Petar Djukic
Deep Dict: Deep Learning-based Lossy Time Series Compressor for IoT Data
Jan 18, 2024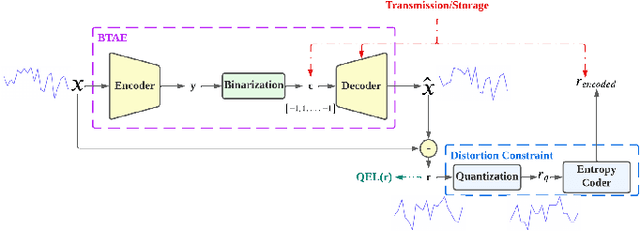
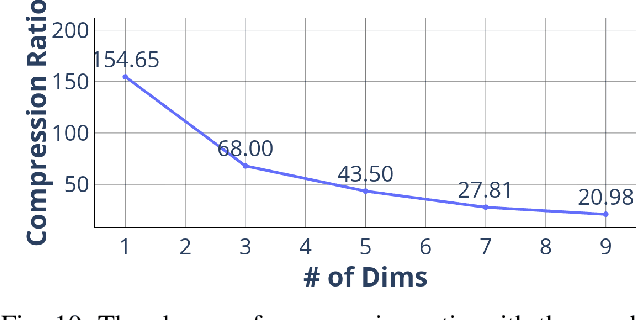
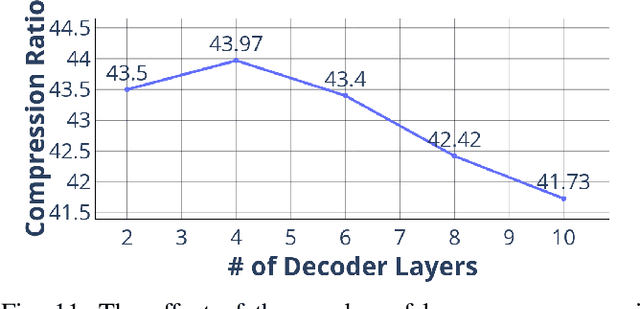
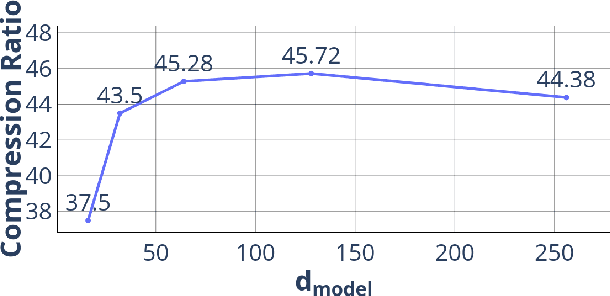
Abstract:We propose Deep Dict, a deep learning-based lossy time series compressor designed to achieve a high compression ratio while maintaining decompression error within a predefined range. Deep Dict incorporates two essential components: the Bernoulli transformer autoencoder (BTAE) and a distortion constraint. BTAE extracts Bernoulli representations from time series data, reducing the size of the representations compared to conventional autoencoders. The distortion constraint limits the prediction error of BTAE to the desired range. Moreover, in order to address the limitations of common regression losses such as L1/L2, we introduce a novel loss function called quantized entropy loss (QEL). QEL takes into account the specific characteristics of the problem, enhancing robustness to outliers and alleviating optimization challenges. Our evaluation of Deep Dict across ten diverse time series datasets from various domains reveals that Deep Dict outperforms state-of-the-art lossy compressors in terms of compression ratio by a significant margin by up to 53.66%.
Host-Based Network Intrusion Detection via Feature Flattening and Two-stage Collaborative Classifier
Jun 15, 2023



Abstract:Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) have been extensively investigated by monitoring real network traffic and analyzing suspicious activities. However, there are limitations in detecting specific types of attacks with NIDS, such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APT). Additionally, NIDS is restricted in observing complete traffic information due to encrypted traffic or a lack of authority. To address these limitations, a Host-based Intrusion Detection system (HIDS) evaluates resources in the host, including logs, files, and folders, to identify APT attacks that routinely inject malicious files into victimized nodes. In this study, a hybrid network intrusion detection system that combines NIDS and HIDS is proposed to improve intrusion detection performance. The feature flattening technique is applied to flatten two-dimensional host-based features into one-dimensional vectors, which can be directly used by traditional Machine Learning (ML) models. A two-stage collaborative classifier is introduced that deploys two levels of ML algorithms to identify network intrusions. In the first stage, a binary classifier is used to detect benign samples. All detected attack types undergo a multi-class classifier to reduce the complexity of the original problem and improve the overall detection performance. The proposed method is shown to generalize across two well-known datasets, CICIDS 2018 and NDSec-1. Performance of XGBoost, which represents conventional ML, is evaluated. Combining host and network features enhances attack detection performance (macro average F1 score) by 8.1% under the CICIDS 2018 dataset and 3.7% under the NDSec-1 dataset. Meanwhile, the two-stage collaborative classifier improves detection performance for most single classes, especially for DoS-LOIC-UDP and DoS-SlowHTTPTest, with improvements of 30.7% and 84.3%, respectively, when compared with the traditional ML XGBoost.
Machine Learning-Enabled IoT Security: Open Issues and Challenges Under Advanced Persistent Threats
Apr 17, 2022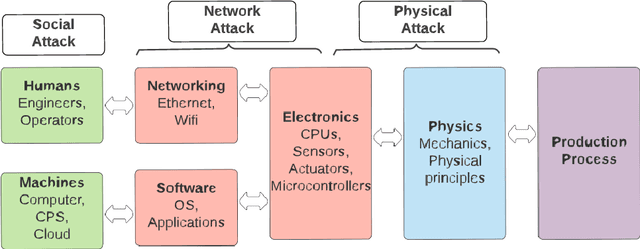
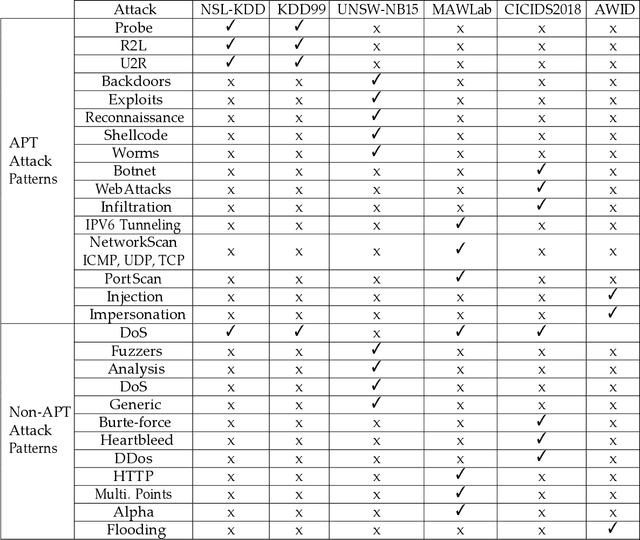
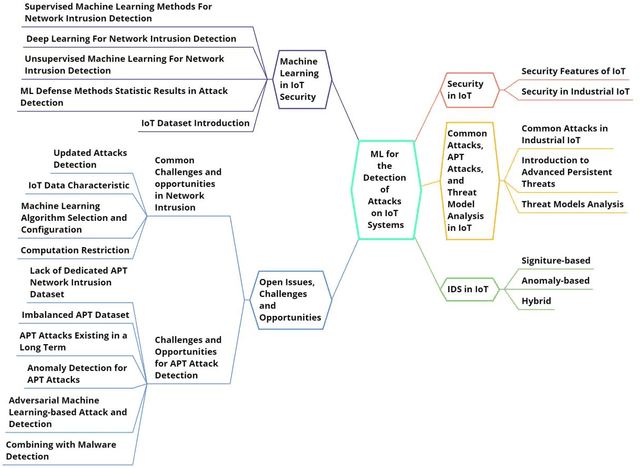
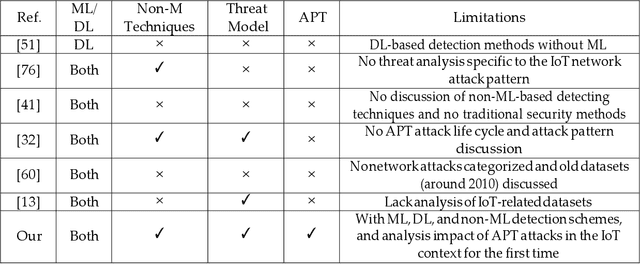
Abstract:Despite its technological benefits, Internet of Things (IoT) has cyber weaknesses due to the vulnerabilities in the wireless medium. Machine learning (ML)-based methods are widely used against cyber threats in IoT networks with promising performance. Advanced persistent threat (APT) is prominent for cybercriminals to compromise networks, and it is crucial to long-term and harmful characteristics. However, it is difficult to apply ML-based approaches to identify APT attacks to obtain a promising detection performance due to an extremely small percentage among normal traffic. There are limited surveys to fully investigate APT attacks in IoT networks due to the lack of public datasets with all types of APT attacks. It is worth to bridge the state-of-the-art in network attack detection with APT attack detection in a comprehensive review article. This survey article reviews the security challenges in IoT networks and presents the well-known attacks, APT attacks, and threat models in IoT systems. Meanwhile, signature-based, anomaly-based, and hybrid intrusion detection systems are summarized for IoT networks. The article highlights statistical insights regarding frequently applied ML-based methods against network intrusion alongside the number of attacks types detected. Finally, open issues and challenges for common network intrusion and APT attacks are presented for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge