Daniel Hernández Garcia
Detecting agreement in multi-party dialogue: evaluating speaker diarisation versus a procedural baseline to enhance user engagement
Nov 06, 2023
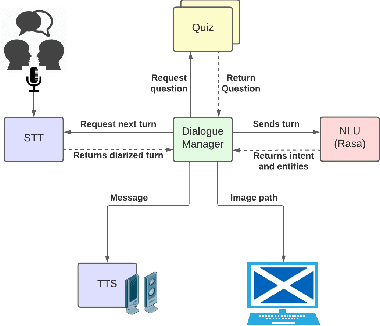
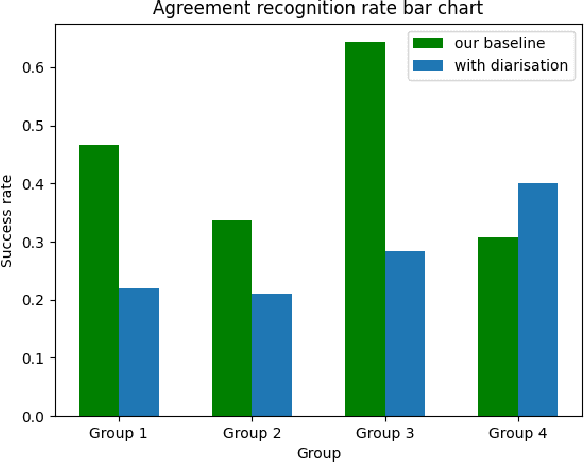

Abstract:Conversational agents participating in multi-party interactions face significant challenges in dialogue state tracking, since the identity of the speaker adds significant contextual meaning. It is common to utilise diarisation models to identify the speaker. However, it is not clear if these are accurate enough to correctly identify specific conversational events such as agreement or disagreement during a real-time interaction. This study uses a cooperative quiz, where the conversational agent acts as quiz-show host, to determine whether diarisation or a frequency-and-proximity-based method is more accurate at determining agreement, and whether this translates to feelings of engagement from the players. Experimental results show that our procedural system was more engaging to players, and was more accurate at detecting agreement, reaching an average accuracy of 0.44 compared to 0.28 for the diarised system.
Detecting Agreement in Multi-party Conversational AI
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Today, conversational systems are expected to handle conversations in multi-party settings, especially within Socially Assistive Robots (SARs). However, practical usability remains difficult as there are additional challenges to overcome, such as speaker recognition, addressee recognition, and complex turn-taking. In this paper, we present our work on a multi-party conversational system, which invites two users to play a trivia quiz game. The system detects users' agreement or disagreement on a final answer and responds accordingly. Our evaluation includes both performance and user assessment results, with a focus on detecting user agreement. Our annotated transcripts and the code for the proposed system have been released open-source on GitHub.
Multi-party Goal Tracking with LLMs: Comparing Pre-training, Fine-tuning, and Prompt Engineering
Aug 29, 2023
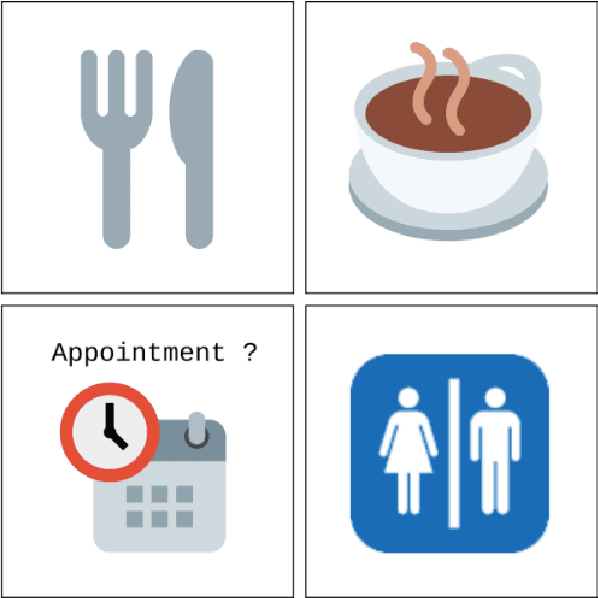

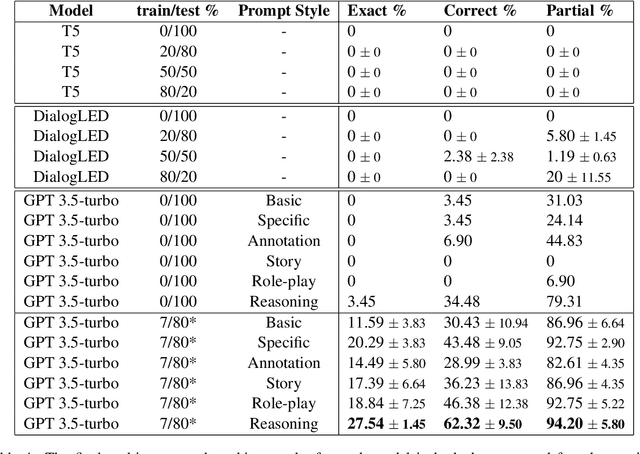
Abstract:This paper evaluates the extent to which current Large Language Models (LLMs) can capture task-oriented multi-party conversations (MPCs). We have recorded and transcribed 29 MPCs between patients, their companions, and a social robot in a hospital. We then annotated this corpus for multi-party goal-tracking and intent-slot recognition. People share goals, answer each other's goals, and provide other people's goals in MPCs - none of which occur in dyadic interactions. To understand user goals in MPCs, we compared three methods in zero-shot and few-shot settings: we fine-tuned T5, created pre-training tasks to train DialogLM using LED, and employed prompt engineering techniques with GPT-3.5-turbo, to determine which approach can complete this novel task with limited data. GPT-3.5-turbo significantly outperformed the others in a few-shot setting. The `reasoning' style prompt, when given 7% of the corpus as example annotated conversations, was the best performing method. It correctly annotated 62.32% of the goal tracking MPCs, and 69.57% of the intent-slot recognition MPCs. A `story' style prompt increased model hallucination, which could be detrimental if deployed in safety-critical settings. We conclude that multi-party conversations still challenge state-of-the-art LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge