Kentaro Mitsui
PSLM: Parallel Generation of Text and Speech with LLMs for Low-Latency Spoken Dialogue Systems
Jun 18, 2024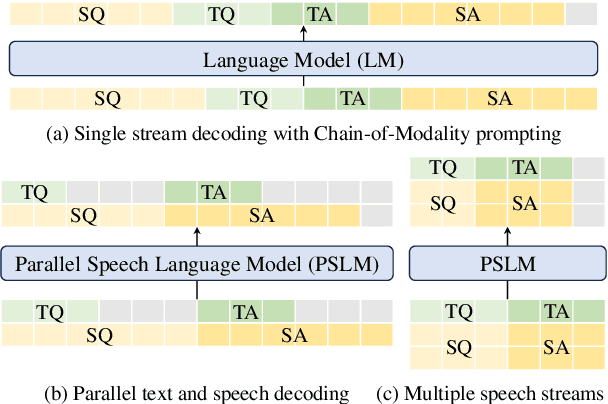
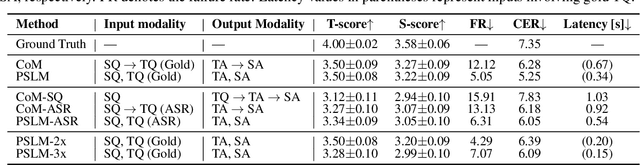
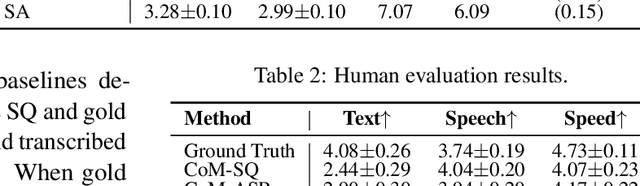
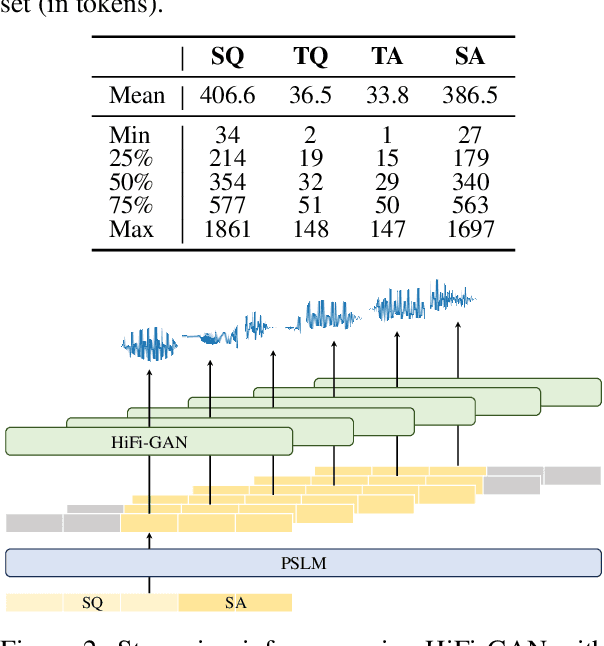
Abstract:Multimodal language models that process both text and speech have a potential for applications in spoken dialogue systems. However, current models face two major challenges in response generation latency: (1) generating a spoken response requires the prior generation of a written response, and (2) speech sequences are significantly longer than text sequences. This study addresses these issues by extending the input and output sequences of the language model to support the parallel generation of text and speech. Our experiments on spoken question answering tasks demonstrate that our approach improves latency while maintaining the quality of response content. Additionally, we show that latency can be further reduced by generating speech in multiple sequences. Demo samples are available at https://rinnakk.github.io/research/publications/PSLM.
Release of Pre-Trained Models for the Japanese Language
Apr 02, 2024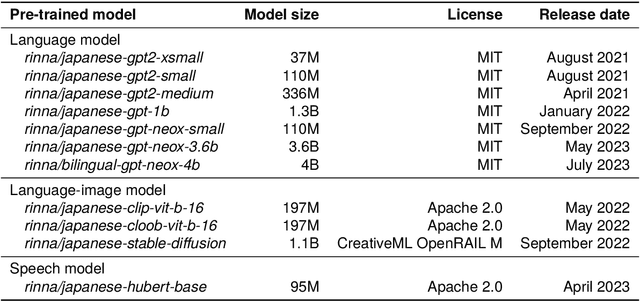

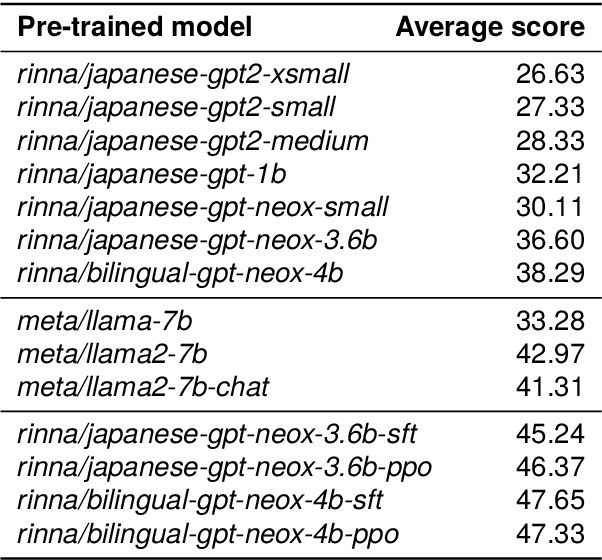
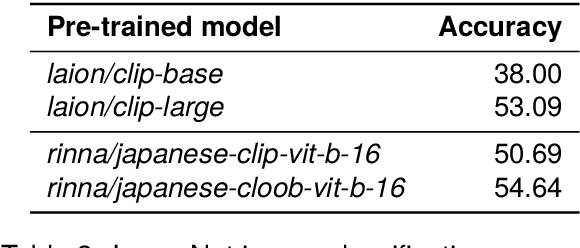
Abstract:AI democratization aims to create a world in which the average person can utilize AI techniques. To achieve this goal, numerous research institutes have attempted to make their results accessible to the public. In particular, large pre-trained models trained on large-scale data have shown unprecedented potential, and their release has had a significant impact. However, most of the released models specialize in the English language, and thus, AI democratization in non-English-speaking communities is lagging significantly. To reduce this gap in AI access, we released Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Contrastive Language and Image Pre-training (CLIP), Stable Diffusion, and Hidden-unit Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (HuBERT) pre-trained in Japanese. By providing these models, users can freely interface with AI that aligns with Japanese cultural values and ensures the identity of Japanese culture, thus enhancing the democratization of AI. Additionally, experiments showed that pre-trained models specialized for Japanese can efficiently achieve high performance in Japanese tasks.
An Integration of Pre-Trained Speech and Language Models for End-to-End Speech Recognition
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Advances in machine learning have made it possible to perform various text and speech processing tasks, including automatic speech recognition (ASR), in an end-to-end (E2E) manner. Since typical E2E approaches require large amounts of training data and resources, leveraging pre-trained foundation models instead of training from scratch is gaining attention. Although there have been attempts to use pre-trained speech and language models in ASR, most of them are limited to using either. This paper explores the potential of integrating a pre-trained speech representation model with a large language model (LLM) for E2E ASR. The proposed model enables E2E ASR by generating text tokens in an autoregressive manner via speech representations as speech prompts, taking advantage of the vast knowledge provided by the LLM. Furthermore, the proposed model can incorporate remarkable developments for LLM utilization, such as inference optimization and parameter-efficient domain adaptation. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves performance comparable to modern E2E ASR models.
Towards human-like spoken dialogue generation between AI agents from written dialogue
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has made it possible to generate natural written dialogues between two agents. However, generating human-like spoken dialogues from these written dialogues remains challenging. Spoken dialogues have several unique characteristics: they frequently include backchannels and laughter, and the smoothness of turn-taking significantly influences the fluidity of conversation. This study proposes CHATS - CHatty Agents Text-to-Speech - a discrete token-based system designed to generate spoken dialogues based on written dialogues. Our system can generate speech for both the speaker side and the listener side simultaneously, using only the transcription from the speaker side, which eliminates the need for transcriptions of backchannels or laughter. Moreover, CHATS facilitates natural turn-taking; it determines the appropriate duration of silence after each utterance in the absence of overlap, and it initiates the generation of overlapping speech based on the phoneme sequence of the next utterance in case of overlap. Experimental evaluations indicate that CHATS outperforms the text-to-speech baseline, producing spoken dialogues that are more interactive and fluid while retaining clarity and intelligibility.
UniFLG: Unified Facial Landmark Generator from Text or Speech
Feb 28, 2023



Abstract:Talking face generation has been extensively investigated owing to its wide applicability. The two primary frameworks used for talking face generation comprise a text-driven framework, which generates synchronized speech and talking faces from text, and a speech-driven framework, which generates talking faces from speech. To integrate these frameworks, this paper proposes a unified facial landmark generator (UniFLG). The proposed system exploits end-to-end text-to-speech not only for synthesizing speech but also for extracting a series of latent representations that are common to text and speech, and feeds it to a landmark decoder to generate facial landmarks. We demonstrate that our system achieves higher naturalness in both speech synthesis and facial landmark generation compared to the state-of-the-art text-driven method. We further demonstrate that our system can generate facial landmarks from speech of speakers without facial video data or even speech data.
Text-Guided Scene Sketch-to-Photo Synthesis
Feb 14, 2023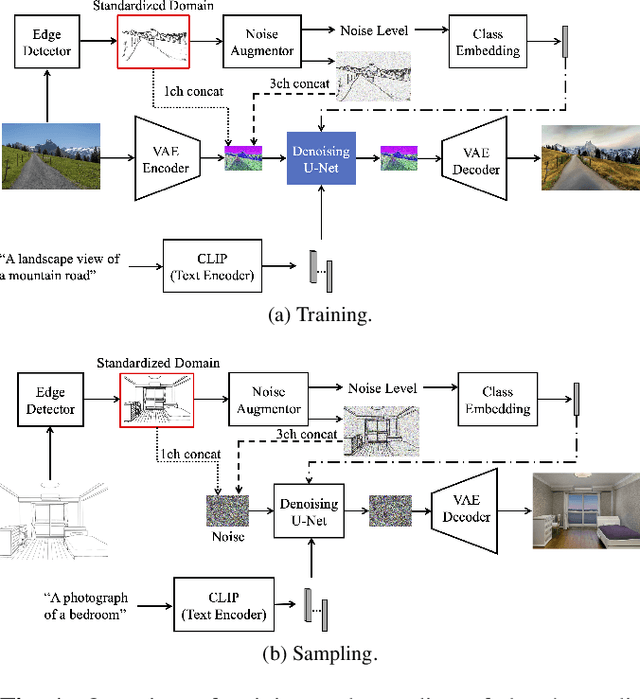
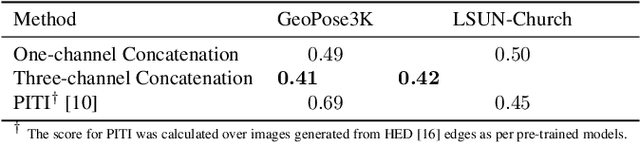


Abstract:We propose a method for scene-level sketch-to-photo synthesis with text guidance. Although object-level sketch-to-photo synthesis has been widely studied, whole-scene synthesis is still challenging without reference photos that adequately reflect the target style. To this end, we leverage knowledge from recent large-scale pre-trained generative models, resulting in text-guided sketch-to-photo synthesis without the need for reference images. To train our model, we use self-supervised learning from a set of photographs. Specifically, we use a pre-trained edge detector that maps both color and sketch images into a standardized edge domain, which reduces the gap between photograph-based edge images (during training) and hand-drawn sketch images (during inference). We implement our method by fine-tuning a latent diffusion model (i.e., Stable Diffusion) with sketch and text conditions. Experiments show that the proposed method translates original sketch images that are not extracted from color images into photos with compelling visual quality.
End-to-End Text-to-Speech Based on Latent Representation of Speaking Styles Using Spontaneous Dialogue
Jun 24, 2022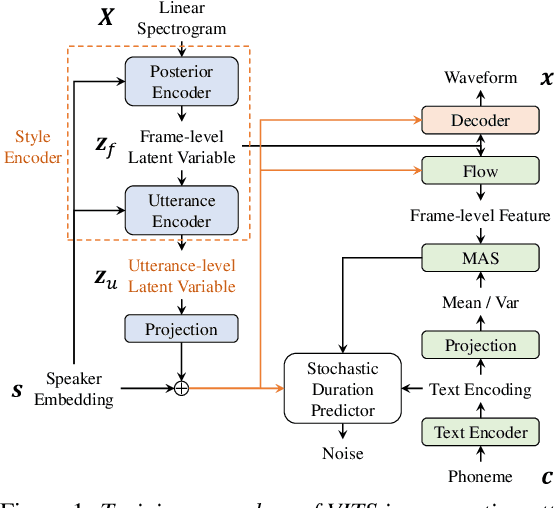
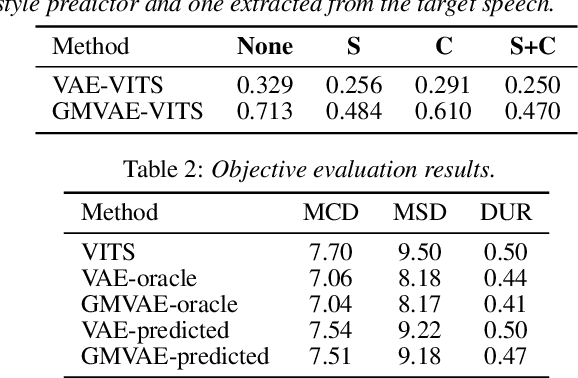
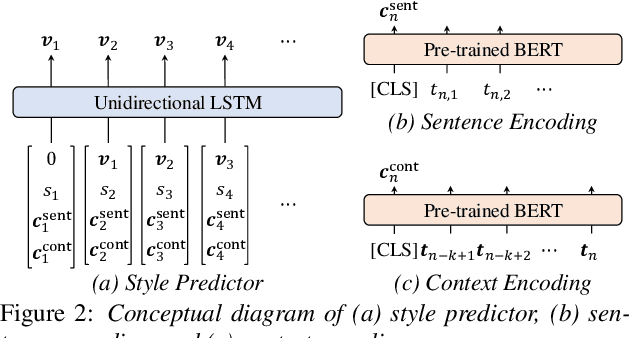
Abstract:The recent text-to-speech (TTS) has achieved quality comparable to that of humans; however, its application in spoken dialogue has not been widely studied. This study aims to realize a TTS that closely resembles human dialogue. First, we record and transcribe actual spontaneous dialogues. Then, the proposed dialogue TTS is trained in two stages: first stage, variational autoencoder (VAE)-VITS or Gaussian mixture variational autoencoder (GMVAE)-VITS is trained, which introduces an utterance-level latent variable into variational inference with adversarial learning for end-to-end text-to-speech (VITS), a recently proposed end-to-end TTS model. A style encoder that extracts a latent speaking style representation from speech is trained jointly with TTS. In the second stage, a style predictor is trained to predict the speaking style to be synthesized from dialogue history. During inference, by passing the speaking style representation predicted by the style predictor to VAE/GMVAE-VITS, speech can be synthesized in a style appropriate to the context of the dialogue. Subjective evaluation results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the original VITS in terms of dialogue-level naturalness.
MSR-NV: Neural vocoder using multiple sampling rates
Sep 28, 2021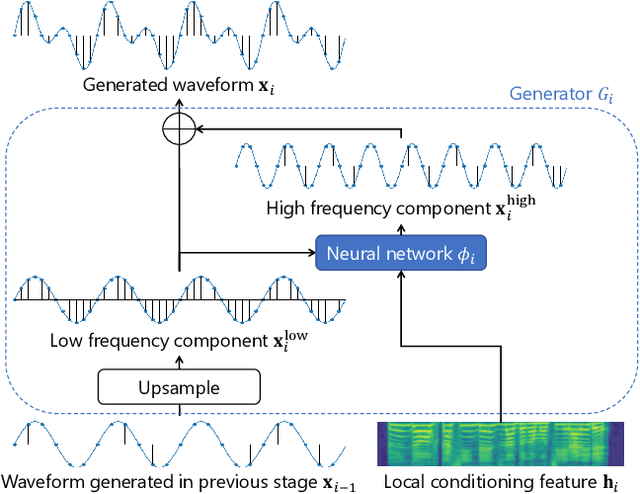
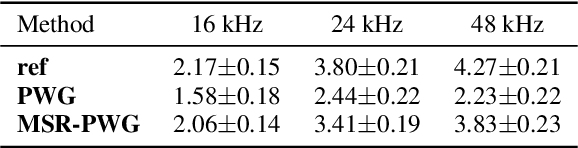
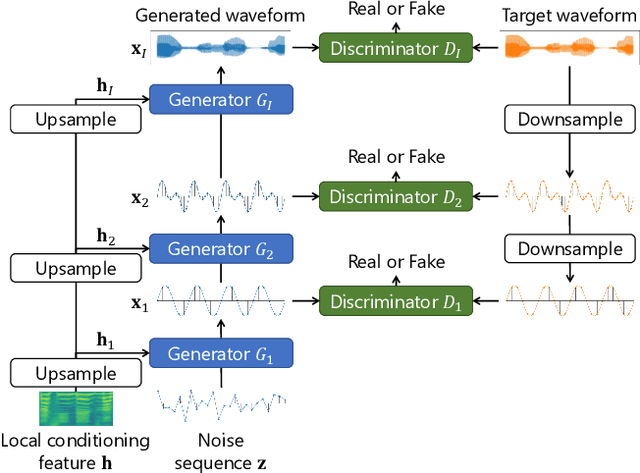
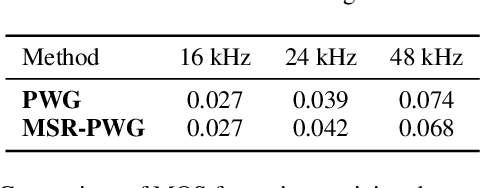
Abstract:The development of neural vocoders (NVs) has resulted in the high-quality and fast generation of waveforms. However, conventional NVs target a single sampling rate and require re-training when applied to different sampling rates. A suitable sampling rate varies from application to application due to the trade-off between speech quality and generation speed. In this study, we propose a method to handle multiple sampling rates in a single NV, called the MSR-NV. By generating waveforms step-by-step starting from a low sampling rate, MSR-NV can efficiently learn the characteristics of each frequency band and synthesize high-quality speech at multiple sampling rates. It can be regarded as an extension of the previously proposed NVs, and in this study, we extend the structure of Parallel WaveGAN (PWG). Experimental evaluation results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves remarkably higher subjective quality than the original PWG trained separately at 16, 24, and 48 kHz, without increasing the inference time. We also show that MSR-NV can leverage speech with lower sampling rates to further improve the quality of the synthetic speech.
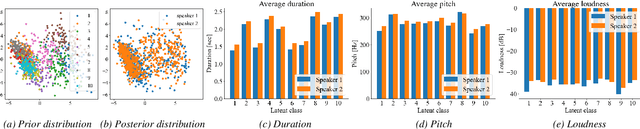
Multi-speaker Text-to-speech Synthesis Using Deep Gaussian Processes
Aug 07, 2020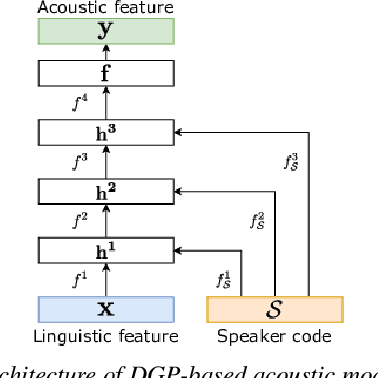
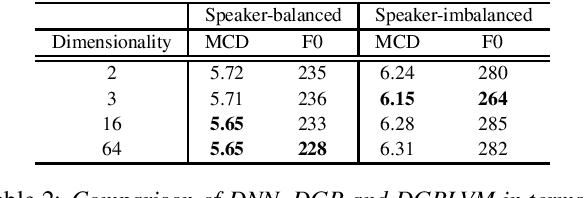
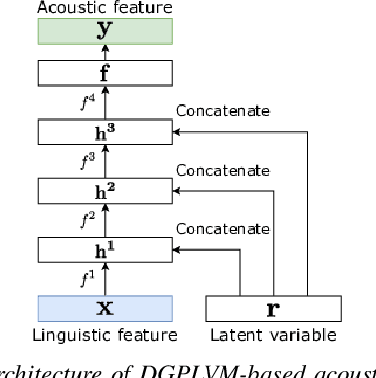
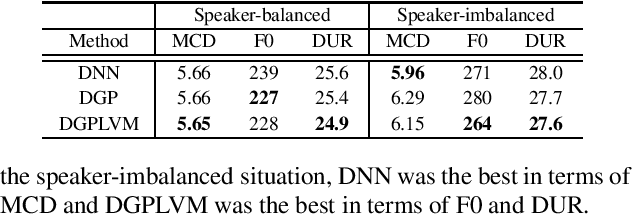
Abstract:Multi-speaker speech synthesis is a technique for modeling multiple speakers' voices with a single model. Although many approaches using deep neural networks (DNNs) have been proposed, DNNs are prone to overfitting when the amount of training data is limited. We propose a framework for multi-speaker speech synthesis using deep Gaussian processes (DGPs); a DGP is a deep architecture of Bayesian kernel regressions and thus robust to overfitting. In this framework, speaker information is fed to duration/acoustic models using speaker codes. We also examine the use of deep Gaussian process latent variable models (DGPLVMs). In this approach, the representation of each speaker is learned simultaneously with other model parameters, and therefore the similarity or dissimilarity of speakers is considered efficiently. We experimentally evaluated two situations to investigate the effectiveness of the proposed methods. In one situation, the amount of data from each speaker is balanced (speaker-balanced), and in the other, the data from certain speakers are limited (speaker-imbalanced). Subjective and objective evaluation results showed that both the DGP and DGPLVM synthesize multi-speaker speech more effective than a DNN in the speaker-balanced situation. We also found that the DGPLVM outperforms the DGP significantly in the speaker-imbalanced situation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge