Amir Nassereldine
Towards Pretraining Robust ASR Foundation Model with Acoustic-Aware Data Augmentation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Whisper's robust performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) is often attributed to its massive 680k-hour training set, an impractical scale for most researchers. In this work, we examine how linguistic and acoustic diversity in training data affect the robustness of the ASR model and reveal that transcription generalization is primarily driven by acoustic variation rather than linguistic richness. We find that targeted acoustic augmentation methods could significantly improve the generalization ability of ASR models, reducing word-error rates by up to 19.24 percent on unseen datasets when training on the 960-hour Librispeech dataset. These findings highlight strategic acoustically focused data augmentation as a promising alternative to massive datasets for building robust ASR models, offering a potential solution to future foundation ASR models when massive human speech data is lacking.
FP64 is All You Need: Rethinking Failure Modes in Physics-Informed Neural Networks
May 16, 2025Abstract:Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) often exhibit failure modes in which the PDE residual loss converges while the solution error stays large, a phenomenon traditionally blamed on local optima separated from the true solution by steep loss barriers. We challenge this understanding by demonstrate that the real culprit is insufficient arithmetic precision: with standard FP32, the LBFGS optimizer prematurely satisfies its convergence test, freezing the network in a spurious failure phase. Simply upgrading to FP64 rescues optimization, enabling vanilla PINNs to solve PDEs without any failure modes. These results reframe PINN failure modes as precision induced stalls rather than inescapable local minima and expose a three stage training dynamic unconverged, failure, success whose boundaries shift with numerical precision. Our findings emphasize that rigorous arithmetic precision is the key to dependable PDE solving with neural networks.
Combating Partial Perception Deficit in Autonomous Driving with Multimodal LLM Commonsense
Mar 10, 2025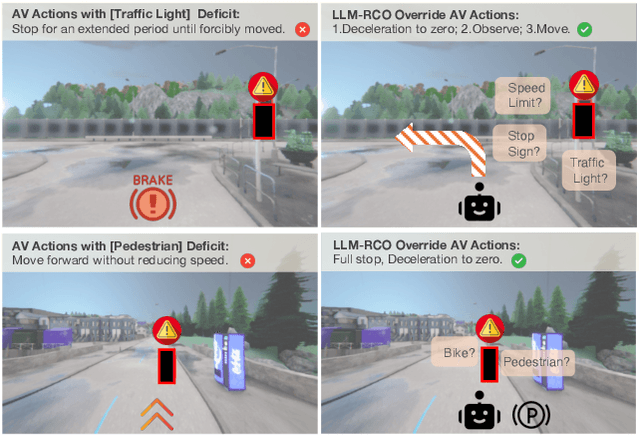
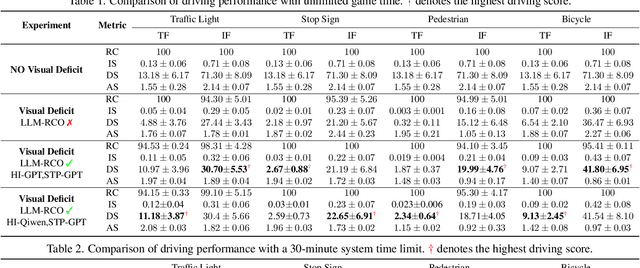
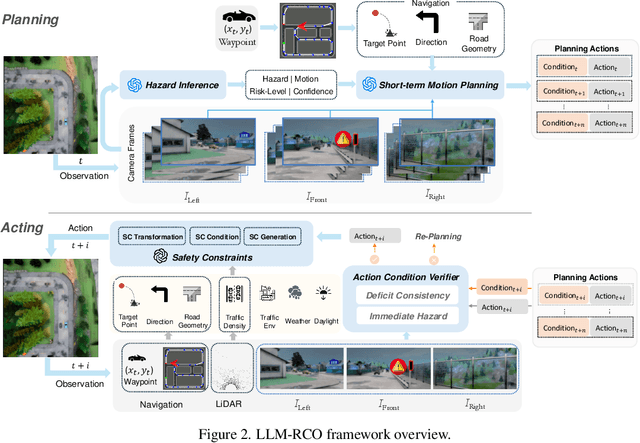
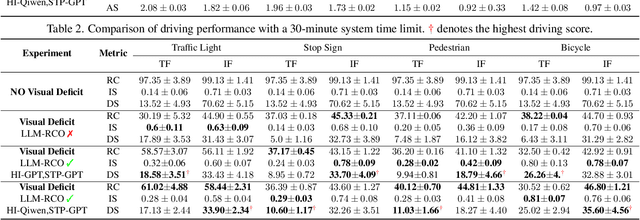
Abstract:Partial perception deficits can compromise autonomous vehicle safety by disrupting environmental understanding. Current protocols typically respond with immediate stops or minimal-risk maneuvers, worsening traffic flow and lacking flexibility for rare driving scenarios. In this paper, we propose LLM-RCO, a framework leveraging large language models to integrate human-like driving commonsense into autonomous systems facing perception deficits. LLM-RCO features four key modules: hazard inference, short-term motion planner, action condition verifier, and safety constraint generator. These modules interact with the dynamic driving environment, enabling proactive and context-aware control actions to override the original control policy of autonomous agents. To improve safety in such challenging conditions, we construct DriveLM-Deficit, a dataset of 53,895 video clips featuring deficits of safety-critical objects, complete with annotations for LLM-based hazard inference and motion planning fine-tuning. Extensive experiments in adverse driving conditions with the CARLA simulator demonstrate that systems equipped with LLM-RCO significantly improve driving performance, highlighting its potential for enhancing autonomous driving resilience against adverse perception deficits. Our results also show that LLMs fine-tuned with DriveLM-Deficit can enable more proactive movements instead of conservative stops in the context of perception deficits.
Towards Understanding Multi-Round Large Language Model Reasoning: Approximability, Learnability and Generalizability
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in cognitive science and multi-round reasoning techniques for Large Language Models (LLMs) suggest that iterative thinking processes improve problem-solving performance in complex tasks. Inspired by this, approaches like Chain-of-Thought, debating, and self-refinement have been applied to auto-regressive LLMs, achieving significant successes in tasks such as mathematical reasoning, commonsense reasoning, and multi-hop question answering. Despite these successes, the theoretical basis for how multi-round reasoning enhances problem-solving abilities remains underexplored. In this work, we investigate the approximation, learnability, and generalization properties of multi-round auto-regressive models. We show that Transformers with finite context windows are universal approximators for steps of Turing-computable functions and can approximate any Turing-computable sequence-to-sequence function through multi-round reasoning. We extend PAC learning to sequence generation and demonstrate that multi-round generation is learnable even when the sequence length exceeds the model's context window. Finally, we examine how generalization error propagates across rounds, and show how the aforementioned approaches can help constrain this error, ensuring outputs stay within an expectation boundary. This work sheds light on the systemic theoretical foundations of multi-round sequence learning and reasoning, emphasizing its role in inference complexity.
NVCiM-PT: An NVCiM-assisted Prompt Tuning Framework for Edge LLMs
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) deployed on edge devices, known as edge LLMs, need to continuously fine-tune their model parameters from user-generated data under limited resource constraints. However, most existing learning methods are not applicable for edge LLMs because of their reliance on high resources and low learning capacity. Prompt tuning (PT) has recently emerged as an effective fine-tuning method for edge LLMs by only modifying a small portion of LLM parameters, but it suffers from user domain shifts, resulting in repetitive training and losing resource efficiency. Conventional techniques to address domain shift issues often involve complex neural networks and sophisticated training, which are incompatible for PT for edge LLMs. Therefore, an open research question is how to address domain shift issues for edge LLMs with limited resources. In this paper, we propose a prompt tuning framework for edge LLMs, exploiting the benefits offered by non-volatile computing-in-memory (NVCiM) architectures. We introduce a novel NVCiM-assisted PT framework, where we narrow down the core operations to matrix-matrix multiplication, which can then be accelerated by performing in-situ computation on NVCiM. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work employing NVCiM to improve the edge LLM PT performance.
Automatic Screening for Children with Speech Disorder using Automatic Speech Recognition: Opportunities and Challenges
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Speech is a fundamental aspect of human life, crucial not only for communication but also for cognitive, social, and academic development. Children with speech disorders (SD) face significant challenges that, if unaddressed, can result in lasting negative impacts. Traditionally, speech and language assessments (SLA) have been conducted by skilled speech-language pathologists (SLPs), but there is a growing need for efficient and scalable SLA methods powered by artificial intelligence. This position paper presents a survey of existing techniques suitable for automating SLA pipelines, with an emphasis on adapting automatic speech recognition (ASR) models for children's speech, an overview of current SLAs and their automated counterparts to demonstrate the feasibility of AI-enhanced SLA pipelines, and a discussion of practical considerations, including accessibility and privacy concerns, associated with the deployment of AI-powered SLAs.
Large Language Models have Intrinsic Self-Correction Ability
Jun 21, 2024
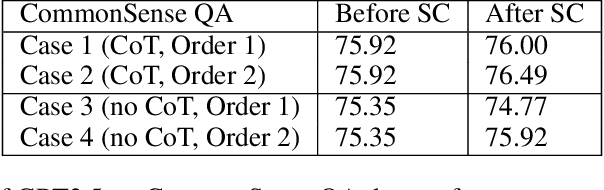
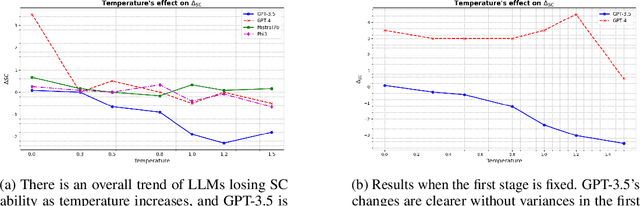
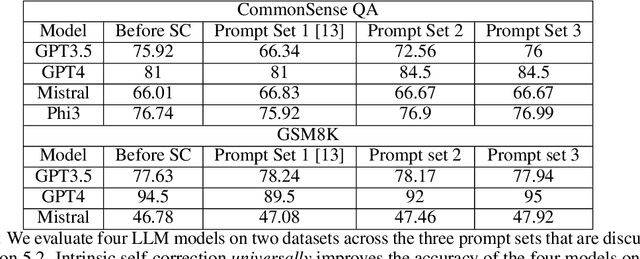
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have attracted significant attention for their remarkable abilities in various natural language processing tasks, but they suffer from hallucinations that will cause performance degradation. One promising solution to improve the LLMs' performance is to ask LLMs to revise their answer after generation, a technique known as self-correction. Among the two types of self-correction, intrinsic self-correction is considered a promising direction because it does not utilize external knowledge. However, recent works doubt the validity of LLM's ability to conduct intrinsic self-correction. In this paper, we present a novel perspective on the intrinsic self-correction capabilities of LLMs through theoretical analyses and empirical experiments. In addition, we identify two critical factors for successful self-correction: zero temperature and fair prompts. Leveraging these factors, we demonstrate that intrinsic self-correction ability is exhibited across multiple existing LLMs. Our findings offer insights into the fundamental theories underlying the self-correction behavior of LLMs and remark on the importance of unbiased prompts and zero temperature settings in harnessing their full potential.
PI-Whisper: An Adaptive and Incremental ASR Framework for Diverse and Evolving Speaker Characteristics
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:As edge-based automatic speech recognition (ASR) technologies become increasingly prevalent for the development of intelligent and personalized assistants, three important challenges must be addressed for these resource-constrained ASR models, i.e., adaptivity, incrementality, and inclusivity. We propose a novel ASR framework, PI-Whisper, in this work and show how it can improve an ASR's recognition capabilities adaptively by identifying different speakers' characteristics in real-time, how such an adaption can be performed incrementally without repetitive retraining, and how it can improve the equity and fairness for diverse speaker groups. More impressively, our proposed PI-Whisper framework attains all of these nice properties while still achieving state-of-the-art accuracy with up to 13.7% reduction of the word error rate (WER) with linear scalability with respect to computing resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge