Atharva Gundawar
Beyond Semantics: The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Reasonless Intermediate Tokens
May 19, 2025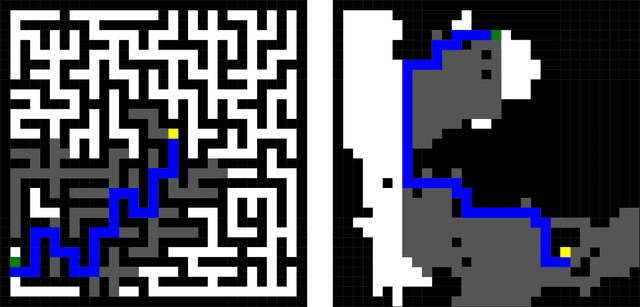
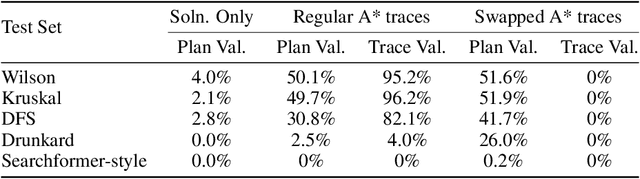
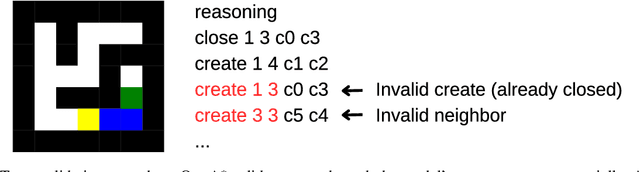
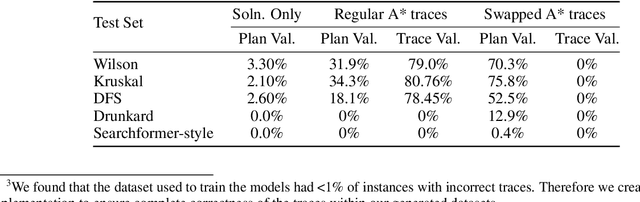
Abstract:Recent impressive results from large reasoning models have been interpreted as a triumph of Chain of Thought (CoT), and especially of the process of training on CoTs sampled from base LLMs in order to help find new reasoning patterns. In this paper, we critically examine that interpretation by investigating how the semantics of intermediate tokens-often anthropomorphized as "thoughts" or reasoning traces and which are claimed to display behaviors like backtracking, self-verification etc.-actually influence model performance. We train transformer models on formally verifiable reasoning traces and solutions, constraining both intermediate steps and final outputs to align with those of a formal solver (in our case, A* search). By constructing a formal interpreter of the semantics of our problems and intended algorithm, we systematically evaluate not only solution accuracy but also the correctness of intermediate traces, thus allowing us to evaluate whether the latter causally influences the former. We notice that, despite significant improvements on the solution-only baseline, models trained on entirely correct traces still produce invalid reasoning traces when arriving at correct solutions. To further show that trace accuracy is only loosely connected to solution accuracy, we then train models on noisy, corrupted traces which have no relation to the specific problem each is paired with, and find that not only does performance remain largely consistent with models trained on correct data, but in some cases can improve upon it and generalize more robustly on out-of-distribution tasks. These results challenge the assumption that intermediate tokens or "Chains of Thought" induce predictable reasoning behaviors and caution against anthropomorphizing such outputs or over-interpreting them (despite their mostly correct forms) as evidence of human-like or algorithmic behaviors in language models.
REAL: Benchmarking Autonomous Agents on Deterministic Simulations of Real Websites
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:We introduce REAL, a benchmark and framework for multi-turn agent evaluations on deterministic simulations of real-world websites. REAL comprises high-fidelity, deterministic replicas of 11 widely-used websites across domains such as e-commerce, travel, communication, and professional networking. We also release a benchmark consisting of 112 practical tasks that mirror everyday complex user interactions requiring both accurate information retrieval and state-changing actions. All interactions occur within this fully controlled setting, eliminating safety risks and enabling robust, reproducible evaluation of agent capability and reliability. Our novel evaluation framework combines programmatic checks of website state for action-based tasks with rubric-guided LLM-based judgments for information retrieval. The framework supports both open-source and proprietary agent systems through a flexible evaluation harness that accommodates black-box commands within browser environments, allowing research labs to test agentic systems without modification. Our empirical results show that frontier language models achieve at most a 41% success rate on REAL, highlighting critical gaps in autonomous web navigation and task completion capabilities. Our framework supports easy integration of new tasks, reproducible evaluation, and scalable data generation for training web agents. The websites, framework, and leaderboard are available at https://realevals.xyz and https://github.com/agi-inc/REAL.
Robust Planning with Compound LLM Architectures: An LLM-Modulo Approach
Nov 20, 2024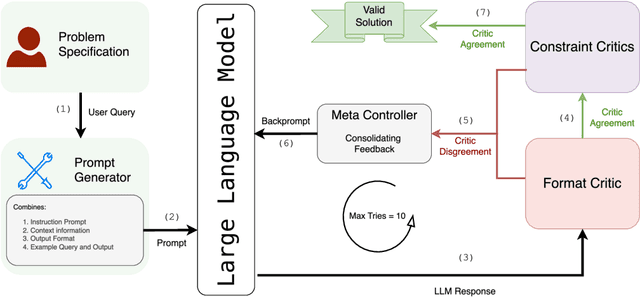

Abstract:Previous work has attempted to boost Large Language Model (LLM) performance on planning and scheduling tasks through a variety of prompt engineering techniques. While these methods can work within the distributions tested, they are neither robust nor predictable. This limitation can be addressed through compound LLM architectures where LLMs work in conjunction with other components to ensure reliability. In this paper, we present a technical evaluation of a compound LLM architecture--the LLM-Modulo framework. In this framework, an LLM is paired with a complete set of sound verifiers that validate its output, re-prompting it if it fails. This approach ensures that the system can never output any fallacious output, and therefore that every output generated is guaranteed correct--something previous techniques have not been able to claim. Our results, evaluated across four scheduling domains, demonstrate significant performance gains with the LLM-Modulo framework using various models. Additionally, we explore modifications to the base configuration of the framework and assess their impact on overall system performance.
Planning in Strawberry Fields: Evaluating and Improving the Planning and Scheduling Capabilities of LRM o1
Oct 03, 2024
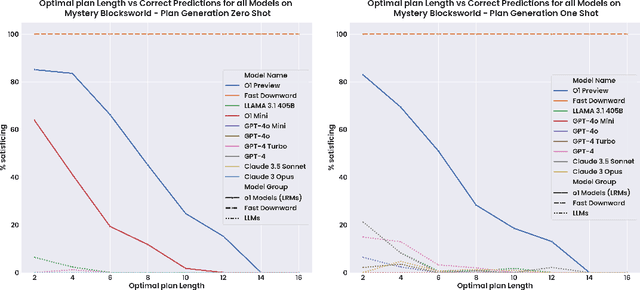
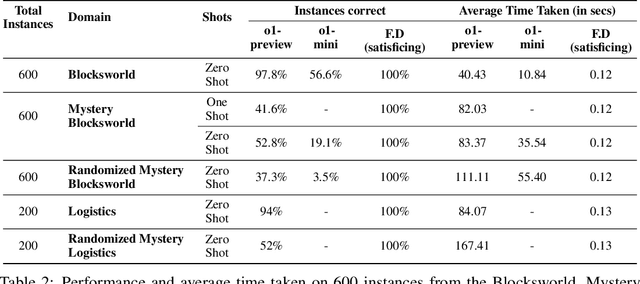
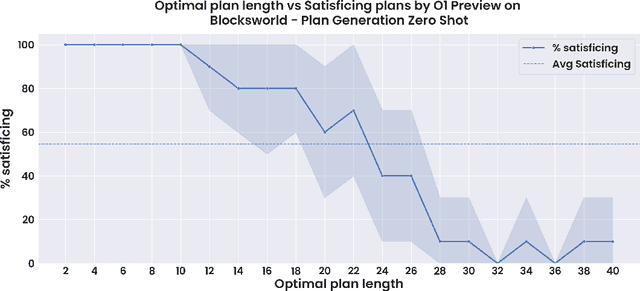
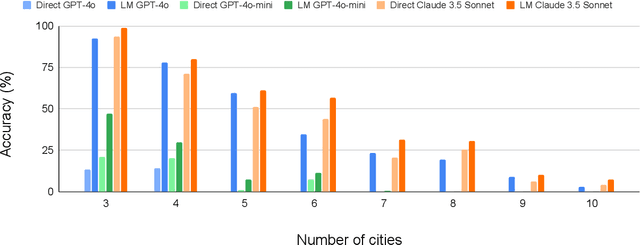
Abstract:The ability to plan a course of action that achieves a desired state of affairs has long been considered a core competence of intelligent agents and has been an integral part of AI research since its inception. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), there has been considerable interest in the question of whether or not they possess such planning abilities, but -- despite the slew of new private and open source LLMs since GPT3 -- progress has remained slow. OpenAI claims that their recent o1 (Strawberry) model has been specifically constructed and trained to escape the normal limitations of autoregressive LLMs -- making it a new kind of model: a Large Reasoning Model (LRM). In this paper, we evaluate the planning capabilities of two LRMs (o1-preview and o1-mini) on both planning and scheduling benchmarks. We see that while o1 does seem to offer significant improvements over autoregressive LLMs, this comes at a steep inference cost, while still failing to provide any guarantees over what it generates. We also show that combining o1 models with external verifiers -- in a so-called LRM-Modulo system -- guarantees the correctness of the combined system's output while further improving performance.
Superior Computer Chess with Model Predictive Control, Reinforcement Learning, and Rollout
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:In this paper we apply model predictive control (MPC), rollout, and reinforcement learning (RL) methodologies to computer chess. We introduce a new architecture for move selection, within which available chess engines are used as components. One engine is used to provide position evaluations in an approximation in value space MPC/RL scheme, while a second engine is used as nominal opponent, to emulate or approximate the moves of the true opponent player. We show that our architecture improves substantially the performance of the position evaluation engine. In other words our architecture provides an additional layer of intelligence, on top of the intelligence of the engines on which it is based. This is true for any engine, regardless of its strength: top engines such as Stockfish and Komodo Dragon (of varying strengths), as well as weaker engines. Structurally, our basic architecture selects moves by a one-move lookahead search, with an intermediate move generated by a nominal opponent engine, and followed by a position evaluation by another chess engine. Simpler schemes that forego the use of the nominal opponent, also perform better than the position evaluator, but not quite by as much. More complex schemes, involving multistep lookahead, may also be used and generally tend to perform better as the length of the lookahead increases. Theoretically, our methodology relies on generic cost improvement properties and the superlinear convergence framework of Newton's method, which fundamentally underlies approximation in value space, and related MPC/RL and rollout/policy iteration schemes. A critical requirement of this framework is that the first lookahead step should be executed exactly. This fact has guided our architectural choices, and is apparently an important factor in improving the performance of even the best available chess engines.
Robust Planning with LLM-Modulo Framework: Case Study in Travel Planning
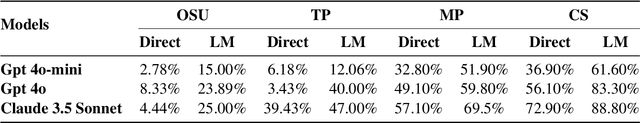
May 31, 2024Abstract:As the applicability of Large Language Models (LLMs) extends beyond traditional text processing tasks, there is a burgeoning interest in their potential to excel in planning and reasoning assignments, realms traditionally reserved for System 2 cognitive competencies. Despite their perceived versatility, the research community is still unraveling effective strategies to harness these models in such complex domains. The recent discourse introduced by the paper on LLM Modulo marks a significant stride, proposing a conceptual framework that enhances the integration of LLMs into diverse planning and reasoning activities. This workshop paper delves into the practical application of this framework within the domain of travel planning, presenting a specific instance of its implementation. We are using the Travel Planning benchmark by the OSU NLP group, a benchmark for evaluating the performance of LLMs in producing valid itineraries based on user queries presented in natural language. While popular methods of enhancing the reasoning abilities of LLMs such as Chain of Thought, ReAct, and Reflexion achieve a meager 0%, 0.6%, and 0% with GPT3.5-Turbo respectively, our operationalization of the LLM-Modulo framework for TravelPlanning domain provides a remarkable improvement, enhancing baseline performances by 4.6x for GPT4-Turbo and even more for older models like GPT3.5-Turbo from 0% to 5%. Furthermore, we highlight the other useful roles of LLMs in the planning pipeline, as suggested in LLM-Modulo, which can be reliably operationalized such as extraction of useful critics and reformulator for critics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge