Auke Ijspeert
Adaptive Negative Damping Control for User-Dependent Multi-Terrain Walking Assistance with a Hip Exoskeleton
Mar 05, 2025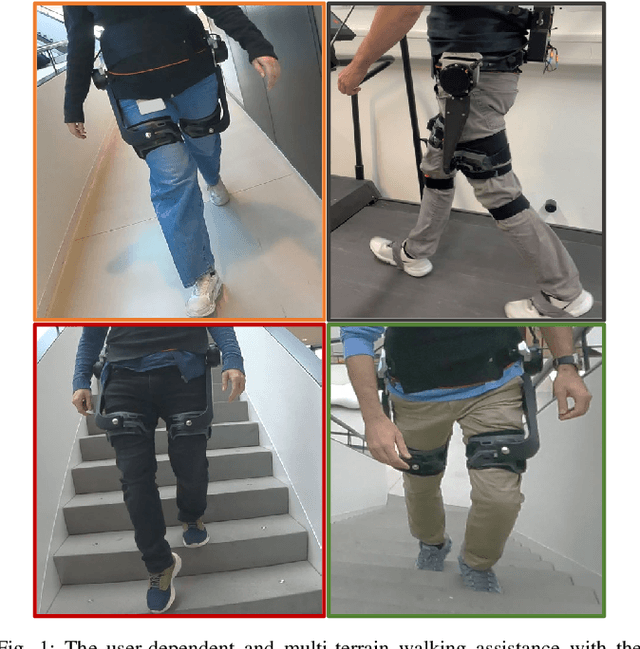
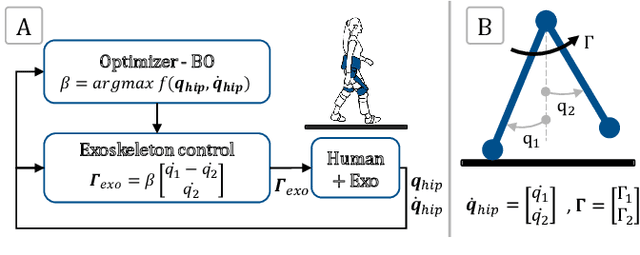
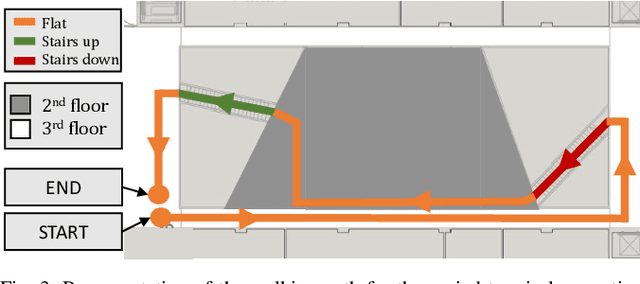
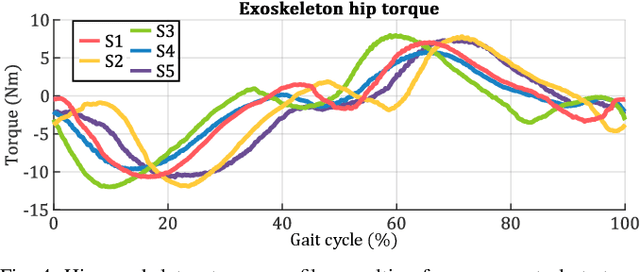
Abstract:Hip exoskeletons are known for their versatility in assisting users across varied scenarios. However, current assistive strategies often lack the flexibility to accommodate for individual walking patterns and adapt to diverse locomotion environments. In this work, we present a novel control strategy that adapts the mechanical impedance of the human-exoskeleton system. We design the hip assistive torques as an adaptive virtual negative damping, which is able to inject energy into the system while allowing the users to remain in control and contribute voluntarily to the movements. Experiments with five healthy subjects demonstrate that our controller reduces the metabolic cost of walking compared to free walking (average reduction of 7.2%), and it preserves the lower-limbs kinematics. Additionally, our method achieves minimal power losses from the exoskeleton across the entire gait cycle (less than 2% negative mechanical power out of the total power), ensuring synchronized action with the users' movements. Moreover, we use Bayesian Optimization to adapt the assistance strength and allow for seamless adaptation and transitions across multi-terrain environments. Our strategy achieves efficient power transmission under all conditions. Our approach demonstrates an individualized, adaptable, and straightforward controller for hip exoskeletons, advancing the development of viable, adaptive, and user-dependent control laws.
* Copyright 2025 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising or promotional purposes, creating new collective works, for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or reuse of any copyrighted component of this work in other works
Rapid Online Learning of Hip Exoskeleton Assistance Preferences
Feb 21, 2025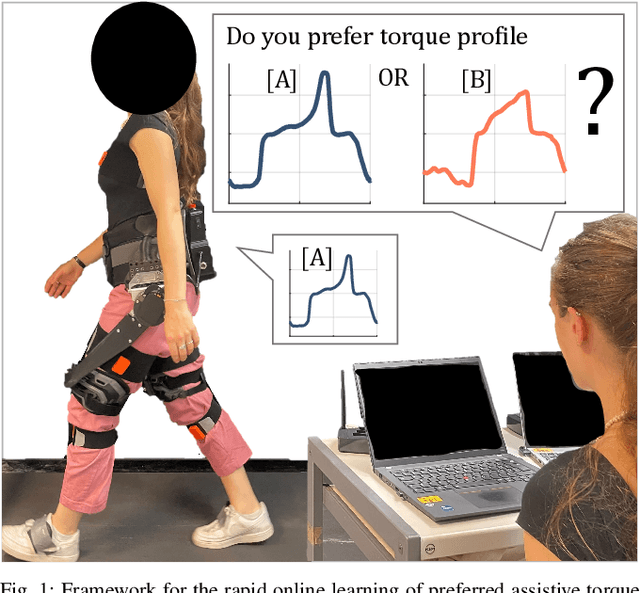
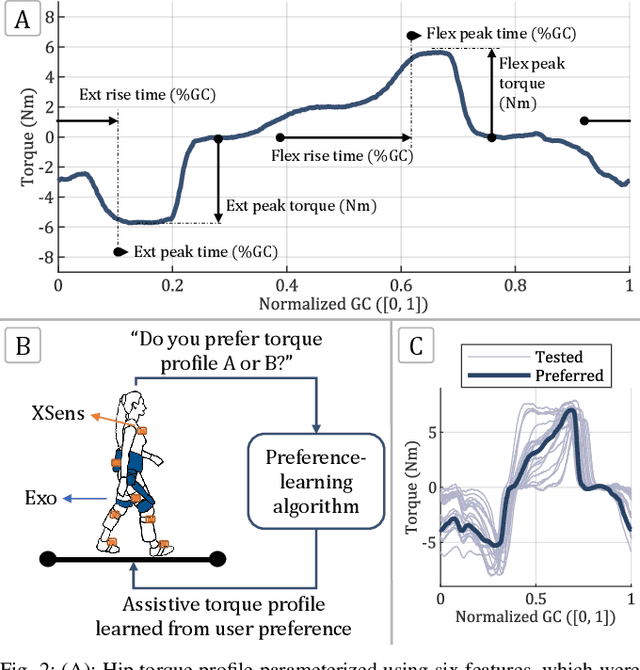
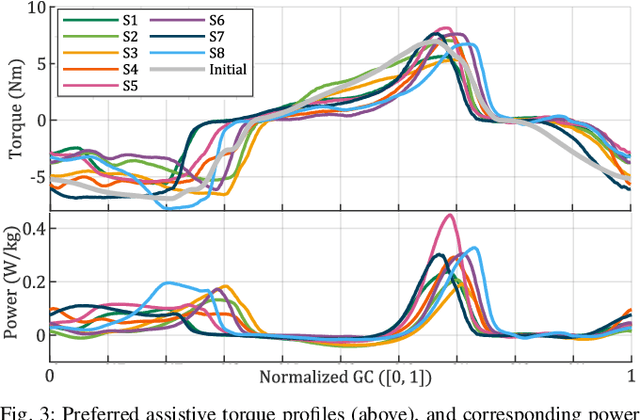
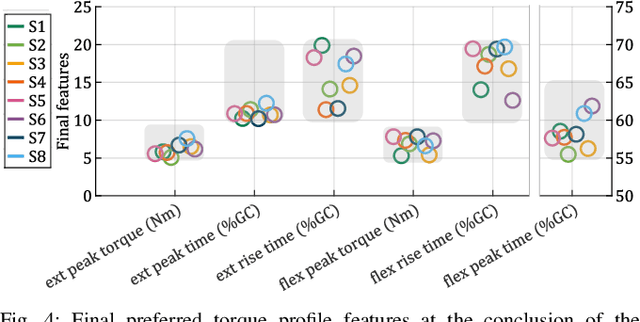
Abstract:Hip exoskeletons are increasing in popularity due to their effectiveness across various scenarios and their ability to adapt to different users. However, personalizing the assistance often requires lengthy tuning procedures and computationally intensive algorithms, and most existing methods do not incorporate user feedback. In this work, we propose a novel approach for rapidly learning users' preferences for hip exoskeleton assistance. We perform pairwise comparisons of distinct randomly generated assistive profiles, and collect participants preferences through active querying. Users' feedback is integrated into a preference-learning algorithm that updates its belief, learns a user-dependent reward function, and changes the assistive torque profiles accordingly. Results from eight healthy subjects display distinct preferred torque profiles, and users' choices remain consistent when compared to a perturbed profile. A comprehensive evaluation of users' preferences reveals a close relationship with individual walking strategies. The tested torque profiles do not disrupt kinematic joint synergies, and participants favor assistive torques that are synchronized with their movements, resulting in lower negative power from the device. This straightforward approach enables the rapid learning of users preferences and rewards, grounding future studies on reward-based human-exoskeleton interaction.
* Copyright 2025 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising or promotional purposes, creating new collective works, for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or reuse of any copyrighted component of this work in other works
SATA: Safe and Adaptive Torque-Based Locomotion Policies Inspired by Animal Learning
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Despite recent advances in learning-based controllers for legged robots, deployments in human-centric environments remain limited by safety concerns. Most of these approaches use position-based control, where policies output target joint angles that must be processed by a low-level controller (e.g., PD or impedance controllers) to compute joint torques. Although impressive results have been achieved in controlled real-world scenarios, these methods often struggle with compliance and adaptability when encountering environments or disturbances unseen during training, potentially resulting in extreme or unsafe behaviors. Inspired by how animals achieve smooth and adaptive movements by controlling muscle extension and contraction, torque-based policies offer a promising alternative by enabling precise and direct control of the actuators in torque space. In principle, this approach facilitates more effective interactions with the environment, resulting in safer and more adaptable behaviors. However, challenges such as a highly nonlinear state space and inefficient exploration during training have hindered their broader adoption. To address these limitations, we propose SATA, a bio-inspired framework that mimics key biomechanical principles and adaptive learning mechanisms observed in animal locomotion. Our approach effectively addresses the inherent challenges of learning torque-based policies by significantly improving early-stage exploration, leading to high-performance final policies. Remarkably, our method achieves zero-shot sim-to-real transfer. Our experimental results indicate that SATA demonstrates remarkable compliance and safety, even in challenging environments such as soft/slippery terrain or narrow passages, and under significant external disturbances, highlighting its potential for practical deployments in human-centric and safety-critical scenarios.
Locomotion Mode Transitions: Tackling System- and User-Specific Variability in Lower-Limb Exoskeletons
Nov 20, 2024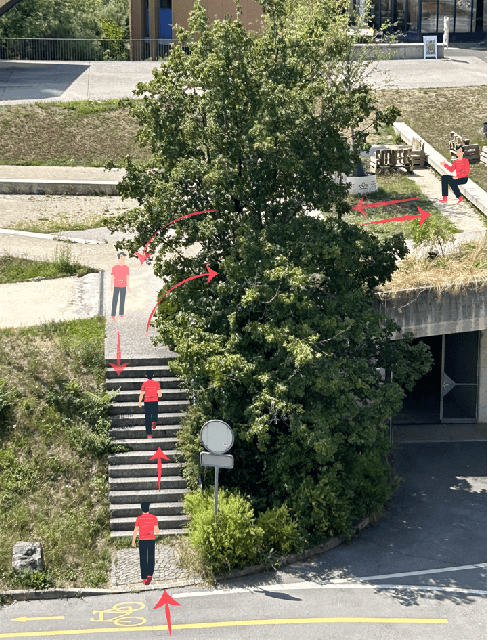
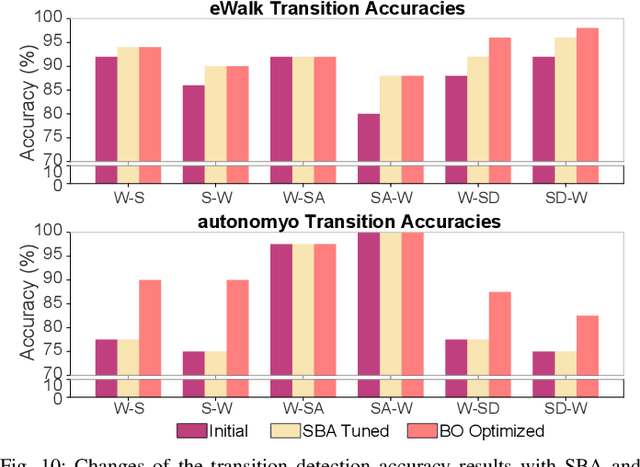
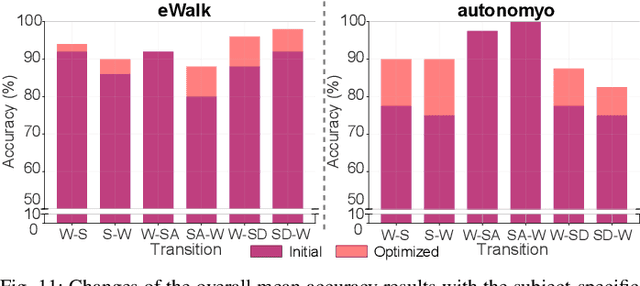
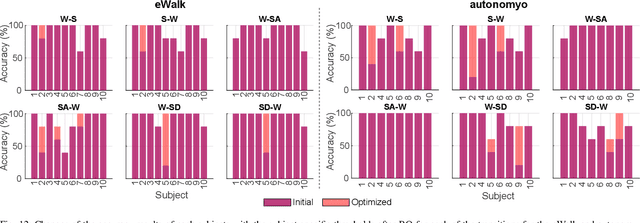
Abstract:Accurate detection of locomotion transitions, such as walk to sit, walk to stair ascent, and descent, is crucial to effectively control robotic assistive devices, such as lower-limb exoskeletons, as each locomotion mode requires specific assistance. Variability in collected sensor data introduced by user- or system-specific characteristics makes it challenging to maintain high transition detection accuracy while avoiding latency using non-adaptive classification models. In this study, we identified key factors influencing transition detection performance, including variations in user behavior, and different mechanical designs of the exoskeletons. To boost the transition detection accuracy, we introduced two methods for adapting a finite-state machine classifier to system- and user-specific variability: a Statistics-Based approach and Bayesian Optimization. Our experimental results demonstrate that both methods remarkably improve transition detection accuracy across diverse users, achieving up to an 80% increase in certain scenarios compared to the non-personalized threshold method. These findings emphasize the importance of personalization in adaptive control systems, underscoring the potential for enhanced user experience and effectiveness in assistive devices. By incorporating subject- and system-specific data into the model training process, our approach offers a precise and reliable solution for detecting locomotion transitions, catering to individual user needs, and ultimately improving the performance of assistive devices.
AllGaits: Learning All Quadruped Gaits and Transitions
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:We present a framework for learning a single policy capable of producing all quadruped gaits and transitions. The framework consists of a policy trained with deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to modulate the parameters of a system of abstract oscillators (i.e. Central Pattern Generator), whose output is mapped to joint commands through a pattern formation layer that sets the gait style, i.e. body height, swing foot ground clearance height, and foot offset. Different gaits are formed by changing the coupling between different oscillators, which can be instantaneously selected at any velocity by a user. With this framework, we systematically investigate which gait should be used at which velocity, and when gait transitions should occur from a Cost of Transport (COT), i.e. energy-efficiency, point of view. Additionally, we note how gait style changes as a function of locomotion speed for each gait to keep the most energy-efficient locomotion. While the currently most popular gait (trot) does not result in the lowest COT, we find that considering different co-dependent metrics such as mean base velocity and joint acceleration result in different `optimal' gaits than those that minimize COT. We deploy our controller in various hardware experiments, showing all 9 typical quadruped animal gaits, and demonstrate generalizability to unseen gaits during training, and robustness to leg failures. Video results can be found at https://youtu.be/OLoWSX_R868.
Online Optimization of Central Pattern Generators for Quadruped Locomotion
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Typical legged locomotion controllers are designed or trained offline. This is in contrast to many animals, which are able to locomote at birth, and rapidly improve their locomotion skills with few real-world interactions. Such motor control is possible through oscillatory neural networks located in the spinal cord of vertebrates, known as Central Pattern Generators (CPGs). Models of the CPG have been widely used to generate locomotion skills in robotics, but can require extensive hand-tuning or offline optimization of inter-connected parameters with genetic algorithms. In this paper, we present a framework for the \textit{online} optimization of the CPG parameters through Bayesian Optimization. We show that our framework can rapidly optimize and adapt to varying velocity commands and changes in the terrain, for example to varying coefficients of friction, terrain slope angles, and added mass payloads placed on the robot. We study the effects of sensory feedback on the CPG, and find that both force feedback in the phase equations, as well as posture control (Virtual Model Control) are both beneficial for robot stability and energy efficiency. In hardware experiments on the Unitree Go1, we show rapid optimization (in under 3 minutes) and adaptation of energy-efficient gaits to varying target velocities in a variety of scenarios: varying coefficients of friction, added payloads up to 15 kg, and variable slopes up to 10 degrees. See demo at: https://youtu.be/4qq5leCI2AI
Dynamic Object Catching with Quadruped Robot Front Legs
Oct 10, 2024
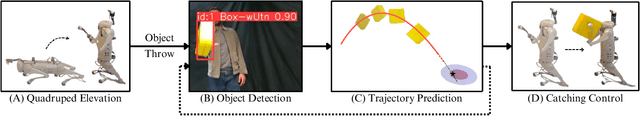
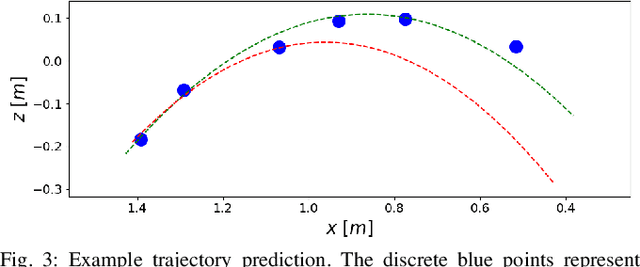
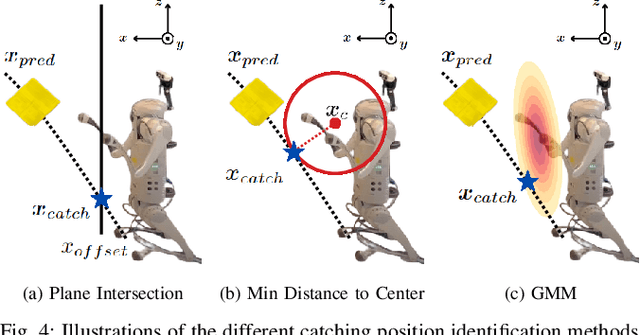
Abstract:This paper presents a framework for dynamic object catching using a quadruped robot's front legs while it stands on its rear legs. The system integrates computer vision, trajectory prediction, and leg control to enable the quadruped to visually detect, track, and successfully catch a thrown object using an onboard camera. Leveraging a fine-tuned YOLOv8 model for object detection and a regression-based trajectory prediction module, the quadruped adapts its front leg positions iteratively to anticipate and intercept the object. The catching maneuver involves identifying the optimal catching position, controlling the front legs with Cartesian PD control, and closing the legs together at the right moment. We propose and validate three different methods for selecting the optimal catching position: 1) intersecting the predicted trajectory with a vertical plane, 2) selecting the point on the predicted trajectory with the minimal distance to the center of the robot's legs in their nominal position, and 3) selecting the point on the predicted trajectory with the highest likelihood on a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) modelling the robot's reachable space. Experimental results demonstrate robust catching capabilities across various scenarios, with the GMM method achieving the best performance, leading to an 80% catching success rate. A video demonstration of the system in action can be found at https://youtu.be/sm7RdxRfIYg .
Learning Human-Robot Handshaking Preferences for Quadruped Robots
Jun 28, 2024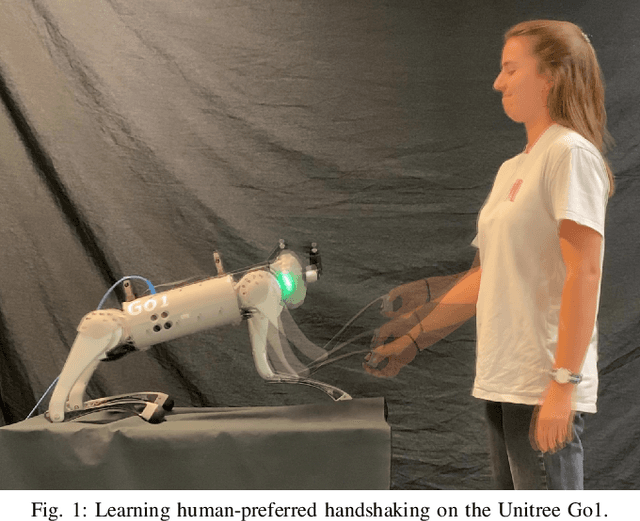
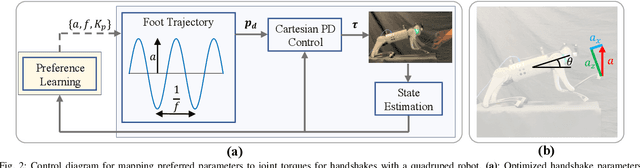


Abstract:Quadruped robots are showing impressive abilities to navigate the real world. If they are to become more integrated into society, social trust in interactions with humans will become increasingly important. Additionally, robots will need to be adaptable to different humans based on individual preferences. In this work, we study the social interaction task of learning optimal handshakes for quadruped robots based on user preferences. While maintaining balance on three legs, we parameterize handshakes with a Central Pattern Generator consisting of an amplitude, frequency, stiffness, and duration. Through 10 binary choices between handshakes, we learn a belief model to fit individual preferences for 25 different subjects. Our results show that this is an effective strategy, with 76% of users feeling happy with their identified optimal handshake parameters, and 20% feeling neutral. Moreover, compared with random and test handshakes, the optimized handshakes have significantly decreased errors in amplitude and frequency, lower Dynamic Time Warping scores, and improved energy efficiency, all of which indicate robot synchronization to the user's preferences. Video results can be found at https://youtu.be/elvPv8mq1KM .
Learning-based Hierarchical Control: Emulating the Central Nervous System for Bio-Inspired Legged Robot Locomotion
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:Animals possess a remarkable ability to navigate challenging terrains, achieved through the interplay of various pathways between the brain, central pattern generators (CPGs) in the spinal cord, and musculoskeletal system. Traditional bioinspired control frameworks often rely on a singular control policy that models both higher (supraspinal) and spinal cord functions. In this work, we build upon our previous research by introducing two distinct neural networks: one tasked with modulating the frequency and amplitude of CPGs to generate the basic locomotor rhythm (referred to as the spinal policy, SCP), and the other responsible for receiving environmental perception data and directly modulating the rhythmic output from the SCP to execute precise movements on challenging terrains (referred to as the descending modulation policy). This division of labor more closely mimics the hierarchical locomotor control systems observed in legged animals, thereby enhancing the robot's ability to navigate various uneven surfaces, including steps, high obstacles, and terrains with gaps. Additionally, we investigate the impact of sensorimotor delays within our framework, validating several biological assumptions about animal locomotion systems. Specifically, we demonstrate that spinal circuits play a crucial role in generating the basic locomotor rhythm, while descending pathways are essential for enabling appropriate gait modifications to accommodate uneven terrain. Notably, our findings also reveal that the multi-layered control inherent in animals exhibits remarkable robustness against time delays. Through these investigations, this paper contributes to a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles of interplay between spinal and supraspinal mechanisms in biological locomotion. It also supports the development of locomotion controllers in parallel to biological structures which are ...
Quadruped-Frog: Rapid Online Optimization of Continuous Quadruped Jumping
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:Legged robots are becoming increasingly agile in exhibiting dynamic behaviors such as running and jumping. Usually, such behaviors are either optimized and engineered offline (i.e. the behavior is designed for before it is needed), either through model-based trajectory optimization, or through deep learning-based methods involving millions of timesteps of simulation interactions. Notably, such offline-designed locomotion controllers cannot perfectly model the true dynamics of the system, such as the motor dynamics. In contrast, in this paper, we consider a quadruped jumping task that we rapidly optimize online. We design foot force profiles parameterized by only a few parameters which we optimize for directly on hardware with Bayesian Optimization. The force profiles are tracked at the joint level, and added to Cartesian PD impedance control and Virtual Model Control to stabilize the jumping motions. After optimization, which takes only a handful of jumps, we show that this control architecture is capable of diverse and omnidirectional jumps including forward, lateral, and twist (turning) jumps, even on uneven terrain, enabling the Unitree Go1 quadruped to jump 0.5 m high, 0.5 m forward, and jump-turn over 2 rad. Video results can be found at https://youtu.be/SvfVNQ90k_w.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge