significantly enhances test coverage and effectiveness. Our method achieves the highest true positive rate (0.719), F1 score (0.689), and precision (0.662) compared to baseline approaches. This paper highlights the value of integrating digital twins with AI-powered scenario generation to create a scalable, automated, and high-fidelity testing solution for autonomous vehicle safety.
CWGAN-GP Augmented CAE for Jamming Detection in 5G-NR in Non-IID Datasets
Jun 18, 2025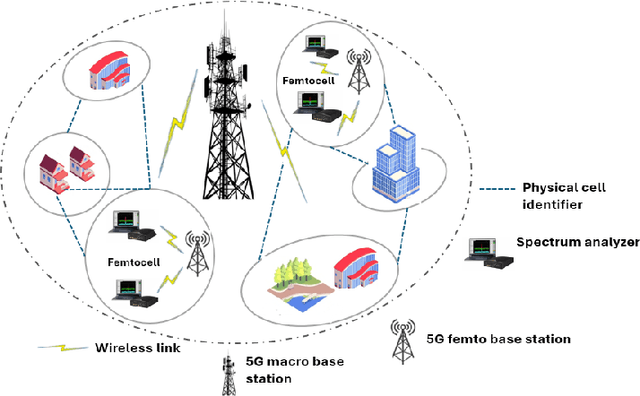
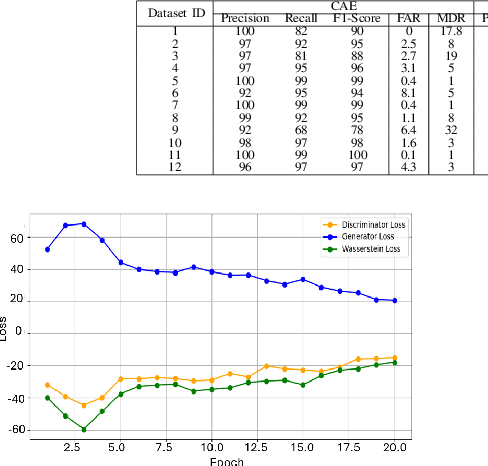
Abstract:In the ever-expanding domain of 5G-NR wireless cellular networks, over-the-air jamming attacks are prevalent as security attacks, compromising the quality of the received signal. We simulate a jamming environment by incorporating additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) into the real-world In-phase and Quadrature (I/Q) OFDM datasets. A Convolutional Autoencoder (CAE) is exploited to implement a jamming detection over various characteristics such as heterogenous I/Q datasets; extracting relevant information on Synchronization Signal Blocks (SSBs), and fewer SSB observations with notable class imbalance. Given the characteristics of datasets, balanced datasets are acquired by employing a Conv1D conditional Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network-Gradient Penalty(CWGAN-GP) on both majority and minority SSB observations. Additionally, we compare the performance and detection ability of the proposed CAE model on augmented datasets with benchmark models: Convolutional Denoising Autoencoder (CDAE) and Convolutional Sparse Autoencoder (CSAE). Despite the complexity of data heterogeneity involved across all datasets, CAE depicts the robustness in detection performance of jammed signal by achieving average values of 97.33% precision, 91.33% recall, 94.08% F1-score, and 94.35% accuracy over CDAE and CSAE.
Partitioned Task Offloading for Low-Latency and Reliable Task Completion in 5G MEC
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:The demand for MEC has increased with the rise of data-intensive applications and 5G networks, while conventional cloud models struggle to satisfy low-latency requirements. While task offloading is crucial for minimizing latency on resource-constrained User Equipment (UE), fully offloading of all tasks to MEC servers may result in overload and possible task drops. Overlooking the effect of number of dropped tasks can significantly undermine system efficiency, as each dropped task results in unfulfilled service demands and reduced reliability, directly impacting user experience and overall network performance. In this paper, we employ task partitioning, enabling partitions of task to be processed locally while assigning the rest to MEC, thus balancing the load and ensuring no task drops. This methodology enhances efficiency via Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) and Cuckoo Search, resulting in effective task assignment and minimum latency. Moreover, we ensure each user's RB allocation stays within the maximum limit while keeping latency low. Experimental results indicate that this strategy surpasses both full offloading and full local processing, providing significant improvements in latency and task completion rates across diverse number of users. In our scenario, MILP task partitioning results in 24% reduction in latency compared to MILP task offloading for the maximum number of users, whereas Cuckoo search task partitioning yields 18% latency reduction in comparison with Cuckoo search task offloading.
A Two-Stage CAE-Based Federated Learning Framework for Efficient Jamming Detection in 5G Networks
Jan 25, 2025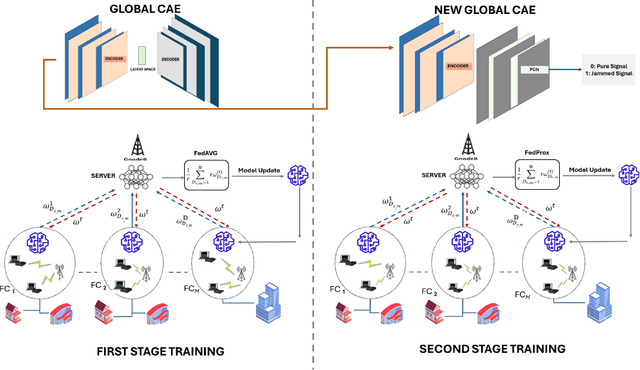
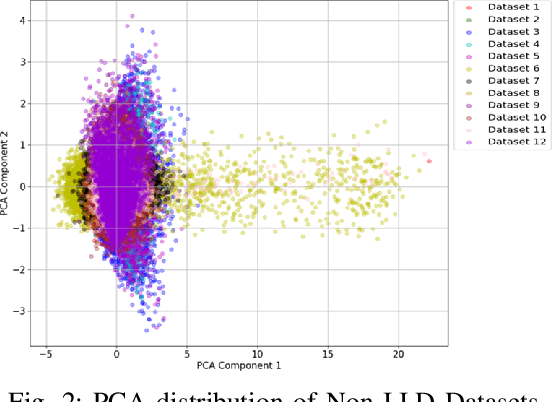
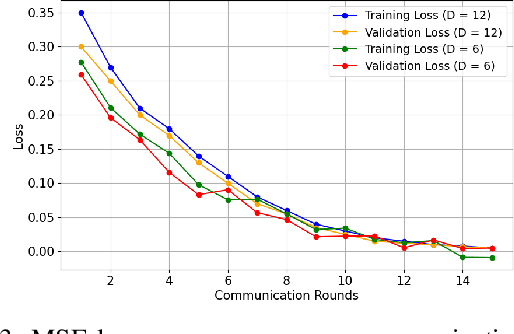
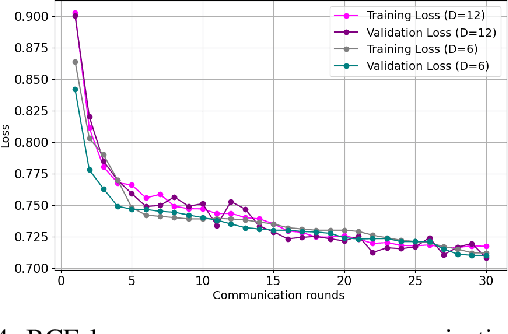
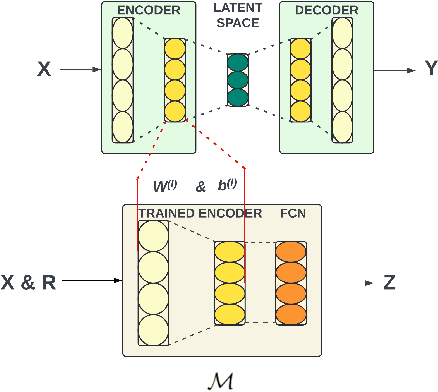
Abstract:Cyber-security for 5G networks is drawing notable attention due to an increase in complex jamming attacks that could target the critical 5G Radio Frequency (RF) domain. These attacks pose a significant risk to heterogeneous network (HetNet) architectures, leading to degradation in network performance. Conventional machine-learning techniques for jamming detection rely on centralized training while increasing the odds of data privacy. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a decentralized two-stage federated learning (FL) framework for jamming detection in 5G femtocells. Our proposed distributed framework encompasses using the Federated Averaging (FedAVG) algorithm to train a Convolutional Autoencoder (CAE) for unsupervised learning. In the second stage, we use a fully connected network (FCN) built on the pre-trained CAE encoder that is trained using Federated Proximal (FedProx) algorithm to perform supervised classification. Our experimental results depict that our proposed framework (FedAVG and FedProx) accomplishes efficient training and prediction across non-IID client datasets without compromising data privacy. Specifically, our framework achieves a precision of 0.94, recall of 0.90, F1-score of 0.92, and an accuracy of 0.92, while minimizing communication rounds to 30 and achieving robust convergence in detecting jammed signals with an optimal client count of 6.
Efficient Prompting for LLM-based Generative Internet of Things
Jun 18, 2024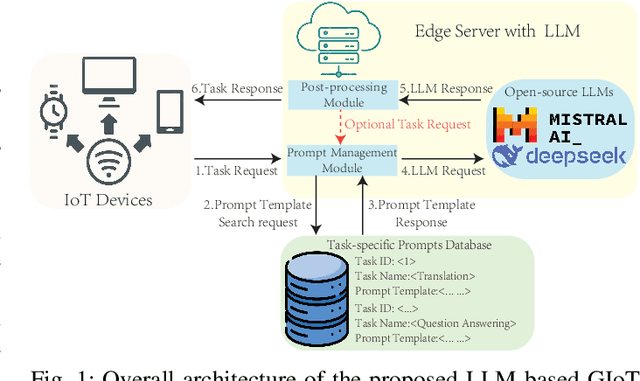

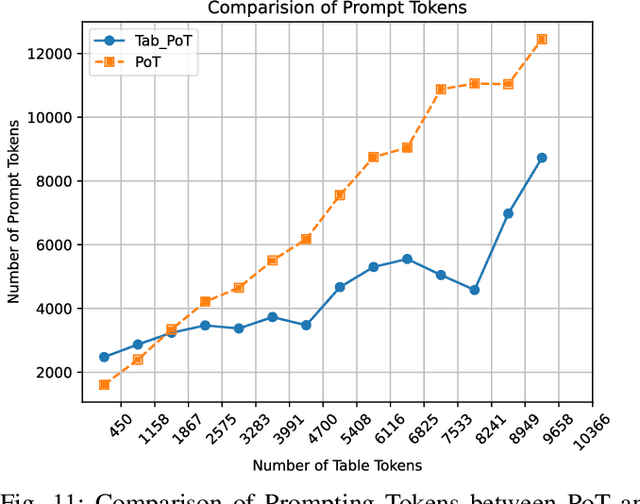
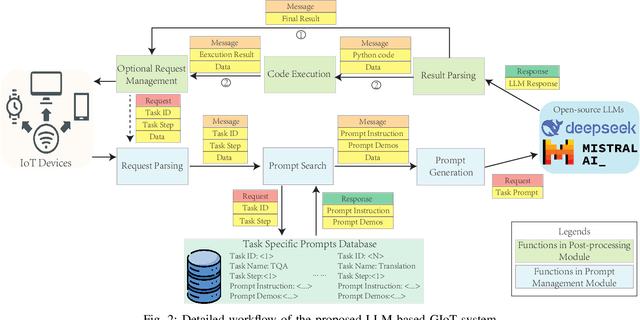
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capacities on various tasks, and integrating the capacities of LLMs into the Internet of Things (IoT) applications has drawn much research attention recently. Due to security concerns, many institutions avoid accessing state-of-the-art commercial LLM services, requiring the deployment and utilization of open-source LLMs in a local network setting. However, open-source LLMs usually have more limitations regarding their performance, such as their arithmetic calculation and reasoning capacities, and practical systems of applying LLMs to IoT have yet to be well-explored. Therefore, we propose a text-based generative IoT (GIoT) system deployed in the local network setting in this study. To alleviate the limitations of LLMs and provide service with competitive performance, we apply prompt engineering methods to enhance the capacities of the open-source LLMs, design a Prompt Management Module and a Post-processing Module to manage the tailored prompts for different tasks and process the results generated by the LLMs. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed system, we discuss a challenging Table Question Answering (Table-QA) task as a case study of the proposed system, as tabular data is usually more challenging than plain text because of their complex structures, heterogeneous data types and sometimes huge sizes. We conduct comprehensive experiments on two popular Table-QA datasets, and the results show that our proposal can achieve competitive performance compared with state-of-the-art LLMs, demonstrating that the proposed LLM-based GIoT system can provide competitive performance with tailored prompting methods and is easily extensible to new tasks without training.
A Novel Joint DRL-Based Utility Optimization for UAV Data Services
Jun 15, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel joint deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based solution to optimize the utility of an uncrewed aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted communication network. To maximize the number of users served within the constraints of the UAV's limited bandwidth and power resources, we employ deep Q-Networks (DQN) and deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithms for optimal resource allocation to ground users with heterogeneous data rate demands. The DQN algorithm dynamically allocates multiple bandwidth resource blocks to different users based on current demand and available resource states. Simultaneously, the DDPG algorithm manages power allocation, continuously adjusting power levels to adapt to varying distances and fading conditions, including Rayleigh fading for non-line-of-sight (NLoS) links and Rician fading for line-of-sight (LoS) links. Our joint DRL-based solution demonstrates an increase of up to 41% in the number of users served compared to scenarios with equal bandwidth and power allocation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge