Brenton Leighton
Field trial on Ocean Estimation for Multi-Vessel Multi-Float-based Active perception
Jun 17, 2021
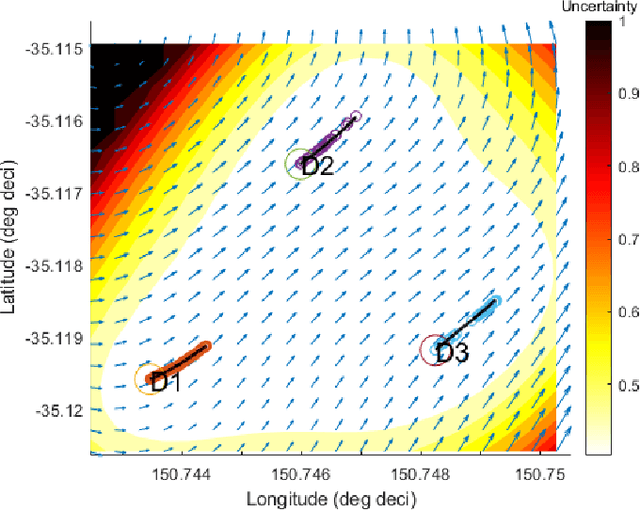
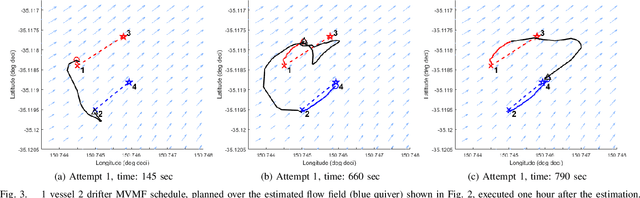
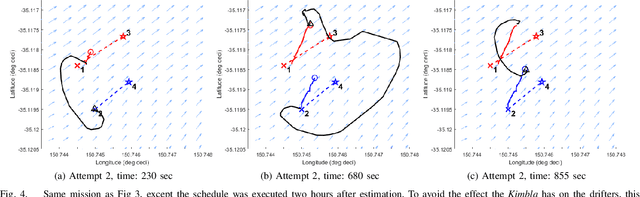
Abstract:Marine vehicles have been used for various scientific missions where information over features of interest is collected. In order to maximise efficiency in collecting information over a large search space, we should be able to deploy a large number of autonomous vehicles that make a decision based on the latest understanding of the target feature in the environment. In our previous work, we have presented a hierarchical framework for the multi-vessel multi-float (MVMF) problem where surface vessels drop and pick up underactuated floats in a time-minimal way. In this paper, we present the field trial results using the framework with a number of drifters and floats. We discovered a number of important aspects that need to be considered in the proposed framework, and present the potential approaches to address the challenges.
Parallax Bundle Adjustment on Manifold with Convexified Initialization
Jul 10, 2018



Abstract:Bundle adjustment (BA) with parallax angle based feature parameterization has been shown to have superior performance over BA using inverse depth or XYZ feature forms. In this paper, we propose an improved version of the parallax BA algorithm (PMBA) by extending it to the manifold domain along with observation-ray based objective function. With this modification, the problem formulation faithfully mimics the projective nature in a camera's image formation, BA is able to achieve better convergence, accuracy and robustness. This is particularly useful in handling diverse outdoor environments and collinear motion modes. Capitalizing on these properties, we further propose a pose-graph simplification to PMBA, with significant dimensionality reduction. This pose-graph model is convex in nature, easy to solve and its solution can serve as a good initial guess to the original BA problem which is intrinsically non-convex. We provide theoretical proof that our global initialization strategy can guarantee a near-optimal solution. Using a series of experiments involving diverse environmental conditions and motions, we demonstrate PMBA's superior convergence performance in comparison to other BA methods. We also show that, without incremental initialization or via third-party information, our global initialization process helps to bootstrap the full BA successfully in various scenarios, sequential or out-of-order, including some datasets from the "Bundle Adjustment in the Large" database.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge