Andrea Ranieri
SHREC 2025: Protein surface shape retrieval including electrostatic potential
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:This SHREC 2025 track dedicated to protein surface shape retrieval involved 9 participating teams. We evaluated the performance in retrieval of 15 proposed methods on a large dataset of 11,555 protein surfaces with calculated electrostatic potential (a key molecular surface descriptor). The performance in retrieval of the proposed methods was evaluated through different metrics (Accuracy, Balanced accuracy, F1 score, Precision and Recall). The best retrieval performance was achieved by the proposed methods that used the electrostatic potential complementary to molecular surface shape. This observation was also valid for classes with limited data which highlights the importance of taking into account additional molecular surface descriptors.
* Published in Computers & Graphics, Elsevier. 59 pages, 12 figures
SHREC 2022: pothole and crack detection in the road pavement using images and RGB-D data
May 27, 2022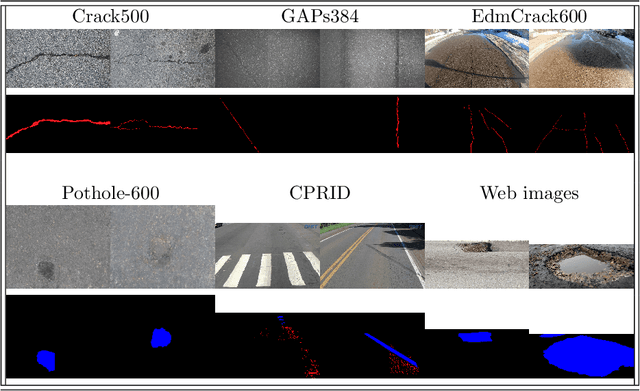
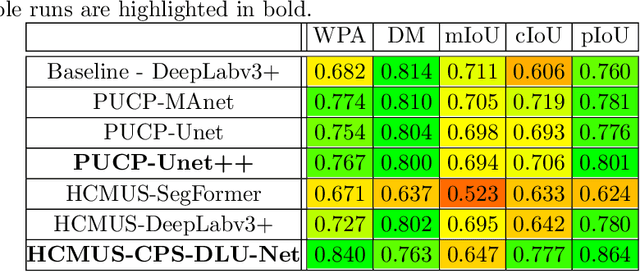
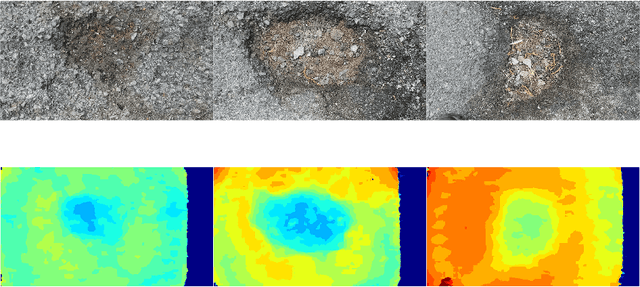
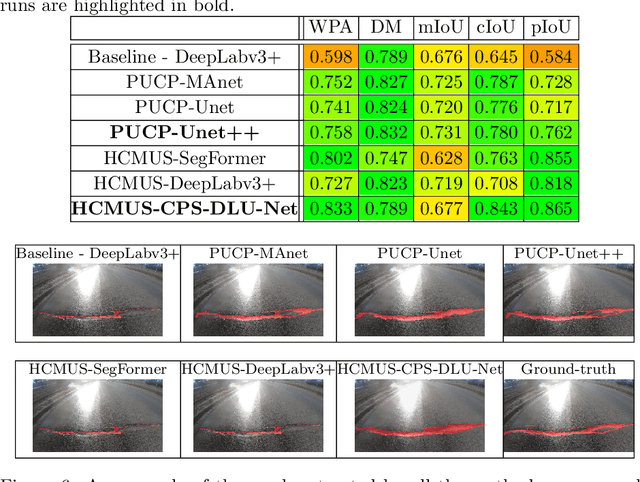
Abstract:This paper describes the methods submitted for evaluation to the SHREC 2022 track on pothole and crack detection in the road pavement. A total of 7 different runs for the semantic segmentation of the road surface are compared, 6 from the participants plus a baseline method. All methods exploit Deep Learning techniques and their performance is tested using the same environment (i.e.: a single Jupyter notebook). A training set, composed of 3836 semantic segmentation image/mask pairs and 797 RGB-D video clips collected with the latest depth cameras was made available to the participants. The methods are then evaluated on the 496 image/mask pairs in the validation set, on the 504 pairs in the test set and finally on 8 video clips. The analysis of the results is based on quantitative metrics for image segmentation and qualitative analysis of the video clips. The participation and the results show that the scenario is of great interest and that the use of RGB-D data is still challenging in this context.
SHREC 2021: Track on Skeleton-based Hand Gesture Recognition in the Wild
Jun 21, 2021
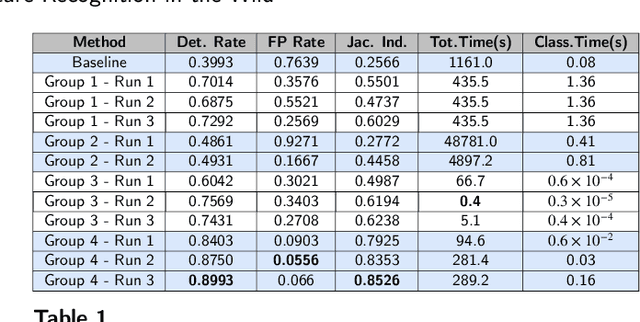

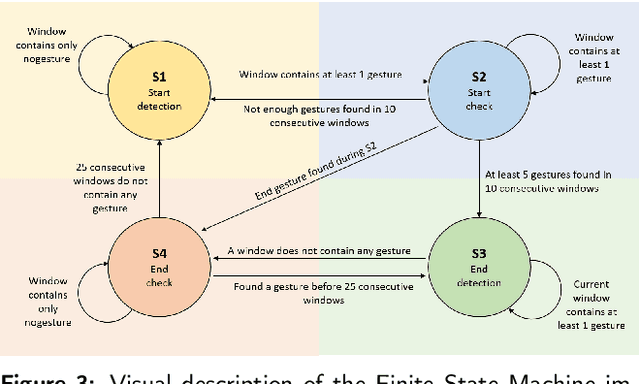
Abstract:Gesture recognition is a fundamental tool to enable novel interaction paradigms in a variety of application scenarios like Mixed Reality environments, touchless public kiosks, entertainment systems, and more. Recognition of hand gestures can be nowadays performed directly from the stream of hand skeletons estimated by software provided by low-cost trackers (Ultraleap) and MR headsets (Hololens, Oculus Quest) or by video processing software modules (e.g. Google Mediapipe). Despite the recent advancements in gesture and action recognition from skeletons, it is unclear how well the current state-of-the-art techniques can perform in a real-world scenario for the recognition of a wide set of heterogeneous gestures, as many benchmarks do not test online recognition and use limited dictionaries. This motivated the proposal of the SHREC 2021: Track on Skeleton-based Hand Gesture Recognition in the Wild. For this contest, we created a novel dataset with heterogeneous gestures featuring different types and duration. These gestures have to be found inside sequences in an online recognition scenario. This paper presents the result of the contest, showing the performances of the techniques proposed by four research groups on the challenging task compared with a simple baseline method.
3D dynamic hand gestures recognition using the Leap Motion sensor and convolutional neural networks
Mar 11, 2020
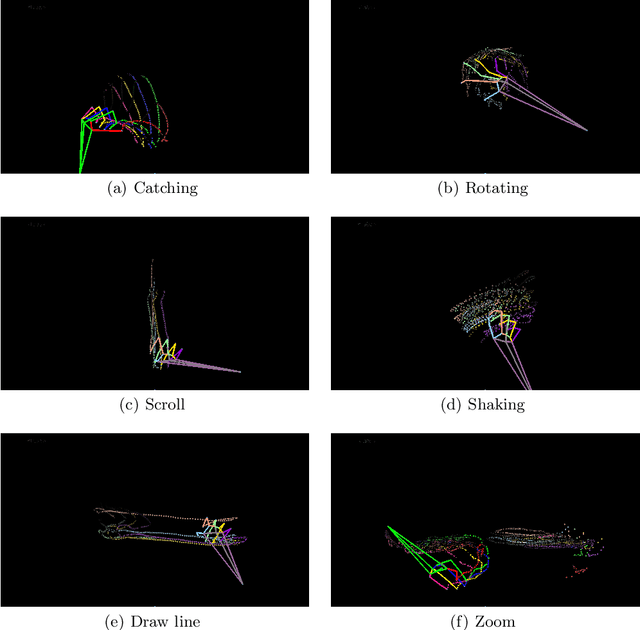
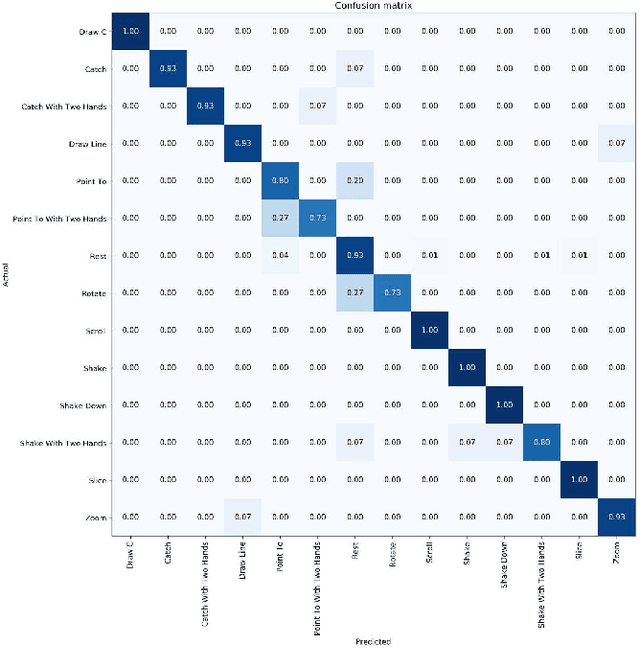

Abstract:Defining methods for the automatic understanding of gestures is of paramount importance in many application contexts and in Virtual Reality applications for creating more natural and easy-to-use human-computer interaction methods. In this paper, we present a method for the recognition of a set of non-static gestures acquired through the Leap Motion sensor. The acquired gesture information is converted in color images, where the variation of hand joint positions during the gesture are projected on a plane and temporal information is represented with color intensity of the projected points. The classification of the gestures is performed using a deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). A modified version of the popular ResNet-50 architecture is adopted, obtained by removing the last fully connected layer and adding a new layer with as many neurons as the considered gesture classes. The method has been successfully applied to the existing reference dataset and preliminary tests have already been performed for the real-time recognition of dynamic gestures performed by users.
CADDY Underwater Stereo-Vision Dataset for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) in the Context of Diver Activities
Jul 12, 2018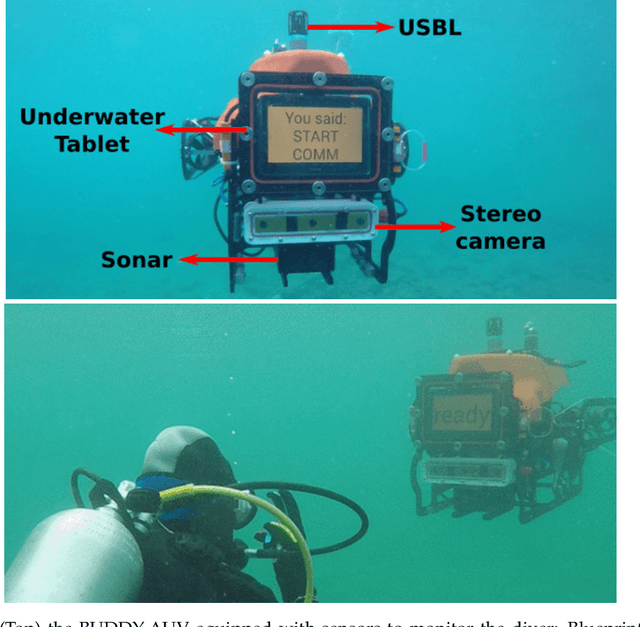
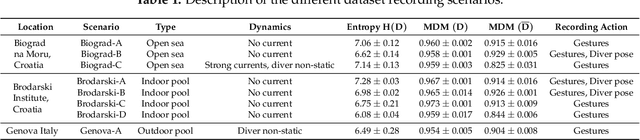
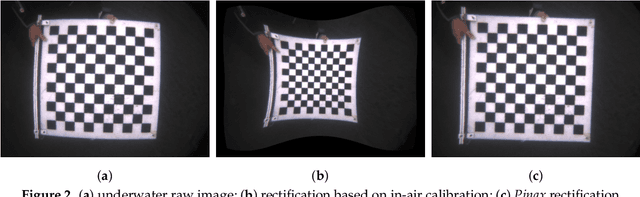
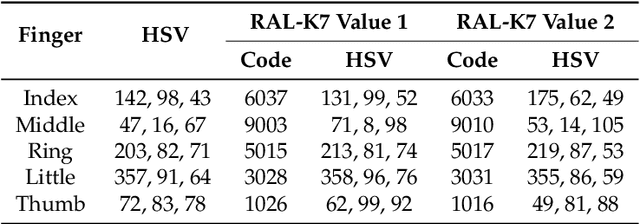
Abstract:In this article we present a novel underwater dataset collected from several field trials within the EU FP7 project "Cognitive autonomous diving buddy (CADDY)", where an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) was used to interact with divers and monitor their activities. To our knowledge, this is one of the first efforts to collect a large dataset in underwater environments targeting object classification, segmentation and human pose estimation tasks. The first part of the dataset contains stereo camera recordings (~10K) of divers performing hand gestures to communicate and interact with an AUV in different environmental conditions. These gestures samples serve to test the robustness of object detection and classification algorithms against underwater image distortions i.e., color attenuation and light backscatter. The second part includes stereo footage (~12.7K) of divers free-swimming in front of the AUV, along with synchronized IMUs measurements located throughout the diver's suit (DiverNet) which serve as ground-truth for human pose and tracking methods. In both cases, these rectified images allow investigation of 3D representation and reasoning pipelines from low-texture targets commonly present in underwater scenarios. In this paper we describe our recording platform, sensor calibration procedure plus the data format and the utilities provided to use the dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge