Avik Santra
XAI-BayesHAR: A novel Framework for Human Activity Recognition with Integrated Uncertainty and Shapely Values
Nov 07, 2022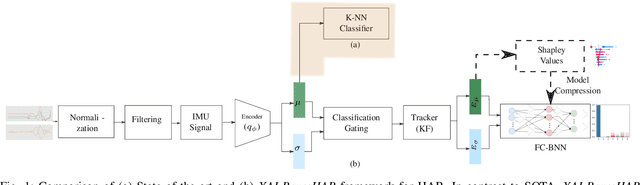
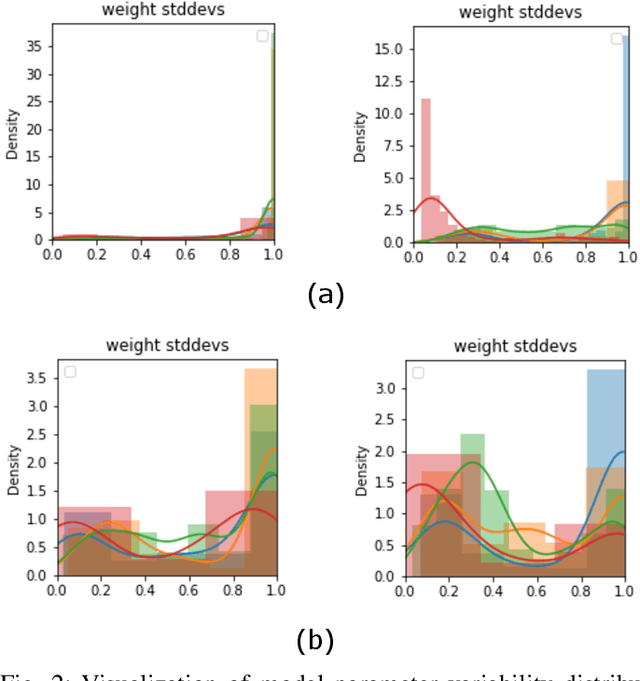
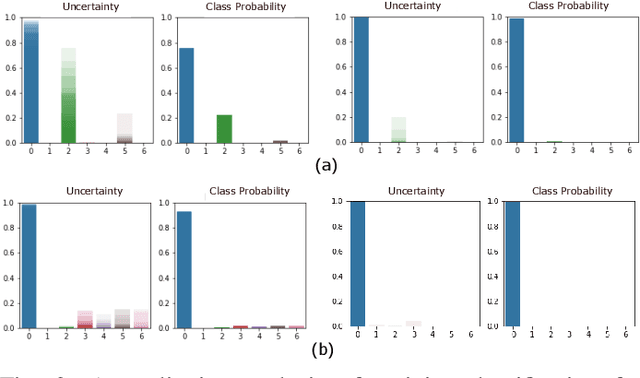
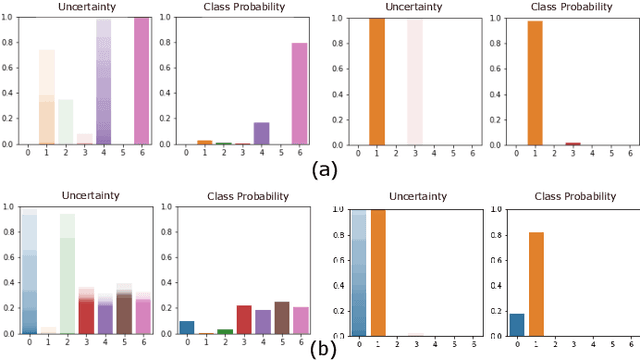
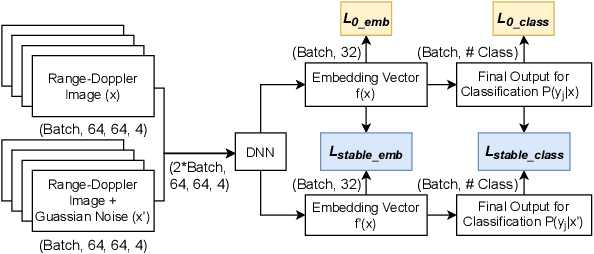
Abstract:Human activity recognition (HAR) using IMU sensors, namely accelerometer and gyroscope, has several applications in smart homes, healthcare and human-machine interface systems. In practice, the IMU-based HAR system is expected to encounter variations in measurement due to sensor degradation, alien environment or sensor noise and will be subjected to unknown activities. In view of practical deployment of the solution, analysis of statistical confidence over the activity class score are important metrics. In this paper, we therefore propose XAI-BayesHAR, an integrated Bayesian framework, that improves the overall activity classification accuracy of IMU-based HAR solutions by recursively tracking the feature embedding vector and its associated uncertainty via Kalman filter. Additionally, XAI-BayesHAR acts as an out of data distribution (OOD) detector using the predictive uncertainty which help to evaluate and detect alien input data distribution. Furthermore, Shapley value-based performance of the proposed framework is also evaluated to understand the importance of the feature embedding vector and accordingly used for model compression
XAI-Increment: A Novel Approach Leveraging LIME Explanations for Improved Incremental Learning
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:Explainability of neural network prediction is essential to understand feature importance and gain interpretable insight into neural network performance. In this work, model explanations are fed back to the feed-forward training to help the model generalize better. To this extent, a custom weighted loss where the weights are generated by considering the Euclidean distances between true LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations) explanations and model-predicted LIME explanations is proposed. Also, in practical training scenarios, developing a solution that can help the model learn sequentially without losing information on previous data distribution is imperative due to the unavailability of all the training data at once. Thus, the framework known as XAI-Increment incorporates the custom weighted loss developed with elastic weight consolidation (EWC), to maintain performance in sequential testing sets. Finally, the training procedure involving the custom weighted loss shows around 1% accuracy improvement compared to the traditional loss based training for the keyword spotting task on the Google Speech Commands dataset and also shows low loss of information when coupled with EWC in the incremental learning setup.
Uncertainty-based Meta-Reinforcement Learning for Robust Radar Tracking
Oct 26, 2022



Abstract:Nowadays, Deep Learning (DL) methods often overcome the limitations of traditional signal processing approaches. Nevertheless, DL methods are barely applied in real-life applications. This is mainly due to limited robustness and distributional shift between training and test data. To this end, recent work has proposed uncertainty mechanisms to increase their reliability. Besides, meta-learning aims at improving the generalization capability of DL models. By taking advantage of that, this paper proposes an uncertainty-based Meta-Reinforcement Learning (Meta-RL) approach with Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection. The presented method performs a given task in unseen environments and provides information about its complexity. This is done by determining first and second-order statistics on the estimated reward. Using information about its complexity, the proposed algorithm is able to point out when tracking is reliable. To evaluate the proposed method, we benchmark it on a radar-tracking dataset. There, we show that our method outperforms related Meta-RL approaches on unseen tracking scenarios in peak performance by 16% and the baseline by 35% while detecting OOD data with an F1-Score of 72%. This shows that our method is robust to environmental changes and reliably detects OOD scenarios.
MEET: A Monte Carlo Exploration-Exploitation Trade-off for Buffer Sampling
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:Data selection is essential for any data-based optimization technique, such as Reinforcement Learning. State-of-the-art sampling strategies for the experience replay buffer improve the performance of the Reinforcement Learning agent. However, they do not incorporate uncertainty in the Q-Value estimation. Consequently, they cannot adapt the sampling strategies, including exploration and exploitation of transitions, to the complexity of the task. To address this, this paper proposes a new sampling strategy that leverages the exploration-exploitation trade-off. This is enabled by the uncertainty estimation of the Q-Value function, which guides the sampling to explore more significant transitions and, thus, learn a more efficient policy. Experiments on classical control environments demonstrate stable results across various environments. They show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art sampling strategies for dense rewards w.r.t. convergence and peak performance by 26% on average.
Utilizing Explainable AI for improving the Performance of Neural Networks
Oct 07, 2022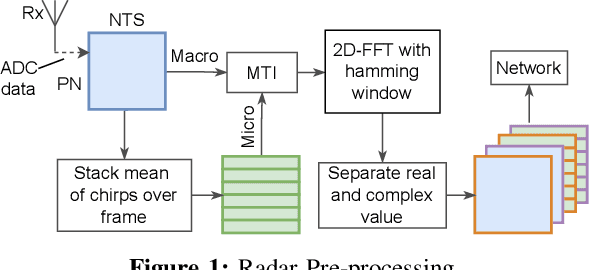

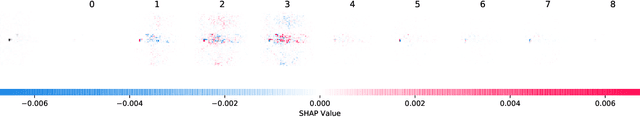
Abstract:Nowadays, deep neural networks are widely used in a variety of fields that have a direct impact on society. Although those models typically show outstanding performance, they have been used for a long time as black boxes. To address this, Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has been developing as a field that aims to improve the transparency of the model and increase their trustworthiness. We propose a retraining pipeline that consistently improves the model predictions starting from XAI and utilizing state-of-the-art techniques. To do that, we use the XAI results, namely SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) values, to give specific training weights to the data samples. This leads to an improved training of the model and, consequently, better performance. In order to benchmark our method, we evaluate it on both real-life and public datasets. First, we perform the method on a radar-based people counting scenario. Afterward, we test it on the CIFAR-10, a public Computer Vision dataset. Experiments using the SHAP-based retraining approach achieve a 4% more accuracy w.r.t. the standard equal weight retraining for people counting tasks. Moreover, on the CIFAR-10, our SHAP-based weighting strategy ends up with a 3% accuracy rate than the training procedure with equal weighted samples.
Cross-modal Learning of Graph Representations using Radar Point Cloud for Long-Range Gesture Recognition
Mar 31, 2022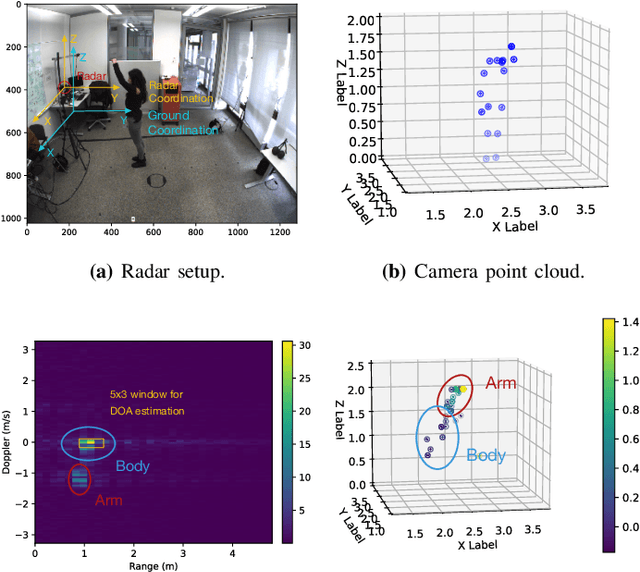
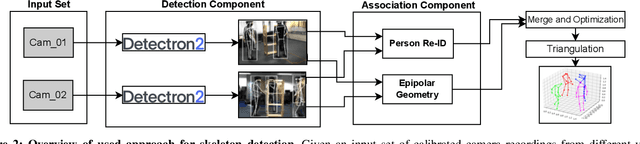
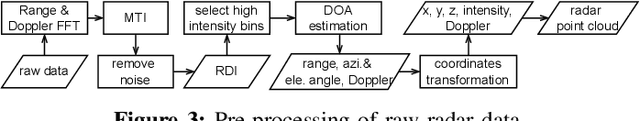
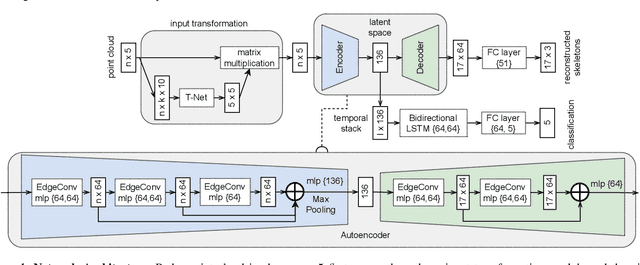
Abstract:Gesture recognition is one of the most intuitive ways of interaction and has gathered particular attention for human computer interaction. Radar sensors possess multiple intrinsic properties, such as their ability to work in low illumination, harsh weather conditions, and being low-cost and compact, making them highly preferable for a gesture recognition solution. However, most literature work focuses on solutions with a limited range that is lower than a meter. We propose a novel architecture for a long-range (1m - 2m) gesture recognition solution that leverages a point cloud-based cross-learning approach from camera point cloud to 60-GHz FMCW radar point cloud, which allows learning better representations while suppressing noise. We use a variant of Dynamic Graph CNN (DGCNN) for the cross-learning, enabling us to model relationships between the points at a local and global level and to model the temporal dynamics a Bi-LSTM network is employed. In the experimental results section, we demonstrate our model's overall accuracy of 98.4% for five gestures and its generalization capability.
Light-weight Gesture Sensing Using FMCW Radar Time Series Data
Nov 22, 2021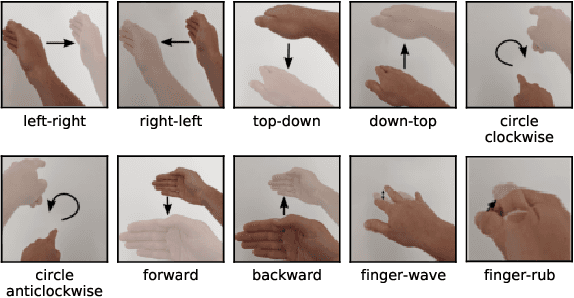
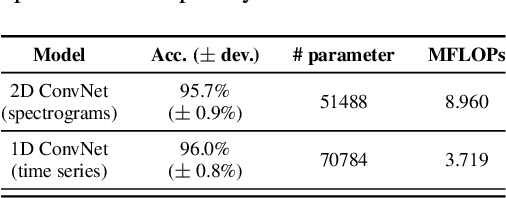

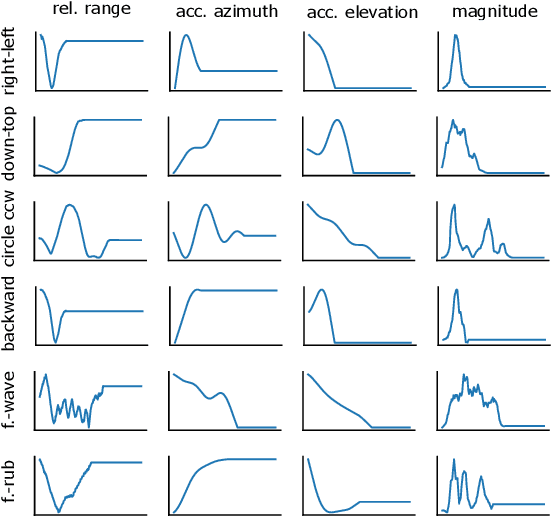
Abstract:The paper proposes a novel feature extraction approach for FMCW radar systems in the field of short-range gesture sensing. A light-weight processing is proposed which reduces a series of 3D radar data cubes to four 1D time signals containing information about range, azimuth angle, elevation angle and magnitude. The processing is entirely performed in the time domain without using any Fourier transformation and enables the training of a deep neural network directly on the raw time domain data. It is shown experimentally on real world data, that the proposed processing retains the same expressive power as conventional radar processing to range-, Doppler- and angle-spectrograms. Further, the computational complexity is significantly reduced which makes it perfectly suitable for embedded devices. The system is able to recognize ten different gestures with an accuracy of about 95% and is running in real time on a Raspberry Pi 3 B. The delay between end of gesture and prediction is only 150 ms.
A Matched-filter based method in the Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Using FMCW radar
Oct 31, 2021



Abstract:The stretch processing architecture is commonly used for frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar due to its inexpensive hardware, low sampling rate, and simple architecture. However, the stretch processing architecture is not able to achieve optimal Signal to Noise ratio (SNR) in comparison to the matched-filter architecture. In this paper, we aim to propose a method whereby stretch processing can achieve optimal SNR. Hence, we develop a novel processing method to enable applying a matched filter to the output of the stretch processing. The proposed architecture achieves optimal SNR while it can operate on a low sampling rate. In addition, the combination of the proposed radar architecture and SAR technique can generate high-quality images. To evaluate the performance of the proposed architecture, four scenarios are considered. Simulation is carried out based on these scenarios. The simulation results show that the proposed radar demonstrates the ability to generate an image with higher quality over stretch processing. This proposed radar can also bring a bigger gain compression.
Label-Aware Ranked Loss for robust People Counting using Automotive in-cabin Radar
Oct 12, 2021
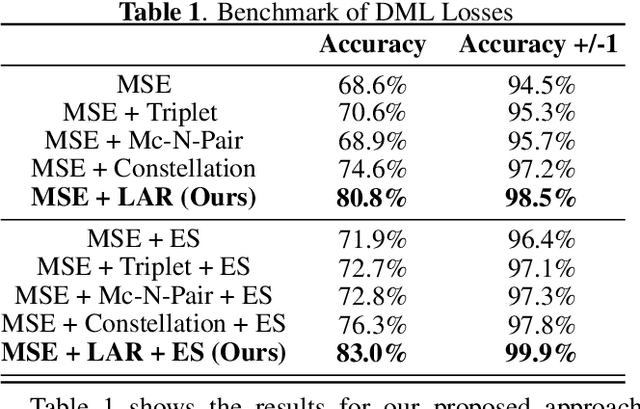
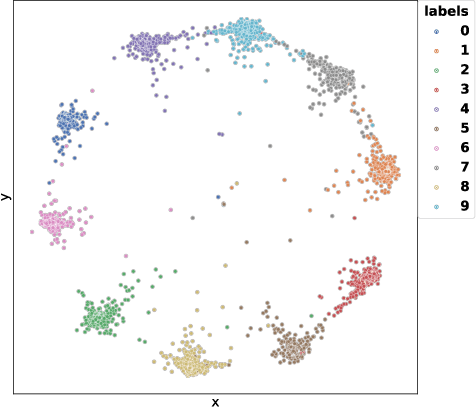
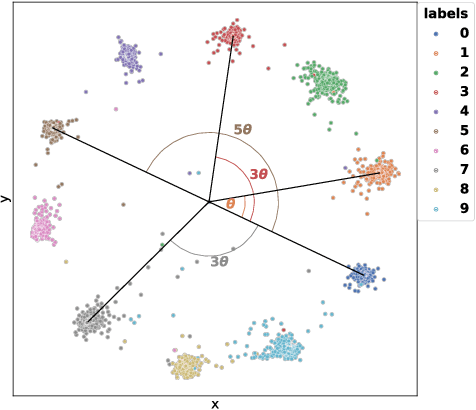
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Label-Aware Ranked loss, a novel metric loss function. Compared to the state-of-the-art Deep Metric Learning losses, this function takes advantage of the ranked ordering of the labels in regression problems. To this end, we first show that the loss minimises when datapoints of different labels are ranked and laid at uniform angles between each other in the embedding space. Then, to measure its performance, we apply the proposed loss on a regression task of people counting with a short-range radar in a challenging scenario, namely a vehicle cabin. The introduced approach improves the accuracy as well as the neighboring labels accuracy up to 83.0% and 99.9%: An increase of 6.7%and 2.1% on state-of-the-art methods, respectively.
COVIDLite: A depth-wise separable deep neural network with white balance and CLAHE for detection of COVID-19
Jun 19, 2020



Abstract:Background and Objective:Currently, the whole world is facing a pandemic disease, novel Coronavirus also known as COVID-19, which spread in more than 200 countries with around 3.3 million active cases and 4.4 lakh deaths approximately. Due to rapid increase in number of cases and limited supply of testing kits, availability of alternative diagnostic method is necessary for containing the spread of COVID-19 cases at an early stage and reducing the death count. For making available an alternative diagnostic method, we proposed a deep neural network based diagnostic method which can be easily integrated with mobile devices for detection of COVID-19 and viral pneumonia using Chest X-rays (CXR) images. Methods:In this study, we have proposed a method named COVIDLite, which is a combination of white balance followed by Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) and depth-wise separable convolutional neural network (DSCNN). In this method, white balance followed by CLAHE is used as an image preprocessing step for enhancing the visibility of CXR images and DSCNN trained using sparse cross entropy is used for image classification with lesser parameters and significantly lighter in size, i.e., 8.4 MB without quantization. Results:The proposed COVIDLite method resulted in improved performance in comparison to vanilla DSCNN with no pre-processing. The proposed method achieved higher accuracy of 99.58% for binary classification, whereas 96.43% for multiclass classification and out-performed various state-of-the-art methods. Conclusion:Our proposed method, COVIDLite achieved exceptional results on various performance metrics. With detailed model interpretations, COVIDLite can assist radiologists in detecting COVID-19 patients from CXR images and can reduce the diagnosis time significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge