Arash Hajisafi
Small Graph Is All You Need: DeepStateGNN for Scalable Traffic Forecasting
Feb 20, 2025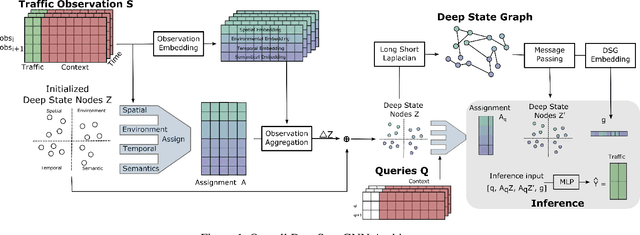
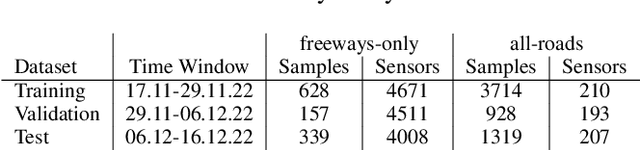
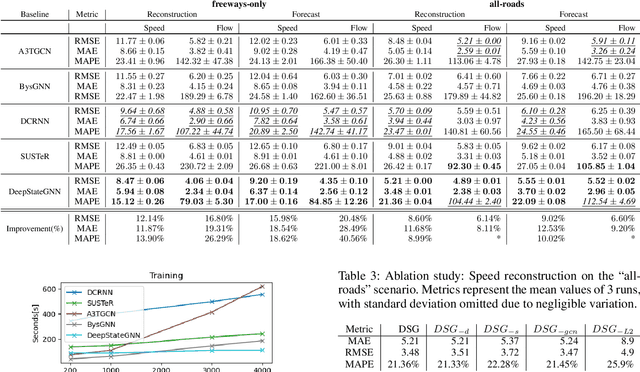
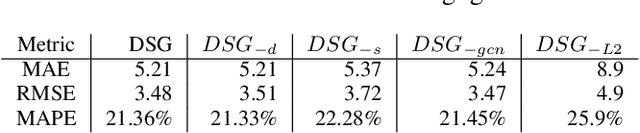
Abstract:We propose a novel Graph Neural Network (GNN) model, named DeepStateGNN, for analyzing traffic data, demonstrating its efficacy in two critical tasks: forecasting and reconstruction. Unlike typical GNN methods that treat each traffic sensor as an individual graph node, DeepStateGNN clusters sensors into higher-level graph nodes, dubbed Deep State Nodes, based on various similarity criteria, resulting in a fixed number of nodes in a Deep State graph. The term "Deep State" nodes is a play on words, referencing hidden networks of power that, like these nodes, secretly govern traffic independently of visible sensors. These Deep State Nodes are defined by several similarity factors, including spatial proximity (e.g., sensors located nearby in the road network), functional similarity (e.g., sensors on similar types of freeways), and behavioral similarity under specific conditions (e.g., traffic behavior during rain). This clustering approach allows for dynamic and adaptive node grouping, as sensors can belong to multiple clusters and clusters may evolve over time. Our experimental results show that DeepStateGNN offers superior scalability and faster training, while also delivering more accurate results than competitors. It effectively handles large-scale sensor networks, outperforming other methods in both traffic forecasting and reconstruction accuracy.
WaveGNN: Modeling Irregular Multivariate Time Series for Accurate Predictions
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Accurately modeling and analyzing time series data is crucial for downstream applications across various fields, including healthcare, finance, astronomy, and epidemiology. However, real-world time series often exhibit irregularities such as misaligned timestamps, missing entries, and variable sampling rates, complicating their analysis. Existing approaches often rely on imputation, which can introduce biases. A few approaches that directly model irregularity tend to focus exclusively on either capturing intra-series patterns or inter-series relationships, missing the benefits of integrating both. To this end, we present WaveGNN, a novel framework designed to directly (i.e., no imputation) embed irregularly sampled multivariate time series data for accurate predictions. WaveGNN utilizes a Transformer-based encoder to capture intra-series patterns by directly encoding the temporal dynamics of each time series. To capture inter-series relationships, WaveGNN uses a dynamic graph neural network model, where each node represents a sensor, and the edges capture the long- and short-term relationships between them. Our experimental results on real-world healthcare datasets demonstrate that WaveGNN consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, with an average relative improvement of 14.7% in F1-score when compared to the second-best baseline in cases with extreme sparsity. Our ablation studies reveal that both intra-series and inter-series modeling significantly contribute to this notable improvement.
Dynamic GNNs for Precise Seizure Detection and Classification from EEG Data
May 08, 2024Abstract:Diagnosing epilepsy requires accurate seizure detection and classification, but traditional manual EEG signal analysis is resource-intensive. Meanwhile, automated algorithms often overlook EEG's geometric and semantic properties critical for interpreting brain activity. This paper introduces NeuroGNN, a dynamic Graph Neural Network (GNN) framework that captures the dynamic interplay between the EEG electrode locations and the semantics of their corresponding brain regions. The specific brain region where an electrode is placed critically shapes the nature of captured EEG signals. Each brain region governs distinct cognitive functions, emotions, and sensory processing, influencing both the semantic and spatial relationships within the EEG data. Understanding and modeling these intricate brain relationships are essential for accurate and meaningful insights into brain activity. This is precisely where the proposed NeuroGNN framework excels by dynamically constructing a graph that encapsulates these evolving spatial, temporal, semantic, and taxonomic correlations to improve precision in seizure detection and classification. Our extensive experiments with real-world data demonstrate that NeuroGNN significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art models.
* This preprint has not undergone any post-submission improvements or corrections. The Version of Record of this contribution is published in the proceedings of the 28th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD 2024), Taipei, Taiwan, May 7-10, 2024, and is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2238-9_16
Holistic Survey of Privacy and Fairness in Machine Learning
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Privacy and fairness are two crucial pillars of responsible Artificial Intelligence (AI) and trustworthy Machine Learning (ML). Each objective has been independently studied in the literature with the aim of reducing utility loss in achieving them. Despite the significant interest attracted from both academia and industry, there remains an immediate demand for more in-depth research to unravel how these two objectives can be simultaneously integrated into ML models. As opposed to well-accepted trade-offs, i.e., privacy-utility and fairness-utility, the interrelation between privacy and fairness is not well-understood. While some works suggest a trade-off between the two objective functions, there are others that demonstrate the alignment of these functions in certain scenarios. To fill this research gap, we provide a thorough review of privacy and fairness in ML, including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning. After examining and consolidating the literature on both objectives, we present a holistic survey on the impact of privacy on fairness, the impact of fairness on privacy, existing architectures, their interaction in application domains, and algorithms that aim to achieve both objectives while minimizing the utility sacrificed. Finally, we identify research challenges in achieving privacy and fairness concurrently in ML, particularly focusing on large language models.
Learning Dynamic Graphs from All Contextual Information for Accurate Point-of-Interest Visit Forecasting
Jun 28, 2023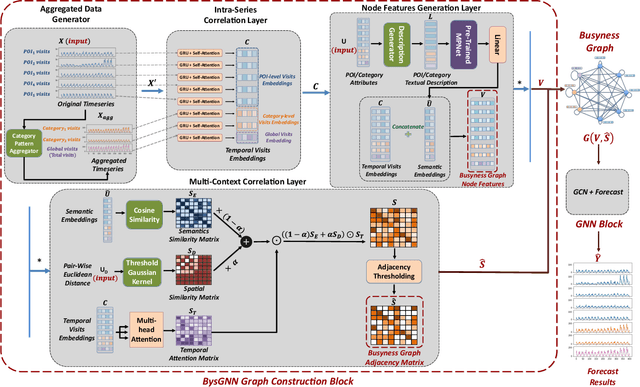
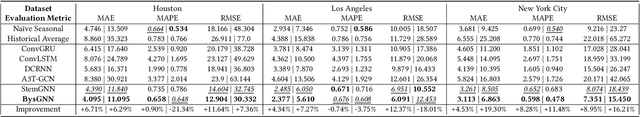
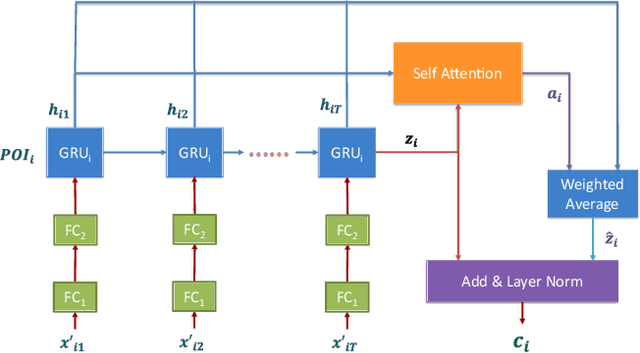
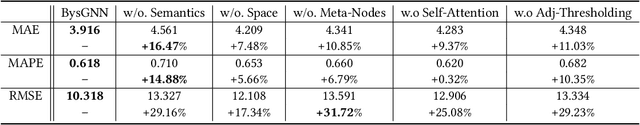
Abstract:Forecasting the number of visits to Points-of-Interest (POI) in an urban area is critical for planning and decision-making for various application domains, from urban planning and transportation management to public health and social studies. Although this forecasting problem can be formulated as a multivariate time-series forecasting task, the current approaches cannot fully exploit the ever-changing multi-context correlations among POIs. Therefore, we propose Busyness Graph Neural Network (BysGNN), a temporal graph neural network designed to learn and uncover the underlying multi-context correlations between POIs for accurate visit forecasting. Unlike other approaches where only time-series data is used to learn a dynamic graph, BysGNN utilizes all contextual information and time-series data to learn an accurate dynamic graph representation. By incorporating all contextual, temporal, and spatial signals, we observe a significant improvement in our forecasting accuracy over state-of-the-art forecasting models in our experiments with real-world datasets across the United States.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge