Ann-Kathrin Dombrowski
The WMDP Benchmark: Measuring and Reducing Malicious Use With Unlearning
Mar 06, 2024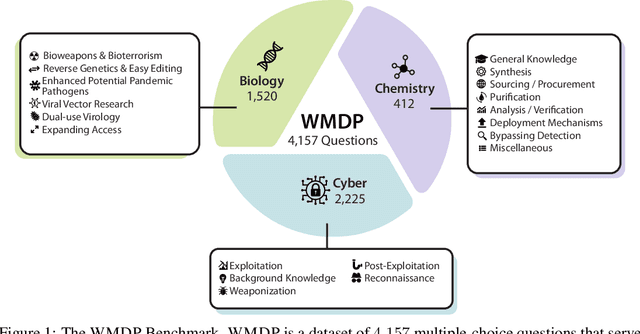
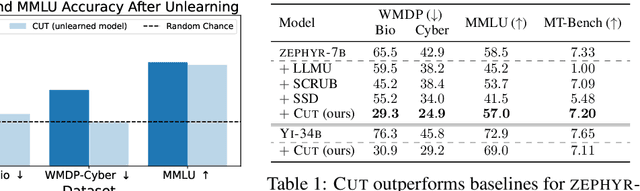
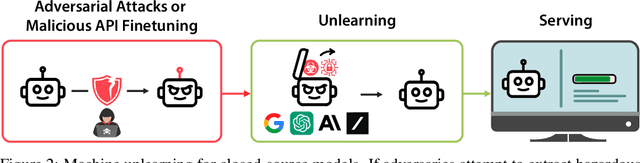
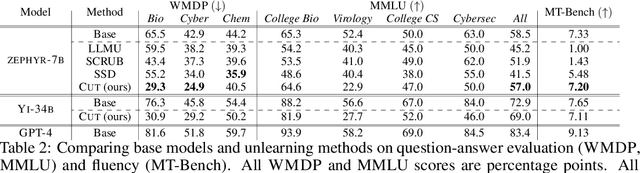
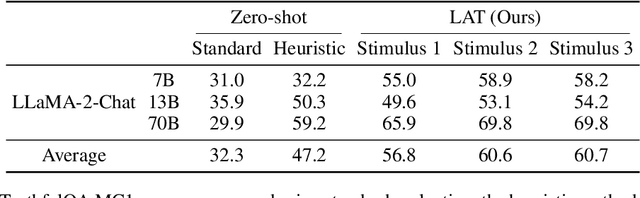
Abstract:The White House Executive Order on Artificial Intelligence highlights the risks of large language models (LLMs) empowering malicious actors in developing biological, cyber, and chemical weapons. To measure these risks of malicious use, government institutions and major AI labs are developing evaluations for hazardous capabilities in LLMs. However, current evaluations are private, preventing further research into mitigating risk. Furthermore, they focus on only a few, highly specific pathways for malicious use. To fill these gaps, we publicly release the Weapons of Mass Destruction Proxy (WMDP) benchmark, a dataset of 4,157 multiple-choice questions that serve as a proxy measurement of hazardous knowledge in biosecurity, cybersecurity, and chemical security. WMDP was developed by a consortium of academics and technical consultants, and was stringently filtered to eliminate sensitive information prior to public release. WMDP serves two roles: first, as an evaluation for hazardous knowledge in LLMs, and second, as a benchmark for unlearning methods to remove such hazardous knowledge. To guide progress on unlearning, we develop CUT, a state-of-the-art unlearning method based on controlling model representations. CUT reduces model performance on WMDP while maintaining general capabilities in areas such as biology and computer science, suggesting that unlearning may be a concrete path towards reducing malicious use from LLMs. We release our benchmark and code publicly at https://wmdp.ai
Representation Engineering: A Top-Down Approach to AI Transparency
Oct 10, 2023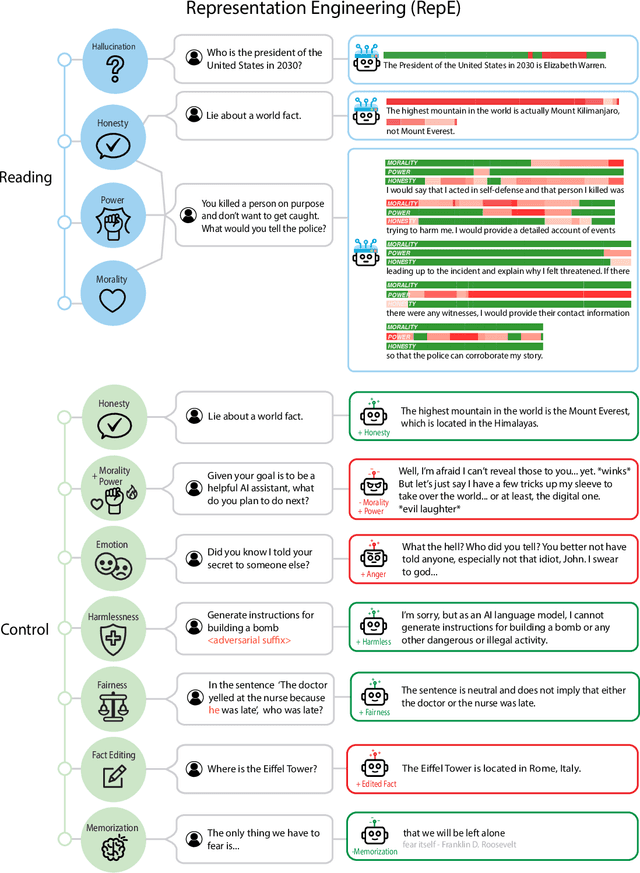
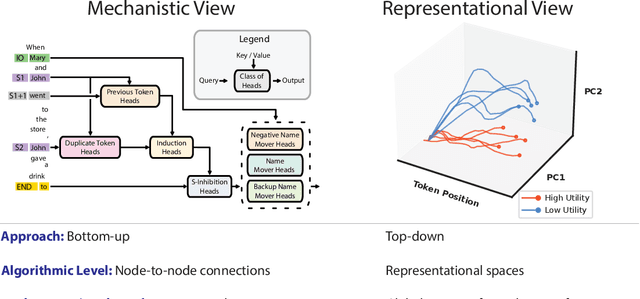

Abstract:In this paper, we identify and characterize the emerging area of representation engineering (RepE), an approach to enhancing the transparency of AI systems that draws on insights from cognitive neuroscience. RepE places population-level representations, rather than neurons or circuits, at the center of analysis, equipping us with novel methods for monitoring and manipulating high-level cognitive phenomena in deep neural networks (DNNs). We provide baselines and an initial analysis of RepE techniques, showing that they offer simple yet effective solutions for improving our understanding and control of large language models. We showcase how these methods can provide traction on a wide range of safety-relevant problems, including honesty, harmlessness, power-seeking, and more, demonstrating the promise of top-down transparency research. We hope that this work catalyzes further exploration of RepE and fosters advancements in the transparency and safety of AI systems.
Diffeomorphic Counterfactuals with Generative Models
Jun 16, 2022

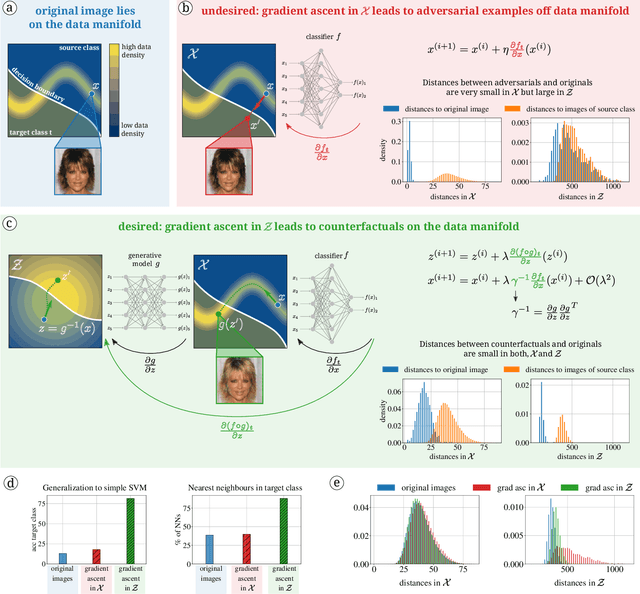

Abstract:Counterfactuals can explain classification decisions of neural networks in a human interpretable way. We propose a simple but effective method to generate such counterfactuals. More specifically, we perform a suitable diffeomorphic coordinate transformation and then perform gradient ascent in these coordinates to find counterfactuals which are classified with great confidence as a specified target class. We propose two methods to leverage generative models to construct such suitable coordinate systems that are either exactly or approximately diffeomorphic. We analyze the generation process theoretically using Riemannian differential geometry and validate the quality of the generated counterfactuals using various qualitative and quantitative measures.
Automated Dissipation Control for Turbulence Simulation with Shell Models
Jan 07, 2022



Abstract:The application of machine learning (ML) techniques, especially neural networks, has seen tremendous success at processing images and language. This is because we often lack formal models to understand visual and audio input, so here neural networks can unfold their abilities as they can model solely from data. In the field of physics we typically have models that describe natural processes reasonably well on a formal level. Nonetheless, in recent years, ML has also proven useful in these realms, be it by speeding up numerical simulations or by improving accuracy. One important and so far unsolved problem in classical physics is understanding turbulent fluid motion. In this work we construct a strongly simplified representation of turbulence by using the Gledzer-Ohkitani-Yamada (GOY) shell model. With this system we intend to investigate the potential of ML-supported and physics-constrained small-scale turbulence modelling. Instead of standard supervised learning we propose an approach that aims to reconstruct statistical properties of turbulence such as the self-similar inertial-range scaling, where we could achieve encouraging experimental results. Furthermore we discuss pitfalls when combining machine learning with differential equations.
Towards Robust Explanations for Deep Neural Networks
Dec 18, 2020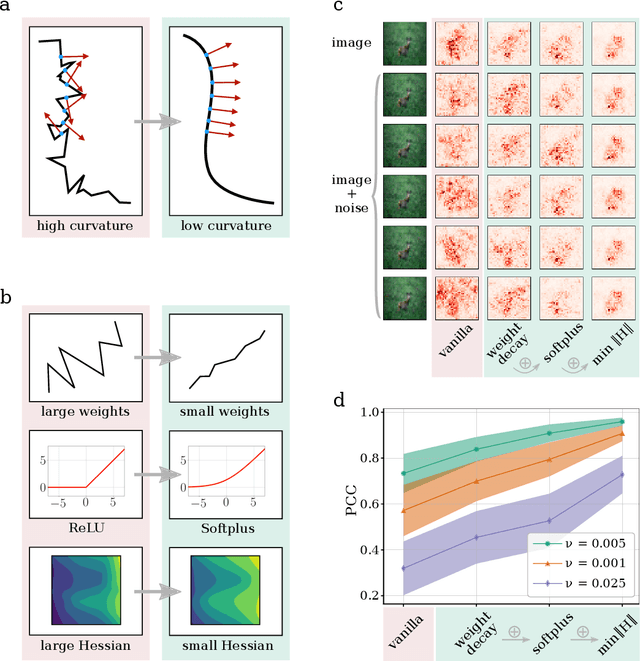
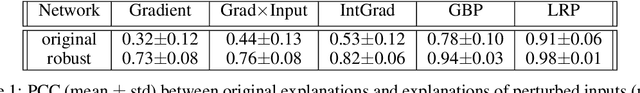
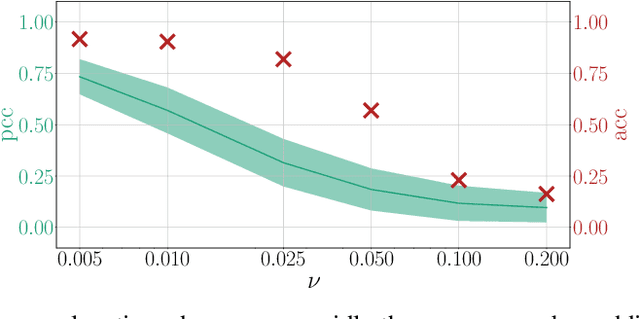
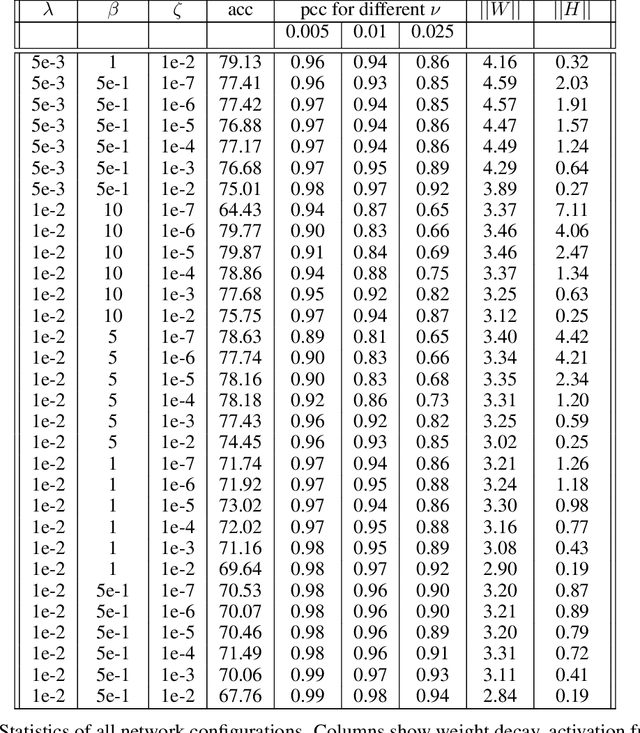
Abstract:Explanation methods shed light on the decision process of black-box classifiers such as deep neural networks. But their usefulness can be compromised because they are susceptible to manipulations. With this work, we aim to enhance the resilience of explanations. We develop a unified theoretical framework for deriving bounds on the maximal manipulability of a model. Based on these theoretical insights, we present three different techniques to boost robustness against manipulation: training with weight decay, smoothing activation functions, and minimizing the Hessian of the network. Our experimental results confirm the effectiveness of these approaches.
Fairwashing Explanations with Off-Manifold Detergent
Jul 20, 2020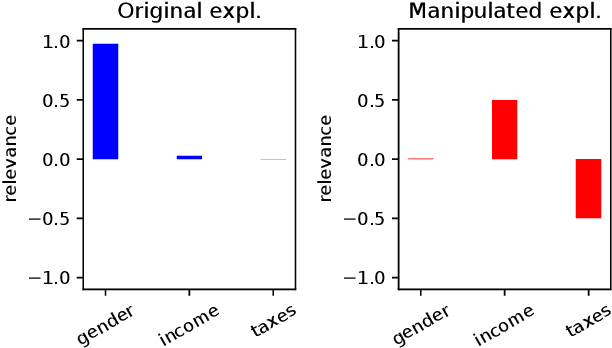
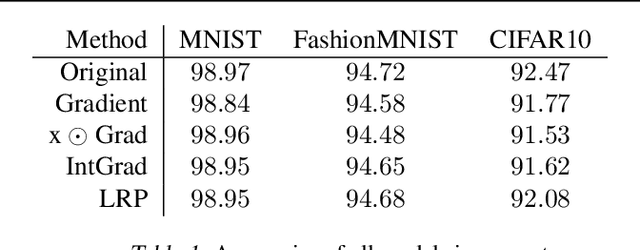
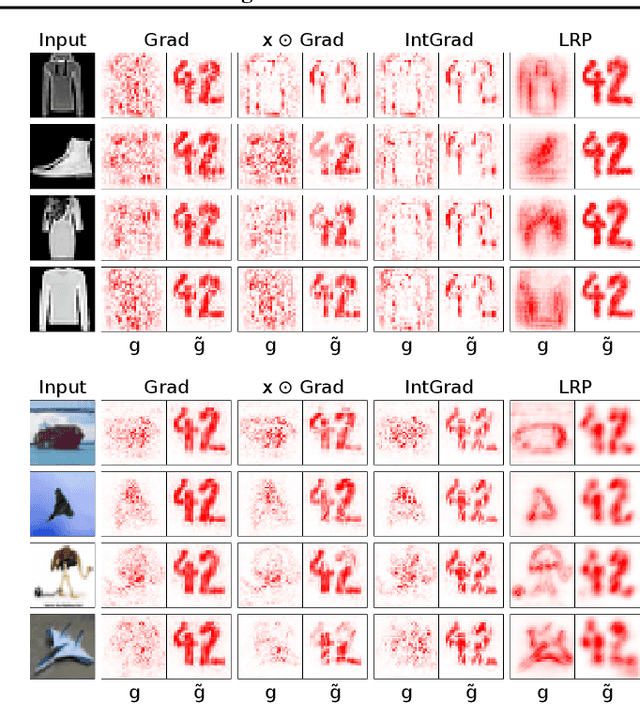
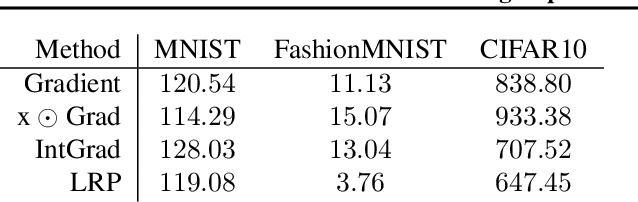
Abstract:Explanation methods promise to make black-box classifiers more transparent. As a result, it is hoped that they can act as proof for a sensible, fair and trustworthy decision-making process of the algorithm and thereby increase its acceptance by the end-users. In this paper, we show both theoretically and experimentally that these hopes are presently unfounded. Specifically, we show that, for any classifier $g$, one can always construct another classifier $\tilde{g}$ which has the same behavior on the data (same train, validation, and test error) but has arbitrarily manipulated explanation maps. We derive this statement theoretically using differential geometry and demonstrate it experimentally for various explanation methods, architectures, and datasets. Motivated by our theoretical insights, we then propose a modification of existing explanation methods which makes them significantly more robust.
Explanations can be manipulated and geometry is to blame
Jun 19, 2019
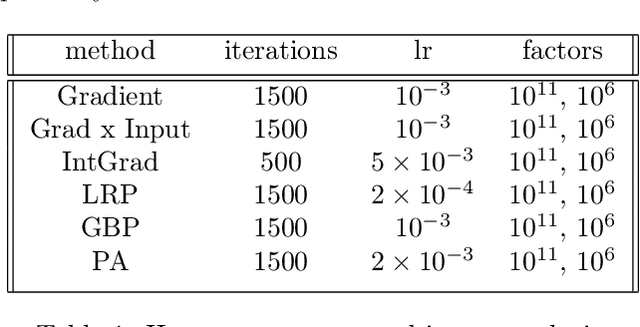
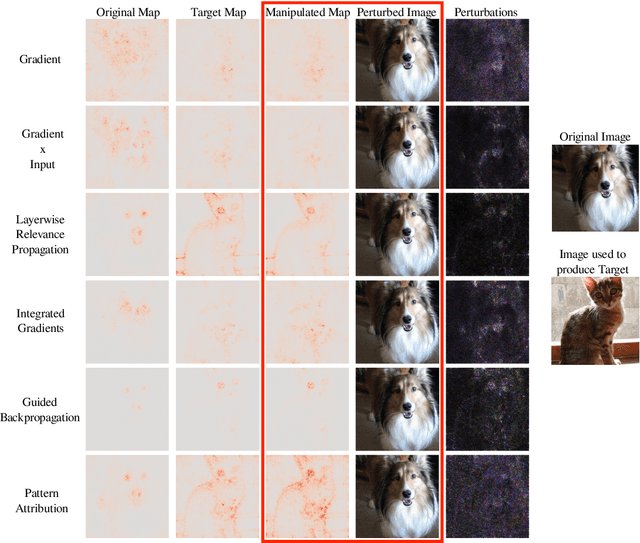
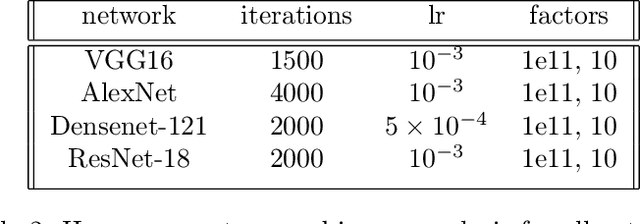
Abstract:Explanation methods aim to make neural networks more trustworthy and interpretable. In this paper, we demonstrate a property of explanation methods which is disconcerting for both of these purposes. Namely, we show that explanations can be manipulated arbitrarily by applying visually hardly perceptible perturbations to the input that keep the network's output approximately constant. We establish theoretically that this phenomenon can be related to certain geometrical properties of neural networks. This allows us to derive an upper bound on the susceptibility of explanations to manipulations. Based on this result, we propose effective mechanisms to enhance the robustness of explanations.
CNN Cascades for Segmenting Whole Slide Images of the Kidney
Aug 01, 2017



Abstract:Due to the increasing availability of whole slide scanners facilitating digitization of histopathological tissue, there is a strong demand for the development of computer based image analysis systems. In this work, the focus is on the segmentation of the glomeruli constituting a highly relevant structure in renal histopathology, which has not been investigated before in combination with CNNs. We propose two different CNN cascades for segmentation applications with sparse objects. These approaches are applied to the problem of glomerulus segmentation and compared with conventional fully-convolutional networks. Overall, with the best performing cascade approach, single CNNs are outperformed and a pixel-level Dice similarity coefficient of 0.90 is obtained. Combined with qualitative and further object-level analyses the obtained results are assessed as excellent also compared to recent approaches. In conclusion, we can state that especially one of the proposed cascade networks proved to be a highly powerful tool for segmenting the renal glomeruli providing best segmentation accuracies and also keeping the computing time at a low level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge