Anastasia Bolotnikova
Locomotion Mode Transitions: Tackling System- and User-Specific Variability in Lower-Limb Exoskeletons
Nov 20, 2024
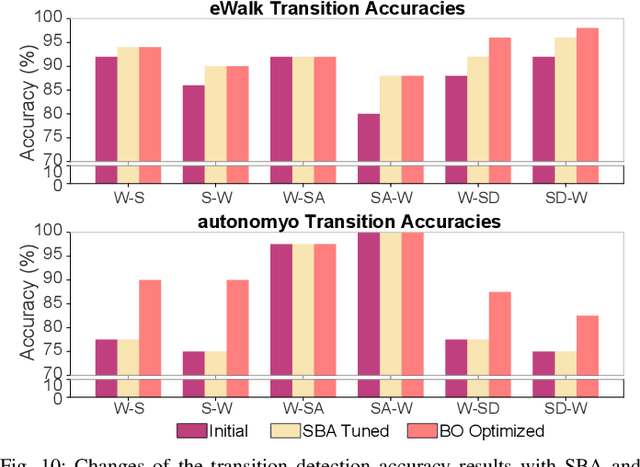
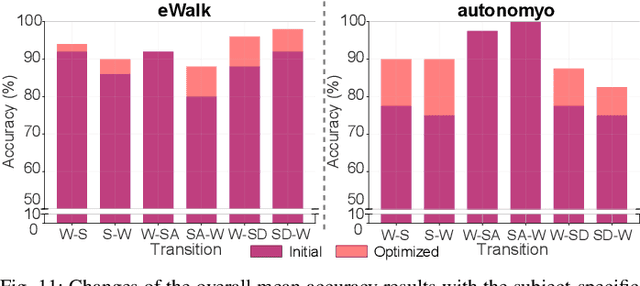
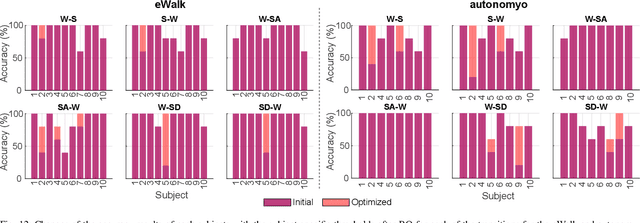
Abstract:Accurate detection of locomotion transitions, such as walk to sit, walk to stair ascent, and descent, is crucial to effectively control robotic assistive devices, such as lower-limb exoskeletons, as each locomotion mode requires specific assistance. Variability in collected sensor data introduced by user- or system-specific characteristics makes it challenging to maintain high transition detection accuracy while avoiding latency using non-adaptive classification models. In this study, we identified key factors influencing transition detection performance, including variations in user behavior, and different mechanical designs of the exoskeletons. To boost the transition detection accuracy, we introduced two methods for adapting a finite-state machine classifier to system- and user-specific variability: a Statistics-Based approach and Bayesian Optimization. Our experimental results demonstrate that both methods remarkably improve transition detection accuracy across diverse users, achieving up to an 80% increase in certain scenarios compared to the non-personalized threshold method. These findings emphasize the importance of personalization in adaptive control systems, underscoring the potential for enhanced user experience and effectiveness in assistive devices. By incorporating subject- and system-specific data into the model training process, our approach offers a precise and reliable solution for detecting locomotion transitions, catering to individual user needs, and ultimately improving the performance of assistive devices.
Maximizing Performance with Minimal Resources for Real-Time Transition Detection
Oct 06, 2023



Abstract:Assistive devices, such as exoskeletons and prostheses, have revolutionized the field of rehabilitation and mobility assistance. Efficiently detecting transitions between different activities, such as walking, stair ascending and descending, and sitting, is crucial for ensuring adaptive control and enhancing user experience. We here present an approach for real-time transition detection, aimed at optimizing the processing-time performance. By establishing activity-specific threshold values through trained machine learning models, we effectively distinguish motion patterns and we identify transition moments between locomotion modes. This threshold-based method improves real-time embedded processing time performance by up to 11 times compared to machine learning approaches. The efficacy of the developed finite-state machine is validated using data collected from three different measurement systems. Moreover, experiments with healthy participants were conducted on an active pelvis orthosis to validate the robustness and reliability of our approach. The proposed algorithm achieved high accuracy in detecting transitions between activities. These promising results show the robustness and reliability of the method, reinforcing its potential for integration into practical applications.
Task-Space Control Interface for SoftBank Humanoid Robots and its Human-Robot Interaction Applications
Oct 09, 2020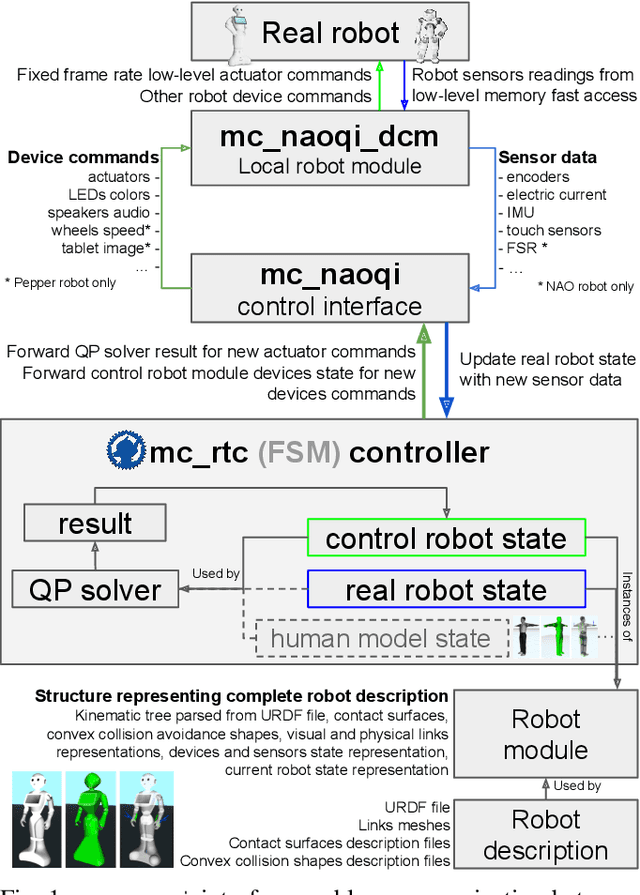


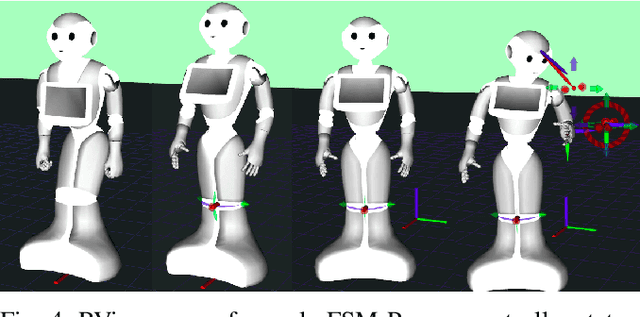
Abstract:We present an open-source software interface, called mc_naoqi, that allows to perform whole-body task-space Quadratic Programming based control, implemented in mc_rtc framework, on the SoftBank Robotics Europe humanoid robots. We describe the control interface, associated robot description packages, robot modules and sample whole-body controllers. We demonstrate the use of these tools in simulation for a robot interacting with a human model. Finally, we showcase and discuss the use of the developed open-source tools for running the human-robot close contact interaction experiments with real human subjects inspired from assistance scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge