AprilPyone MaungMaung
Mitigating Backdoor Attacks using Activation-Guided Model Editing
Jul 10, 2024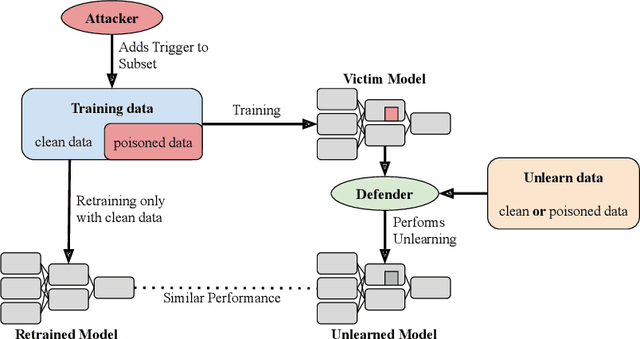
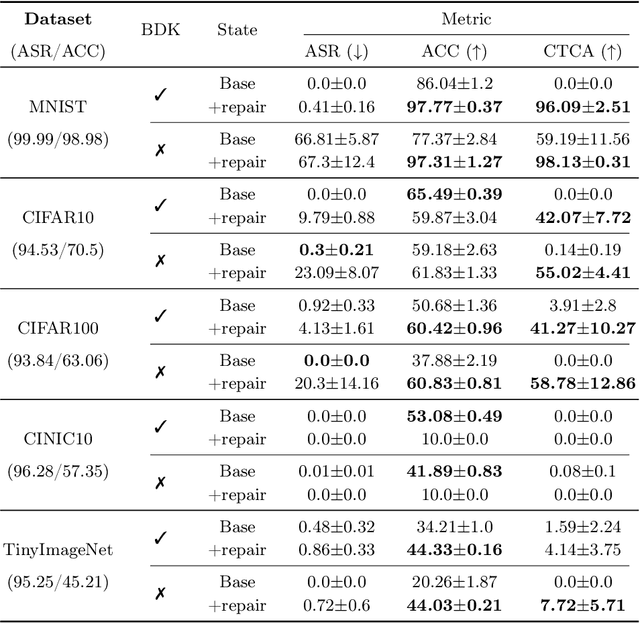

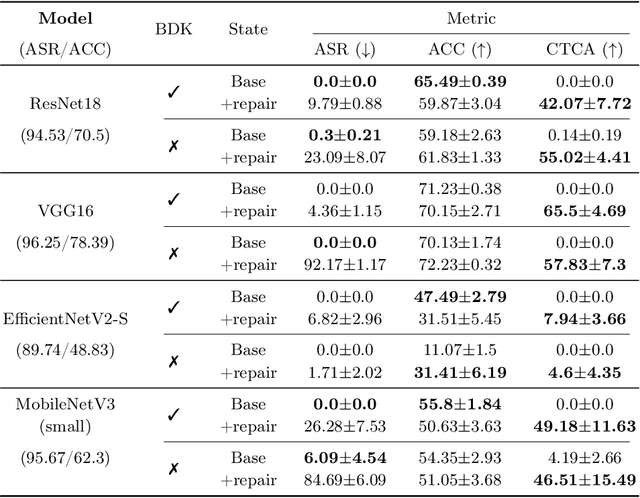
Abstract:Backdoor attacks compromise the integrity and reliability of machine learning models by embedding a hidden trigger during the training process, which can later be activated to cause unintended misbehavior. We propose a novel backdoor mitigation approach via machine unlearning to counter such backdoor attacks. The proposed method utilizes model activation of domain-equivalent unseen data to guide the editing of the model's weights. Unlike the previous unlearning-based mitigation methods, ours is computationally inexpensive and achieves state-of-the-art performance while only requiring a handful of unseen samples for unlearning. In addition, we also point out that unlearning the backdoor may cause the whole targeted class to be unlearned, thus introducing an additional repair step to preserve the model's utility after editing the model. Experiment results show that the proposed method is effective in unlearning the backdoor on different datasets and trigger patterns.
Fine-Tuning Text-To-Image Diffusion Models for Class-Wise Spurious Feature Generation
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:We propose a method for generating spurious features by leveraging large-scale text-to-image diffusion models. Although the previous work detects spurious features in a large-scale dataset like ImageNet and introduces Spurious ImageNet, we found that not all spurious images are spurious across different classifiers. Although spurious images help measure the reliance of a classifier, filtering many images from the Internet to find more spurious features is time-consuming. To this end, we utilize an existing approach of personalizing large-scale text-to-image diffusion models with available discovered spurious images and propose a new spurious feature similarity loss based on neural features of an adversarially robust model. Precisely, we fine-tune Stable Diffusion with several reference images from Spurious ImageNet with a modified objective incorporating the proposed spurious-feature similarity loss. Experiment results show that our method can generate spurious images that are consistently spurious across different classifiers. Moreover, the generated spurious images are visually similar to reference images from Spurious ImageNet.
Stability Analysis of ChatGPT-based Sentiment Analysis in AI Quality Assurance
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:In the era of large AI models, the complex architecture and vast parameters present substantial challenges for effective AI quality management (AIQM), e.g. large language model (LLM). This paper focuses on investigating the quality assurance of a specific LLM-based AI product--a ChatGPT-based sentiment analysis system. The study delves into stability issues related to both the operation and robustness of the expansive AI model on which ChatGPT is based. Experimental analysis is conducted using benchmark datasets for sentiment analysis. The results reveal that the constructed ChatGPT-based sentiment analysis system exhibits uncertainty, which is attributed to various operational factors. It demonstrated that the system also exhibits stability issues in handling conventional small text attacks involving robustness.
Efficient Key-Based Adversarial Defense for ImageNet by Using Pre-trained Model
Nov 28, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose key-based defense model proliferation by leveraging pre-trained models and utilizing recent efficient fine-tuning techniques on ImageNet-1k classification. First, we stress that deploying key-based models on edge devices is feasible with the latest model deployment advancements, such as Apple CoreML, although the mainstream enterprise edge artificial intelligence (Edge AI) has been focused on the Cloud. Then, we point out that the previous key-based defense on on-device image classification is impractical for two reasons: (1) training many classifiers from scratch is not feasible, and (2) key-based defenses still need to be thoroughly tested on large datasets like ImageNet. To this end, we propose to leverage pre-trained models and utilize efficient fine-tuning techniques to proliferate key-based models even on limited computing resources. Experiments were carried out on the ImageNet-1k dataset using adaptive and non-adaptive attacks. The results show that our proposed fine-tuned key-based models achieve a superior classification accuracy (more than 10% increase) compared to the previous key-based models on classifying clean and adversarial examples.
Hindering Adversarial Attacks with Multiple Encrypted Patch Embeddings
Sep 04, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new key-based defense focusing on both efficiency and robustness. Although the previous key-based defense seems effective in defending against adversarial examples, carefully designed adaptive attacks can bypass the previous defense, and it is difficult to train the previous defense on large datasets like ImageNet. We build upon the previous defense with two major improvements: (1) efficient training and (2) optional randomization. The proposed defense utilizes one or more secret patch embeddings and classifier heads with a pre-trained isotropic network. When more than one secret embeddings are used, the proposed defense enables randomization on inference. Experiments were carried out on the ImageNet dataset, and the proposed defense was evaluated against an arsenal of state-of-the-art attacks, including adaptive ones. The results show that the proposed defense achieves a high robust accuracy and a comparable clean accuracy compared to the previous key-based defense.
Generative Model-Based Attack on Learnable Image Encryption for Privacy-Preserving Deep Learning
Mar 09, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel generative model-based attack on learnable image encryption methods proposed for privacy-preserving deep learning. Various learnable encryption methods have been studied to protect the sensitive visual information of plain images, and some of them have been investigated to be robust enough against all existing attacks. However, previous attacks on image encryption focus only on traditional cryptanalytic attacks or reverse translation models, so these attacks cannot recover any visual information if a block-scrambling encryption step, which effectively destroys global information, is applied. Accordingly, in this paper, generative models are explored to evaluate whether such models can restore sensitive visual information from encrypted images for the first time. We first point out that encrypted images have some similarity with plain images in the embedding space. By taking advantage of leaked information from encrypted images, we propose a guided generative model as an attack on learnable image encryption to recover personally identifiable visual information. We implement the proposed attack in two ways by utilizing two state-of-the-art generative models: a StyleGAN-based model and latent diffusion-based one. Experiments were carried out on the CelebA-HQ and ImageNet datasets. Results show that images reconstructed by the proposed method have perceptual similarities to plain images.
Text-Guided Scene Sketch-to-Photo Synthesis
Feb 14, 2023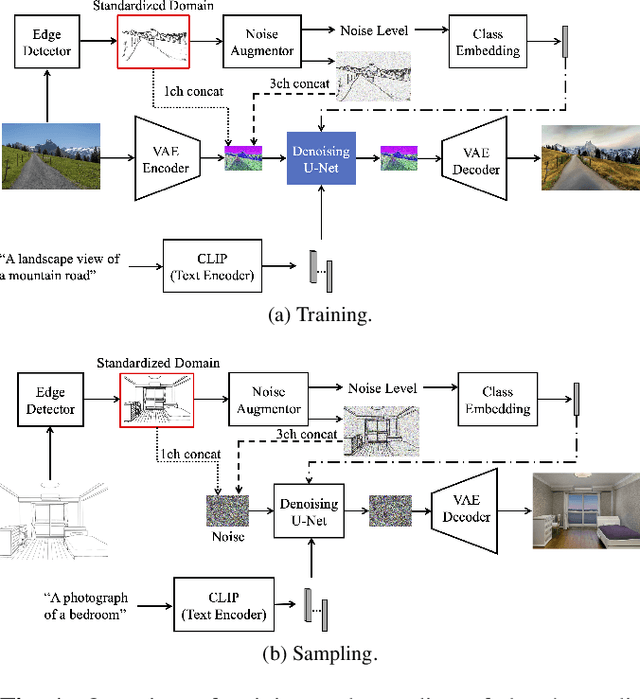
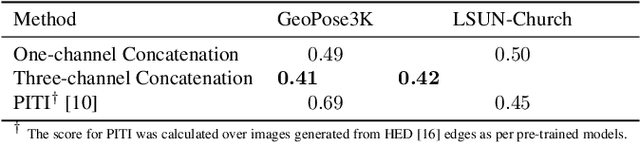


Abstract:We propose a method for scene-level sketch-to-photo synthesis with text guidance. Although object-level sketch-to-photo synthesis has been widely studied, whole-scene synthesis is still challenging without reference photos that adequately reflect the target style. To this end, we leverage knowledge from recent large-scale pre-trained generative models, resulting in text-guided sketch-to-photo synthesis without the need for reference images. To train our model, we use self-supervised learning from a set of photographs. Specifically, we use a pre-trained edge detector that maps both color and sketch images into a standardized edge domain, which reduces the gap between photograph-based edge images (during training) and hand-drawn sketch images (during inference). We implement our method by fine-tuning a latent diffusion model (i.e., Stable Diffusion) with sketch and text conditions. Experiments show that the proposed method translates original sketch images that are not extracted from color images into photos with compelling visual quality.
Color-NeuraCrypt: Privacy-Preserving Color-Image Classification Using Extended Random Neural Networks
Jan 12, 2023Abstract:In recent years, with the development of cloud computing platforms, privacy-preserving methods for deep learning have become an urgent problem. NeuraCrypt is a private random neural network for privacy-preserving that allows data owners to encrypt the medical data before the data uploading, and data owners can train and then test their models in a cloud server with the encrypted data directly. However, we point out that the performance of NeuraCrypt is heavily degraded when using color images. In this paper, we propose a Color-NeuraCrypt to solve this problem. Experiment results show that our proposed Color-NeuraCrypt can achieve a better classification accuracy than the original one and other privacy-preserving methods.
Access Control with Encrypted Feature Maps for Object Detection Models
Sep 29, 2022

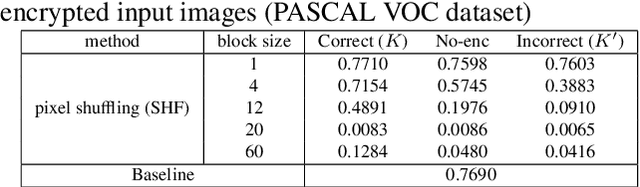

Abstract:In this paper, we propose an access control method with a secret key for object detection models for the first time so that unauthorized users without a secret key cannot benefit from the performance of trained models. The method enables us not only to provide a high detection performance to authorized users but to also degrade the performance for unauthorized users. The use of transformed images was proposed for the access control of image classification models, but these images cannot be used for object detection models due to performance degradation. Accordingly, in this paper, selected feature maps are encrypted with a secret key for training and testing models, instead of input images. In an experiment, the protected models allowed authorized users to obtain almost the same performance as that of non-protected models but also with robustness against unauthorized access without a key.
StyleGAN Encoder-Based Attack for Block Scrambled Face Images
Sep 16, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we propose an attack method to block scrambled face images, particularly Encryption-then-Compression (EtC) applied images by utilizing the existing powerful StyleGAN encoder and decoder for the first time. Instead of reconstructing identical images as plain ones from encrypted images, we focus on recovering styles that can reveal identifiable information from the encrypted images. The proposed method trains an encoder by using plain and encrypted image pairs with a particular training strategy. While state-of-the-art attack methods cannot recover any perceptual information from EtC images, the proposed method discloses personally identifiable information such as hair color, skin color, eyeglasses, gender, etc. Experiments were carried out on the CelebA dataset, and results show that reconstructed images have some perceptual similarities compared to plain images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge