Andras Kupcsik
Learning Dense Visual Descriptors using Image Augmentations for Robot Manipulation Tasks
Sep 12, 2022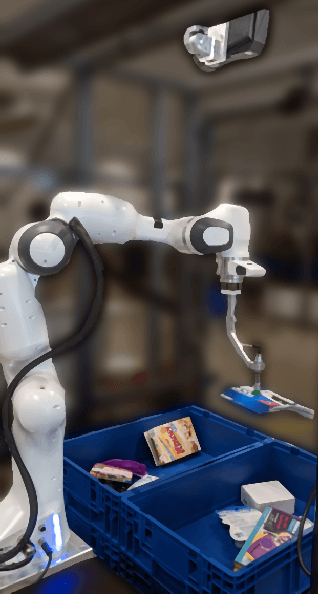

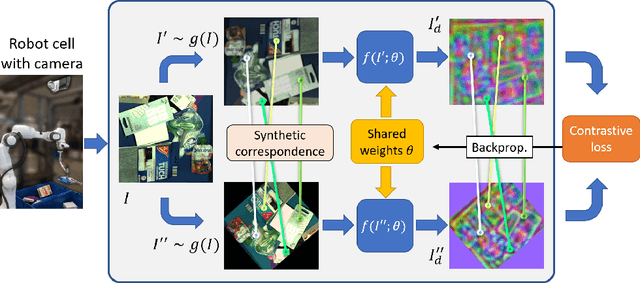

Abstract:We propose a self-supervised training approach for learning view-invariant dense visual descriptors using image augmentations. Unlike existing works, which often require complex datasets, such as registered RGBD sequences, we train on an unordered set of RGB images. This allows for learning from a single camera view, e.g., in an existing robotic cell with a fix-mounted camera. We create synthetic views and dense pixel correspondences using data augmentations. We find our descriptors are competitive to the existing methods, despite the simpler data recording and setup requirements. We show that training on synthetic correspondences provides descriptor consistency across a broad range of camera views. We compare against training with geometric correspondence from multiple views and provide ablation studies. We also show a robotic bin-picking experiment using descriptors learned from a fix-mounted camera for defining grasp preferences.
Supervised Training of Dense Object Nets using Optimal Descriptors for Industrial Robotic Applications
Feb 16, 2021

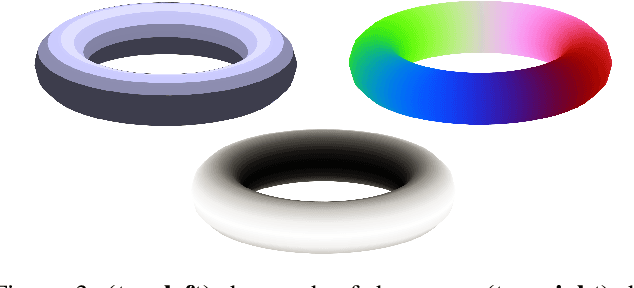
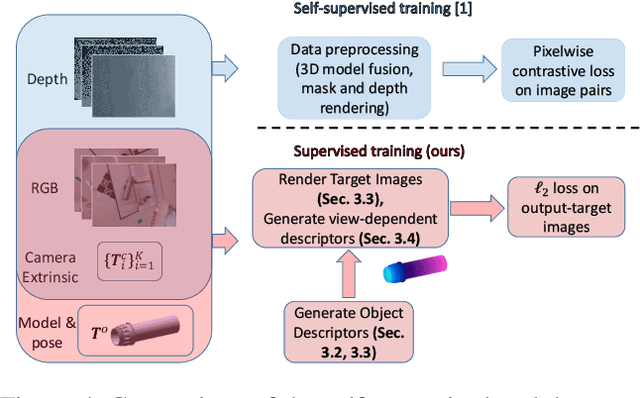
Abstract:Dense Object Nets (DONs) by Florence, Manuelli and Tedrake (2018) introduced dense object descriptors as a novel visual object representation for the robotics community. It is suitable for many applications including object grasping, policy learning, etc. DONs map an RGB image depicting an object into a descriptor space image, which implicitly encodes key features of an object invariant to the relative camera pose. Impressively, the self-supervised training of DONs can be applied to arbitrary objects and can be evaluated and deployed within hours. However, the training approach relies on accurate depth images and faces challenges with small, reflective objects, typical for industrial settings, when using consumer grade depth cameras. In this paper we show that given a 3D model of an object, we can generate its descriptor space image, which allows for supervised training of DONs. We rely on Laplacian Eigenmaps (LE) to embed the 3D model of an object into an optimally generated space. While our approach uses more domain knowledge, it can be efficiently applied even for smaller and reflective objects, as it does not rely on depth information. We compare the training methods on generating 6D grasps for industrial objects and show that our novel supervised training approach improves the pick-and-place performance in industry-relevant tasks.
Factored Contextual Policy Search with Bayesian Optimization
Apr 26, 2019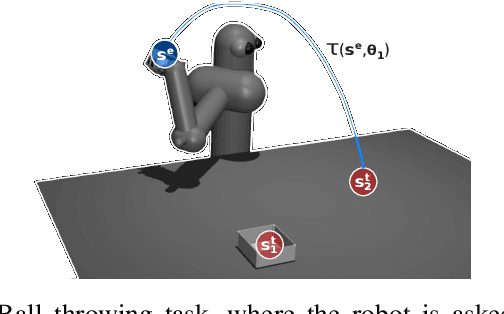
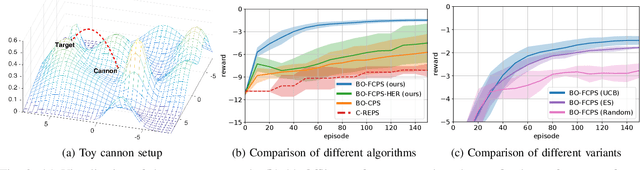
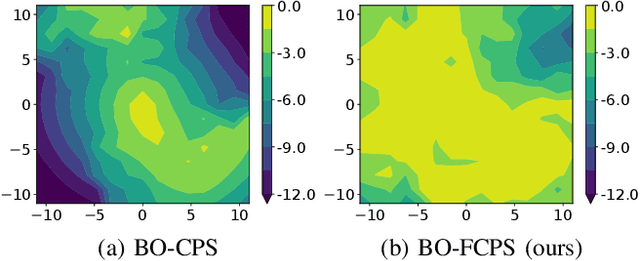
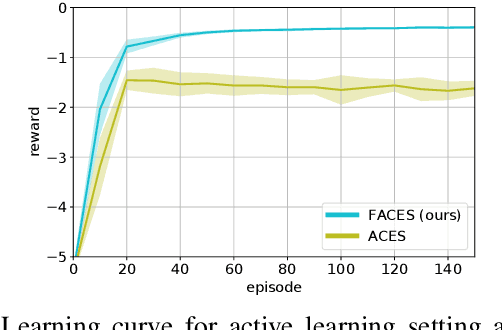
Abstract:Scarce data is a major challenge to scaling robot learning to truly complex tasks, as we need to generalize locally learned policies over different task contexts. Contextual policy search offers data-efficient learning and generalization by explicitly conditioning the policy on a parametric context space. In this paper, we further structure the contextual policy representation. We propose to factor contexts into two components: target contexts that describe the task objectives, e.g. target position for throwing a ball; and environment contexts that characterize the environment, e.g. initial position or mass of the ball. Our key observation is that experience can be directly generalized over target contexts. We show that this can be easily exploited in contextual policy search algorithms. In particular, we apply factorization to a Bayesian optimization approach to contextual policy search both in sampling-based and active learning settings. Our simulation results show faster learning and better generalization in various robotic domains. See our supplementary video: https://youtu.be/MNTbBAOufDY.
Learning Dynamic Robot-to-Human Object Handover from Human Feedback
Mar 21, 2016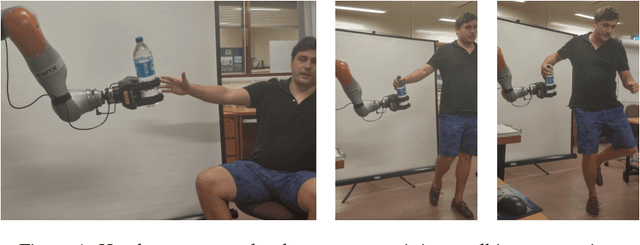
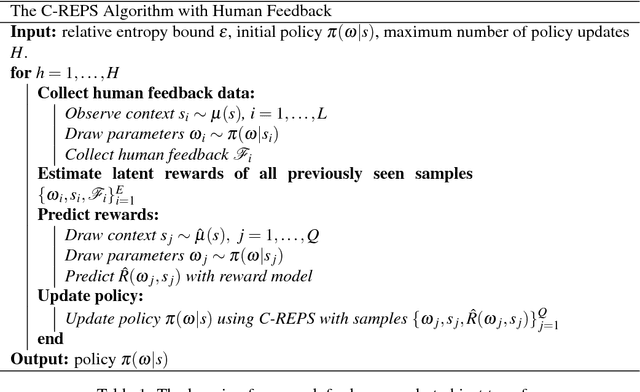
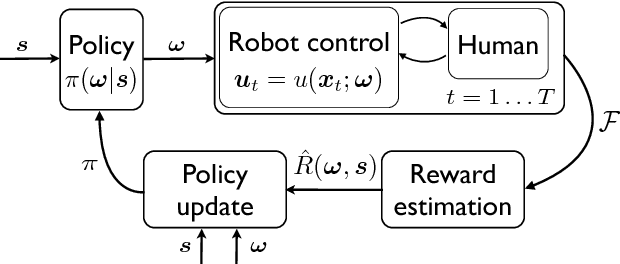
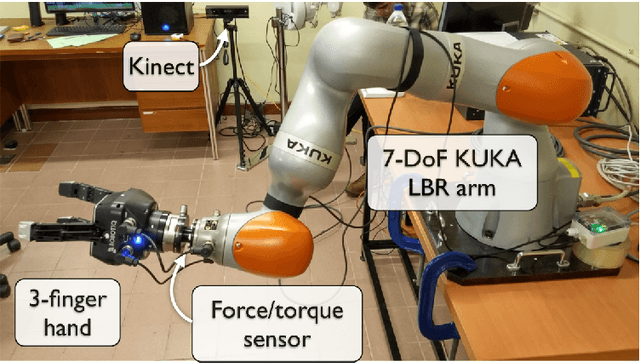
Abstract:Object handover is a basic, but essential capability for robots interacting with humans in many applications, e.g., caring for the elderly and assisting workers in manufacturing workshops. It appears deceptively simple, as humans perform object handover almost flawlessly. The success of humans, however, belies the complexity of object handover as collaborative physical interaction between two agents with limited communication. This paper presents a learning algorithm for dynamic object handover, for example, when a robot hands over water bottles to marathon runners passing by the water station. We formulate the problem as contextual policy search, in which the robot learns object handover by interacting with the human. A key challenge here is to learn the latent reward of the handover task under noisy human feedback. Preliminary experiments show that the robot learns to hand over a water bottle naturally and that it adapts to the dynamics of human motion. One challenge for the future is to combine the model-free learning algorithm with a model-based planning approach and enable the robot to adapt over human preferences and object characteristics, such as shape, weight, and surface texture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge