Yannick Wölker
SUSTeR: Sparse Unstructured Spatio Temporal Reconstruction on Traffic Prediction
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Mining spatio-temporal correlation patterns for traffic prediction is a well-studied field. However, most approaches are based on the assumption of the availability of and accessibility to a sufficiently dense data source, which is rather the rare case in reality. Traffic sensors in road networks are generally highly sparse in their distribution: fleet-based traffic sensing is sparse in space but also sparse in time. There are also other traffic application, besides road traffic, like moving objects in the marine space, where observations are sparsely and arbitrarily distributed in space. In this paper, we tackle the problem of traffic prediction on sparse and spatially irregular and non-deterministic traffic observations. We draw a border between imputations and this work as we consider high sparsity rates and no fixed sensor locations. We advance correlation mining methods with a Sparse Unstructured Spatio Temporal Reconstruction (SUSTeR) framework that reconstructs traffic states from sparse non-stationary observations. For the prediction the framework creates a hidden context traffic state which is enriched in a residual fashion with each observation. Such an assimilated hidden traffic state can be used by existing traffic prediction methods to predict future traffic states. We query these states with query locations from the spatial domain.
Small Graph Is All You Need: DeepStateGNN for Scalable Traffic Forecasting
Feb 20, 2025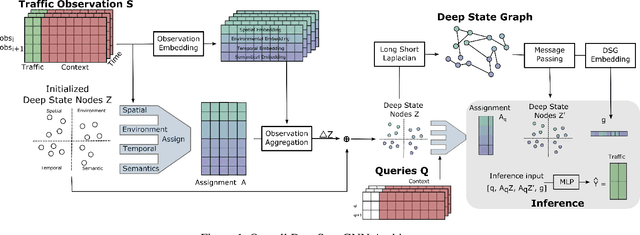
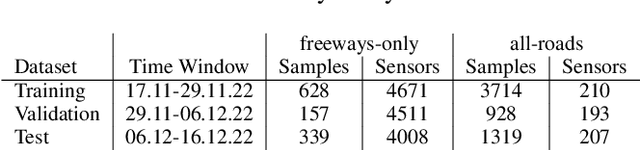
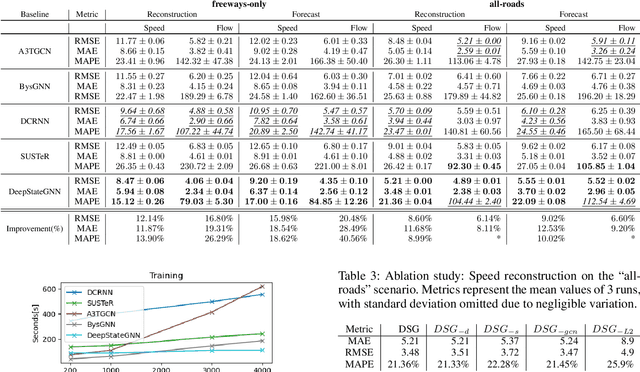
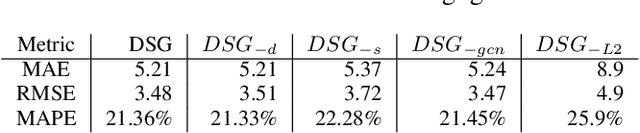
Abstract:We propose a novel Graph Neural Network (GNN) model, named DeepStateGNN, for analyzing traffic data, demonstrating its efficacy in two critical tasks: forecasting and reconstruction. Unlike typical GNN methods that treat each traffic sensor as an individual graph node, DeepStateGNN clusters sensors into higher-level graph nodes, dubbed Deep State Nodes, based on various similarity criteria, resulting in a fixed number of nodes in a Deep State graph. The term "Deep State" nodes is a play on words, referencing hidden networks of power that, like these nodes, secretly govern traffic independently of visible sensors. These Deep State Nodes are defined by several similarity factors, including spatial proximity (e.g., sensors located nearby in the road network), functional similarity (e.g., sensors on similar types of freeways), and behavioral similarity under specific conditions (e.g., traffic behavior during rain). This clustering approach allows for dynamic and adaptive node grouping, as sensors can belong to multiple clusters and clusters may evolve over time. Our experimental results show that DeepStateGNN offers superior scalability and faster training, while also delivering more accurate results than competitors. It effectively handles large-scale sensor networks, outperforming other methods in both traffic forecasting and reconstruction accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge