Arman Eshaghi
for the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
Quantifying white matter hyperintensity and brain volumes in heterogeneous clinical and low-field portable MRI
Dec 08, 2023
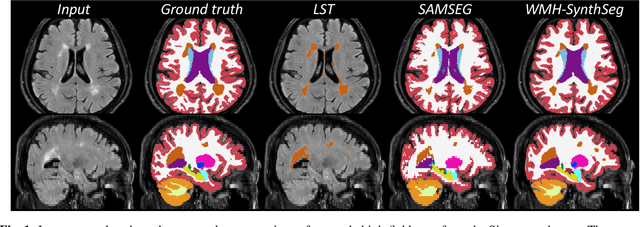
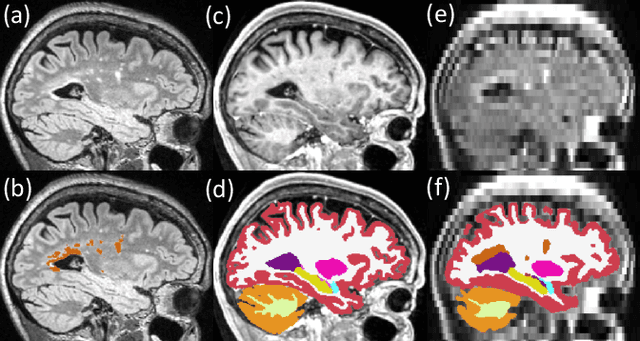

Abstract:Brain atrophy and white matter hyperintensity (WMH) are critical neuroimaging features for ascertaining brain injury in cerebrovascular disease and multiple sclerosis. Automated segmentation and quantification is desirable but existing methods require high-resolution MRI with good signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This precludes application to clinical and low-field portable MRI (pMRI) scans, thus hampering large-scale tracking of atrophy and WMH progression, especially in underserved areas where pMRI has huge potential. Here we present a method that segments white matter hyperintensity and 36 brain regions from scans of any resolution and contrast (including pMRI) without retraining. We show results on six public datasets and on a private dataset with paired high- and low-field scans (3T and 64mT), where we attain strong correlation between the WMH ($\rho$=.85) and hippocampal volumes (r=.89) estimated at both fields. Our method is publicly available as part of FreeSurfer, at: http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/WMH-SynthSeg.
DeepBrainPrint: A Novel Contrastive Framework for Brain MRI Re-Identification
Feb 25, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in MRI have led to the creation of large datasets. With the increase in data volume, it has become difficult to locate previous scans of the same patient within these datasets (a process known as re-identification). To address this issue, we propose an AI-powered medical imaging retrieval framework called DeepBrainPrint, which is designed to retrieve brain MRI scans of the same patient. Our framework is a semi-self-supervised contrastive deep learning approach with three main innovations. First, we use a combination of self-supervised and supervised paradigms to create an effective brain fingerprint from MRI scans that can be used for real-time image retrieval. Second, we use a special weighting function to guide the training and improve model convergence. Third, we introduce new imaging transformations to improve retrieval robustness in the presence of intensity variations (i.e. different scan contrasts), and to account for age and disease progression in patients. We tested DeepBrainPrint on a large dataset of T1-weighted brain MRIs from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and on a synthetic dataset designed to evaluate retrieval performance with different image modalities. Our results show that DeepBrainPrint outperforms previous methods, including simple similarity metrics and more advanced contrastive deep learning frameworks.
An efficient semi-supervised quality control system trained using physics-based MRI-artefact generators and adversarial training
Jun 07, 2022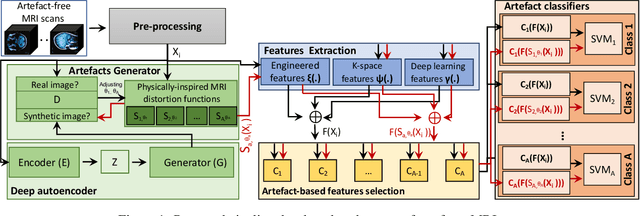

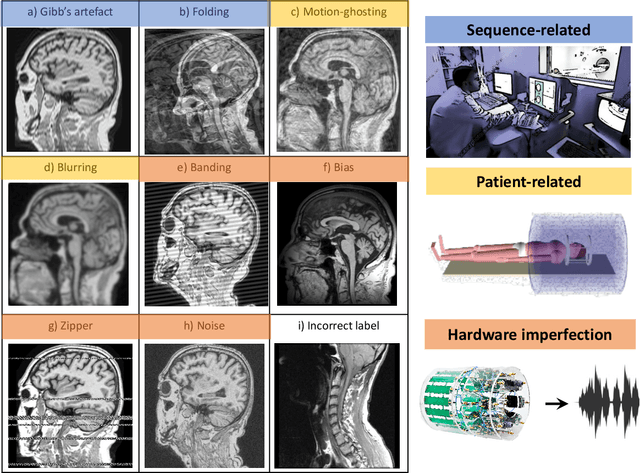

Abstract:Large medical imaging data sets are becoming increasingly available. A common challenge in these data sets is to ensure that each sample meets minimum quality requirements devoid of significant artefacts. Despite a wide range of existing automatic methods having been developed to identify imperfections and artefacts in medical imaging, they mostly rely on data-hungry methods. In particular, the lack of sufficient scans with artefacts available for training has created a barrier in designing and deploying machine learning in clinical research. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel framework having four main components: (1) a set of artefact generators inspired by magnetic resonance physics to corrupt brain MRI scans and augment a training dataset, (2) a set of abstract and engineered features to represent images compactly, (3) a feature selection process that depends on the class of artefact to improve classification performance, and (4) a set of Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifiers trained to identify artefacts. Our novel contributions are threefold: first, we use the novel physics-based artefact generators to generate synthetic brain MRI scans with controlled artefacts as a data augmentation technique. This will avoid the labour-intensive collection and labelling process of scans with rare artefacts. Second, we propose a large pool of abstract and engineered image features developed to identify 9 different artefacts for structural MRI. Finally, we use an artefact-based feature selection block that, for each class of artefacts, finds the set of features that provide the best classification performance. We performed validation experiments on a large data set of scans with artificially-generated artefacts, and in a multiple sclerosis clinical trial where real artefacts were identified by experts, showing that the proposed pipeline outperforms traditional methods.
DIVE: A spatiotemporal progression model of brain pathology in neurodegenerative disorders
Jan 11, 2019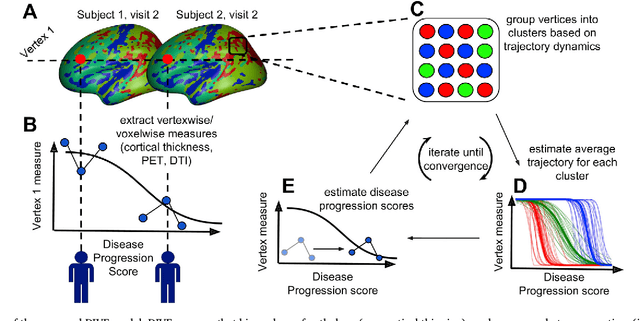
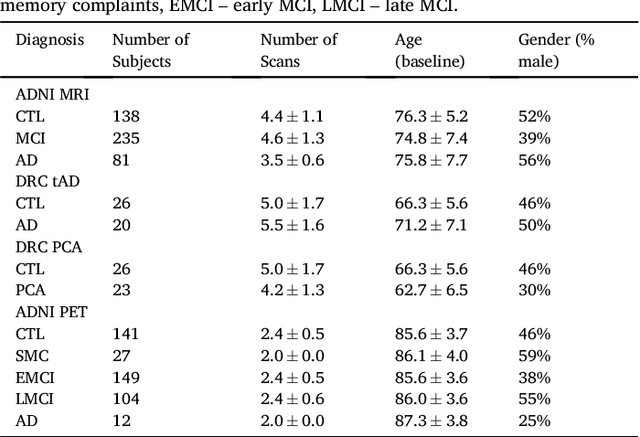
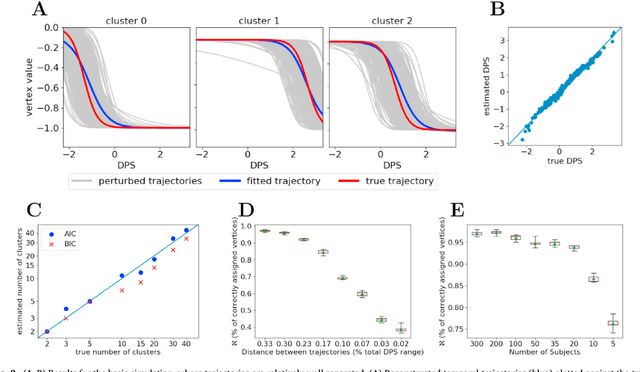
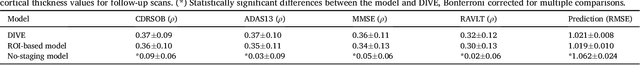
Abstract:Here we present DIVE: Data-driven Inference of Vertexwise Evolution. DIVE is an image-based disease progression model with single-vertex resolution, designed to reconstruct long-term patterns of brain pathology from short-term longitudinal data sets. DIVE clusters vertex-wise biomarker measurements on the cortical surface that have similar temporal dynamics across a patient population, and concurrently estimates an average trajectory of vertex measurements in each cluster. DIVE uniquely outputs a parcellation of the cortex into areas with common progression patterns, leading to a new signature for individual diseases. DIVE further estimates the disease stage and progression speed for every visit of every subject, potentially enhancing stratification for clinical trials or management. On simulated data, DIVE can recover ground truth clusters and their underlying trajectory, provided the average trajectories are sufficiently different between clusters. We demonstrate DIVE on data from two cohorts: the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and the Dementia Research Centre (DRC), UK, containing patients with Posterior Cortical Atrophy (PCA) as well as typical Alzheimer's disease (tAD). DIVE finds similar spatial patterns of atrophy for tAD subjects in the two independent datasets (ADNI and DRC), and further reveals distinct patterns of pathology in different diseases (tAD vs PCA) and for distinct types of biomarker data: cortical thickness from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) vs amyloid load from Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Finally, DIVE can be used to estimate a fine-grained spatial distribution of pathology in the brain using any kind of voxelwise or vertexwise measures including Jacobian compression maps, fractional anisotropy (FA) maps from diffusion imaging or other PET measures. DIVE source code is available online: https://github.com/mrazvan22/dive
Disease Knowledge Transfer across Neurodegenerative Diseases
Jan 11, 2019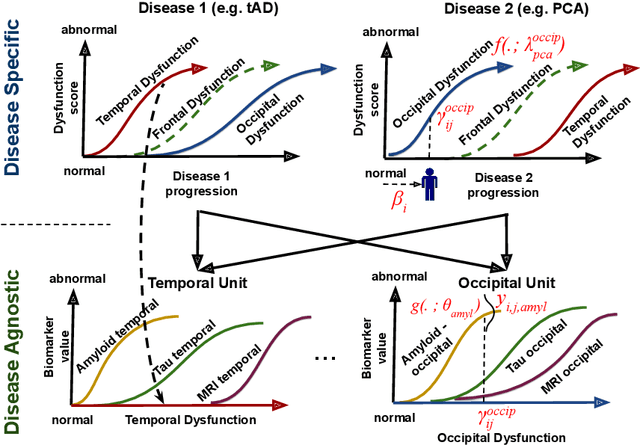
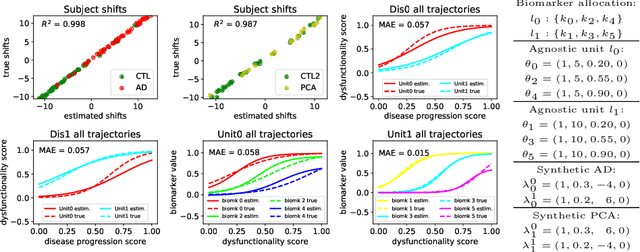
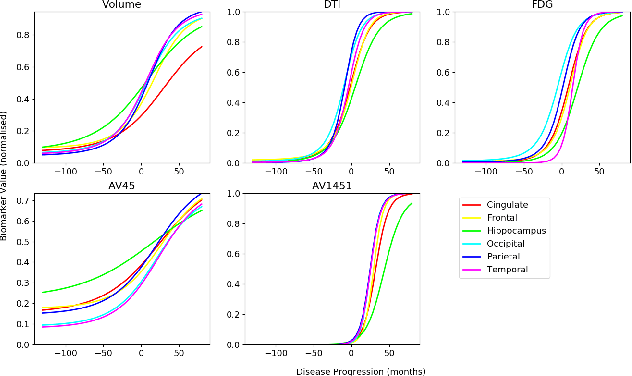
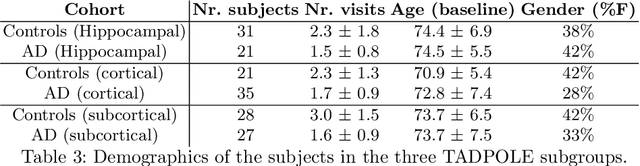
Abstract:We introduce Disease Knowledge Transfer (DKT), a novel technique for transferring biomarker information between related neurodegenerative diseases. DKT infers robust multimodal biomarker trajectories in rare neurodegenerative diseases even when only limited, unimodal data is available, by transferring information from larger multimodal datasets from common neurodegenerative diseases. DKT is a joint-disease generative model of biomarker progressions, which exploits biomarker relationships that are shared across diseases. As opposed to current deep learning approaches, DKT is interpretable, which allows us to understand underlying disease mechanisms. Here we demonstrate DKT on Alzheimer's disease (AD) variants and its ability to predict trajectories for multimodal biomarkers in Posterior Cortical Atrophy (PCA), in lack of such data from PCA subjects. For this we train DKT on a combined dataset containing subjects with two distinct diseases and sizes of data available: 1) a larger, multimodal typical AD (tAD) dataset from the TADPOLE Challenge, and 2) a smaller unimodal Posterior Cortical Atrophy (PCA) dataset from the Dementia Research Centre (DRC) UK, for which only a limited number of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans are available. We first show that DKT estimates plausible multimodal trajectories in PCA that agree with previous literature. We further validate DKT in two situations: (1) on synthetic data, showing that it can accurately estimate the ground truth parameters and (2) on 20 DTI scans from controls and PCA patients, showing that it has favourable predictive performance compared to standard approaches. While we demonstrated DKT on Alzheimer's variants, we note DKT is generalisable to other forms of related neurodegenerative diseases. Source code for DKT is available online: https://github.com/mrazvan22/dkt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge