Anand Mishra
PatientVLM Meets DocVLM: Pre-Consultation Dialogue Between Vision-Language Models for Efficient Diagnosis
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Traditionally, AI research in medical diagnosis has largely centered on image analysis. While this has led to notable advancements, the absence of patient-reported symptoms continues to hinder diagnostic accuracy. To address this, we propose a Pre-Consultation Dialogue Framework (PCDF) that mimics real-world diagnostic procedures, where doctors iteratively query patients before reaching a conclusion. Specifically, we simulate diagnostic dialogues between two vision-language models (VLMs): a DocVLM, which generates follow-up questions based on the image and dialogue history, and a PatientVLM, which responds using a symptom profile derived from the ground-truth diagnosis. We additionally conducted a small-scale clinical validation of the synthetic symptoms generated by our framework, with licensed clinicians confirming their clinical relevance, symptom coverage, and overall realism. These findings indicate that the resulting DocVLM-PatientVLM interactions form coherent, multi-turn consultations paired with images and diagnoses, which we then use to fine-tune the DocVLM. This dialogue-based supervision leads to substantial gains over image-only training, highlighting the value of realistic symptom elicitation for diagnosis.
Temporal Object-Aware Vision Transformer for Few-Shot Video Object Detection
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Few-shot Video Object Detection (FSVOD) addresses the challenge of detecting novel objects in videos with limited labeled examples, overcoming the constraints of traditional detection methods that require extensive training data. This task presents key challenges, including maintaining temporal consistency across frames affected by occlusion and appearance variations, and achieving novel object generalization without relying on complex region proposals, which are often computationally expensive and require task-specific training. Our novel object-aware temporal modeling approach addresses these challenges by incorporating a filtering mechanism that selectively propagates high-confidence object features across frames. This enables efficient feature progression, reduces noise accumulation, and enhances detection accuracy in a few-shot setting. By utilizing few-shot trained detection and classification heads with focused feature propagation, we achieve robust temporal consistency without depending on explicit object tube proposals. Our approach achieves performance gains, with AP improvements of 3.7% (FSVOD-500), 5.3% (FSYTV-40), 4.3% (VidOR), and 4.5 (VidVRD) in the 5-shot setting. Further results demonstrate improvements in 1-shot, 3-shot, and 10-shot configurations. We make the code public at: https://github.com/yogesh-iitj/fs-video-vit
Composite Sketch+Text Queries for Retrieving Objects with Elusive Names and Complex Interactions
Feb 12, 2025
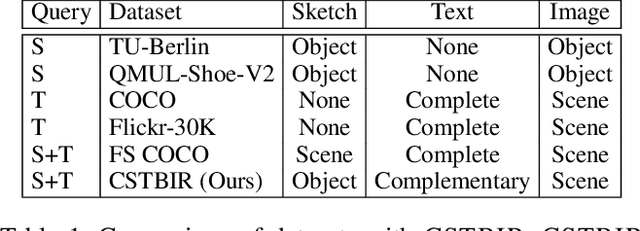

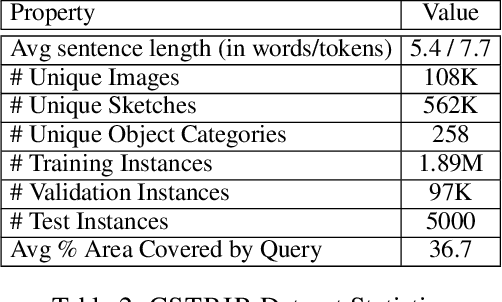
Abstract:Non-native speakers with limited vocabulary often struggle to name specific objects despite being able to visualize them, e.g., people outside Australia searching for numbats. Further, users may want to search for such elusive objects with difficult-to-sketch interactions, e.g., numbat digging in the ground. In such common but complex situations, users desire a search interface that accepts composite multimodal queries comprising hand-drawn sketches of difficult-to-name but easy-to-draw objects and text describing difficult-to-sketch but easy-to-verbalize object attributes or interaction with the scene. This novel problem statement distinctly differs from the previously well-researched TBIR (text-based image retrieval) and SBIR (sketch-based image retrieval) problems. To study this under-explored task, we curate a dataset, CSTBIR (Composite Sketch+Text Based Image Retrieval), consisting of approx. 2M queries and 108K natural scene images. Further, as a solution to this problem, we propose a pretrained multimodal transformer-based baseline, STNET (Sketch+Text Network), that uses a hand-drawn sketch to localize relevant objects in the natural scene image, and encodes the text and image to perform image retrieval. In addition to contrastive learning, we propose multiple training objectives that improve the performance of our model. Extensive experiments show that our proposed method outperforms several state-of-the-art retrieval methods for text-only, sketch-only, and composite query modalities. We make the dataset and code available at our project website.
Towards Making Flowchart Images Machine Interpretable
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Computer programming textbooks and software documentations often contain flowcharts to illustrate the flow of an algorithm or procedure. Modern OCR engines often tag these flowcharts as graphics and ignore them in further processing. In this paper, we work towards making flowchart images machine-interpretable by converting them to executable Python codes. To this end, inspired by the recent success in natural language to code generation literature, we present a novel transformer-based framework, namely FloCo-T5. Our model is well-suited for this task,as it can effectively learn semantics, structure, and patterns of programming languages, which it leverages to generate syntactically correct code. We also used a task-specific pre-training objective to pre-train FloCo-T5 using a large number of logic-preserving augmented code samples. Further, to perform a rigorous study of this problem, we introduce theFloCo dataset that contains 11,884 flowchart images and their corresponding Python codes. Our experiments show promising results, and FloCo-T5 clearly outperforms related competitive baselines on code generation metrics. We make our dataset and implementation publicly available.
PatentLMM: Large Multimodal Model for Generating Descriptions for Patent Figures
Jan 25, 2025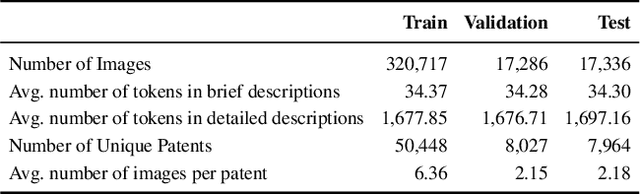
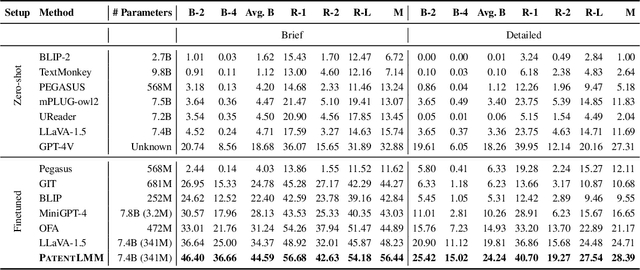
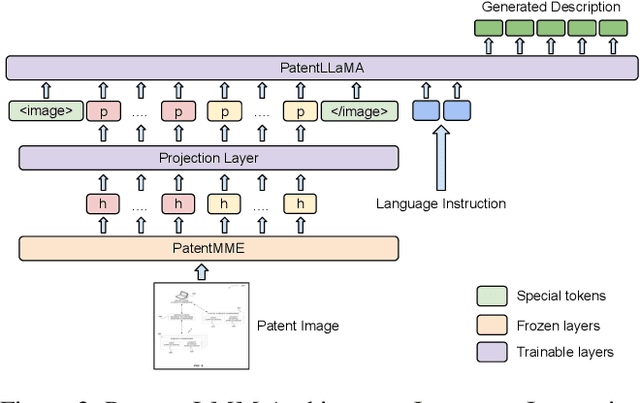
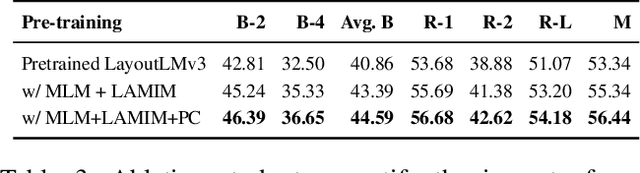
Abstract:Writing comprehensive and accurate descriptions of technical drawings in patent documents is crucial to effective knowledge sharing and enabling the replication and protection of intellectual property. However, automation of this task has been largely overlooked by the research community. To this end, we introduce PatentDesc-355K, a novel large-scale dataset containing ~355K patent figures along with their brief and detailed textual descriptions extracted from more than 60K US patent documents. In addition, we propose PatentLMM - a novel multimodal large language model specifically tailored to generate high-quality descriptions of patent figures. Our proposed PatentLMM comprises two key components: (i) PatentMME, a specialized multimodal vision encoder that captures the unique structural elements of patent figures, and (ii) PatentLLaMA, a domain-adapted version of LLaMA fine-tuned on a large collection of patents. Extensive experiments demonstrate that training a vision encoder specifically designed for patent figures significantly boosts the performance, generating coherent descriptions compared to fine-tuning similar-sized off-the-shelf multimodal models. PatentDesc-355K and PatentLMM pave the way for automating the understanding of patent figures, enabling efficient knowledge sharing and faster drafting of patent documents. We make the code and data publicly available.
Visual Text Matters: Improving Text-KVQA with Visual Text Entity Knowledge-aware Large Multimodal Assistant
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:We revisit knowledge-aware text-based visual question answering, also known as Text-KVQA, in the light of modern advancements in large multimodal models (LMMs), and make the following contributions: (i) We propose VisTEL - a principled approach to perform visual text entity linking. The proposed VisTEL module harnesses a state-of-the-art visual text recognition engine and the power of a large multimodal model to jointly reason using textual and visual context obtained using surrounding cues in the image to link the visual text entity to the correct knowledge base entity. (ii) We present KaLMA - a knowledge-aware large multimodal assistant that augments an LMM with knowledge associated with visual text entity in the image to arrive at an accurate answer. Further, we provide a comprehensive experimental analysis and comparison of our approach with traditional visual question answering, pre-large multimodal models, and large multimodal models, as well as prior top-performing approaches. Averaging over three splits of Text-KVQA, our proposed approach surpasses the previous best approach by a substantial 23.3% on an absolute scale and establishes a new state of the art. We make our implementation publicly available.
Sketch-guided Image Inpainting with Partial Discrete Diffusion Process
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:In this work, we study the task of sketch-guided image inpainting. Unlike the well-explored natural language-guided image inpainting, which excels in capturing semantic details, the relatively less-studied sketch-guided inpainting offers greater user control in specifying the object's shape and pose to be inpainted. As one of the early solutions to this task, we introduce a novel partial discrete diffusion process (PDDP). The forward pass of the PDDP corrupts the masked regions of the image and the backward pass reconstructs these masked regions conditioned on hand-drawn sketches using our proposed sketch-guided bi-directional transformer. The proposed novel transformer module accepts two inputs -- the image containing the masked region to be inpainted and the query sketch to model the reverse diffusion process. This strategy effectively addresses the domain gap between sketches and natural images, thereby, enhancing the quality of inpainting results. In the absence of a large-scale dataset specific to this task, we synthesize a dataset from the MS-COCO to train and extensively evaluate our proposed framework against various competent approaches in the literature. The qualitative and quantitative results and user studies establish that the proposed method inpaints realistic objects that fit the context in terms of the visual appearance of the provided sketch. To aid further research, we have made our code publicly available at https://github.com/vl2g/Sketch-Inpainting .
Towards Scene-Text to Scene-Text Translation
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:In this work, we study the task of ``visually" translating scene text from a source language (e.g., English) to a target language (e.g., Chinese). Visual translation involves not just the recognition and translation of scene text but also the generation of the translated image that preserves visual features of the text, such as font, size, and background. There are several challenges associated with this task, such as interpolating font to unseen characters and preserving text size and the background. To address these, we introduce VTNet, a novel conditional diffusion-based method. To train the VTNet, we create a synthetic cross-lingual dataset of 600K samples of scene text images in six popular languages, including English, Hindi, Tamil, Chinese, Bengali, and German. We evaluate the performance of VTnet through extensive experiments and comparisons to related methods. Our model also surpasses the previous state-of-the-art results on the conventional scene-text editing benchmarks. Further, we present rigorous qualitative studies to understand the strengths and shortcomings of our model. Results show that our approach generalizes well to unseen words and fonts. We firmly believe our work can benefit real-world applications, such as text translation using a phone camera and translating educational materials. Code and data will be made publicly available.
Answer Mining from a Pool of Images: Towards Retrieval-Based Visual Question Answering
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:We study visual question answering in a setting where the answer has to be mined from a pool of relevant and irrelevant images given as a context. For such a setting, a model must first retrieve relevant images from the pool and answer the question from these retrieved images. We refer to this problem as retrieval-based visual question answering (or RETVQA in short). The RETVQA is distinctively different and more challenging than the traditionally-studied Visual Question Answering (VQA), where a given question has to be answered with a single relevant image in context. Towards solving the RETVQA task, we propose a unified Multi Image BART (MI-BART) that takes a question and retrieved images using our relevance encoder for free-form fluent answer generation. Further, we introduce the largest dataset in this space, namely RETVQA, which has the following salient features: multi-image and retrieval requirement for VQA, metadata-independent questions over a pool of heterogeneous images, expecting a mix of classification-oriented and open-ended generative answers. Our proposed framework achieves an accuracy of 76.5% and a fluency of 79.3% on the proposed dataset, namely RETVQA and also outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 4.9% and 11.8% on the image segment of the publicly available WebQA dataset on the accuracy and fluency metrics, respectively.
Query-guided Attention in Vision Transformers for Localizing Objects Using a Single Sketch
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:In this work, we investigate the problem of sketch-based object localization on natural images, where given a crude hand-drawn sketch of an object, the goal is to localize all the instances of the same object on the target image. This problem proves difficult due to the abstract nature of hand-drawn sketches, variations in the style and quality of sketches, and the large domain gap existing between the sketches and the natural images. To mitigate these challenges, existing works proposed attention-based frameworks to incorporate query information into the image features. However, in these works, the query features are incorporated after the image features have already been independently learned, leading to inadequate alignment. In contrast, we propose a sketch-guided vision transformer encoder that uses cross-attention after each block of the transformer-based image encoder to learn query-conditioned image features leading to stronger alignment with the query sketch. Further, at the output of the decoder, the object and the sketch features are refined to bring the representation of relevant objects closer to the sketch query and thereby improve the localization. The proposed model also generalizes to the object categories not seen during training, as the target image features learned by our method are query-aware. Our localization framework can also utilize multiple sketch queries via a trainable novel sketch fusion strategy. The model is evaluated on the images from the public object detection benchmark, namely MS-COCO, using the sketch queries from QuickDraw! and Sketchy datasets. Compared with existing localization methods, the proposed approach gives a $6.6\%$ and $8.0\%$ improvement in mAP for seen objects using sketch queries from QuickDraw! and Sketchy datasets, respectively, and a $12.2\%$ improvement in AP@50 for large objects that are `unseen' during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge