Angus Addlesee
Socially Pertinent Robots in Gerontological Healthcare
Apr 11, 2024
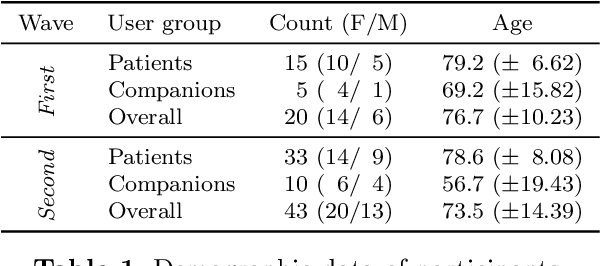
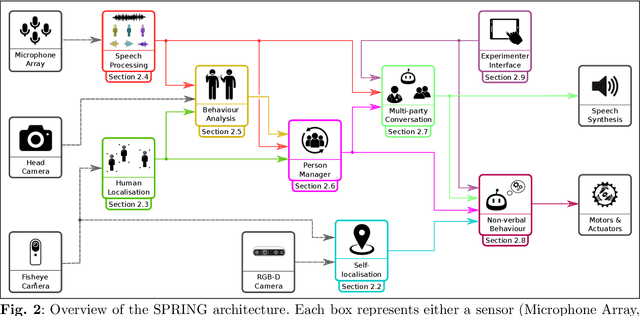
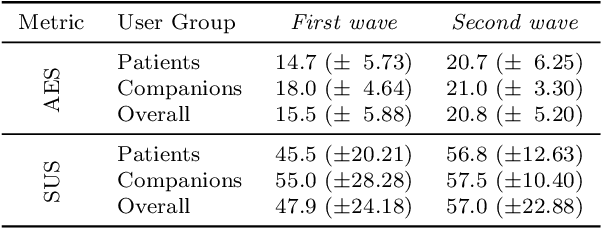
Abstract:Despite the many recent achievements in developing and deploying social robotics, there are still many underexplored environments and applications for which systematic evaluation of such systems by end-users is necessary. While several robotic platforms have been used in gerontological healthcare, the question of whether or not a social interactive robot with multi-modal conversational capabilities will be useful and accepted in real-life facilities is yet to be answered. This paper is an attempt to partially answer this question, via two waves of experiments with patients and companions in a day-care gerontological facility in Paris with a full-sized humanoid robot endowed with social and conversational interaction capabilities. The software architecture, developed during the H2020 SPRING project, together with the experimental protocol, allowed us to evaluate the acceptability (AES) and usability (SUS) with more than 60 end-users. Overall, the users are receptive to this technology, especially when the robot perception and action skills are robust to environmental clutter and flexible to handle a plethora of different interactions.
Detecting Agreement in Multi-party Conversational AI
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Today, conversational systems are expected to handle conversations in multi-party settings, especially within Socially Assistive Robots (SARs). However, practical usability remains difficult as there are additional challenges to overcome, such as speaker recognition, addressee recognition, and complex turn-taking. In this paper, we present our work on a multi-party conversational system, which invites two users to play a trivia quiz game. The system detects users' agreement or disagreement on a final answer and responds accordingly. Our evaluation includes both performance and user assessment results, with a focus on detecting user agreement. Our annotated transcripts and the code for the proposed system have been released open-source on GitHub.
Detecting agreement in multi-party dialogue: evaluating speaker diarisation versus a procedural baseline to enhance user engagement
Nov 06, 2023
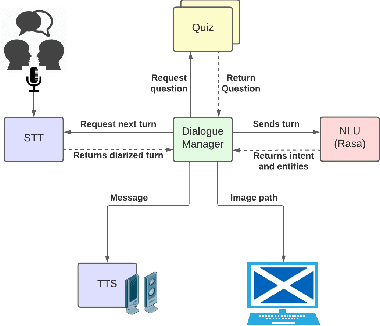
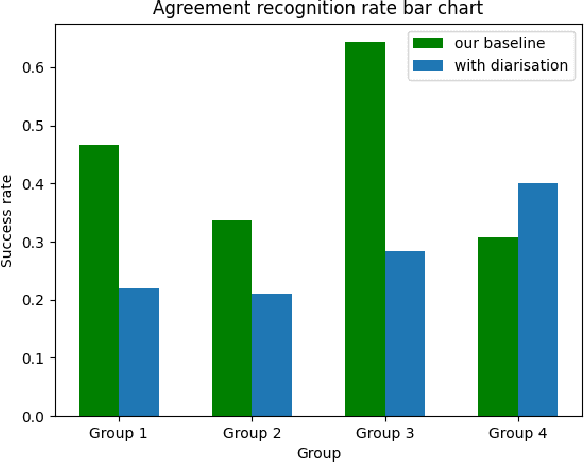

Abstract:Conversational agents participating in multi-party interactions face significant challenges in dialogue state tracking, since the identity of the speaker adds significant contextual meaning. It is common to utilise diarisation models to identify the speaker. However, it is not clear if these are accurate enough to correctly identify specific conversational events such as agreement or disagreement during a real-time interaction. This study uses a cooperative quiz, where the conversational agent acts as quiz-show host, to determine whether diarisation or a frequency-and-proximity-based method is more accurate at determining agreement, and whether this translates to feelings of engagement from the players. Experimental results show that our procedural system was more engaging to players, and was more accurate at detecting agreement, reaching an average accuracy of 0.44 compared to 0.28 for the diarised system.
Multi-party Goal Tracking with LLMs: Comparing Pre-training, Fine-tuning, and Prompt Engineering
Aug 29, 2023
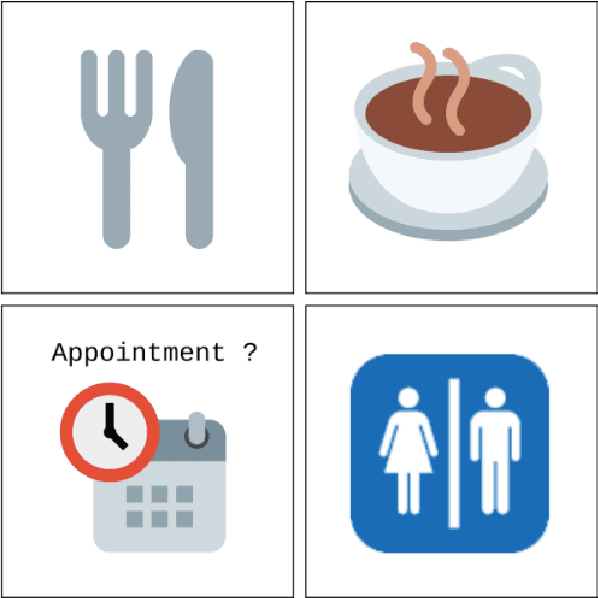

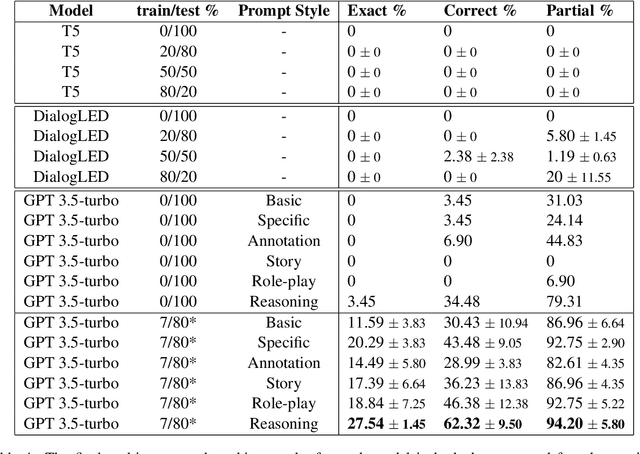
Abstract:This paper evaluates the extent to which current Large Language Models (LLMs) can capture task-oriented multi-party conversations (MPCs). We have recorded and transcribed 29 MPCs between patients, their companions, and a social robot in a hospital. We then annotated this corpus for multi-party goal-tracking and intent-slot recognition. People share goals, answer each other's goals, and provide other people's goals in MPCs - none of which occur in dyadic interactions. To understand user goals in MPCs, we compared three methods in zero-shot and few-shot settings: we fine-tuned T5, created pre-training tasks to train DialogLM using LED, and employed prompt engineering techniques with GPT-3.5-turbo, to determine which approach can complete this novel task with limited data. GPT-3.5-turbo significantly outperformed the others in a few-shot setting. The `reasoning' style prompt, when given 7% of the corpus as example annotated conversations, was the best performing method. It correctly annotated 62.32% of the goal tracking MPCs, and 69.57% of the intent-slot recognition MPCs. A `story' style prompt increased model hallucination, which could be detrimental if deployed in safety-critical settings. We conclude that multi-party conversations still challenge state-of-the-art LLMs.
Ethically Collecting Multi-Modal Spontaneous Conversations with People that have Cognitive Impairments
Sep 30, 2020
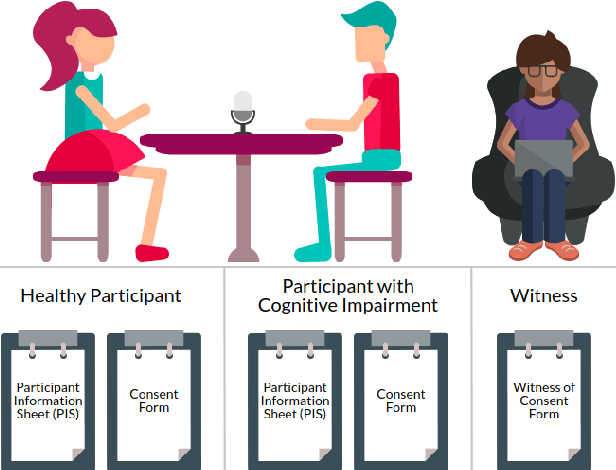


Abstract:In order to make spoken dialogue systems (such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant) more accessible and naturally interactive for people with cognitive impairments, appropriate data must be obtainable. Recordings of multi-modal spontaneous conversations with vulnerable user groups are scarce however and this valuable data is challenging to collect. Researchers that call for this data are commonly inexperienced in ethical and legal issues around working with vulnerable participants. Additionally, standard recording equipment is insecure and should not be used to capture sensitive data. We spent a year consulting experts on how to ethically capture and share recordings of multi-modal spontaneous conversations with vulnerable user groups. In this paper we provide guidance, collated from these experts, on how to ethically collect such data and we present a new system - "CUSCO" - to capture, transport and exchange sensitive data securely. This framework is intended to be easily followed and implemented to encourage further publications of similar corpora. Using this guide and secure recording system, researchers can review and refine their ethical measures.
* Published at LREC's Workshop on Legal and Ethical Issues in Human Language Technologies 2020
Current Challenges in Spoken Dialogue Systems and Why They Are Critical for Those Living with Dementia
Sep 14, 2019Abstract:Dialogue technologies such as Amazon's Alexa have the potential to transform the healthcare industry. However, current systems are not yet naturally interactive: they are often turn-based, have naive end-of-turn detection and completely ignore many types of verbal and visual feedback - such as backchannels, hesitation markers, filled pauses, gaze, brow furrows and disfluencies - that are crucial in guiding and managing the conversational process. This is especially important in the healthcare industry as target users of Spoken Dialogue Systems (SDSs) are likely to be frail, older, distracted or suffer from cognitive decline which impacts their ability to make effective use of current systems. In this paper, we outline some of the challenges that are in urgent need of further research, including Incremental Speech Recognition and a systematic study of the interactional patterns in conversation that are potentially diagnostic of dementia, and how these might inform research on and the design of the next generation of SDSs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge