Ali Imran
Are Open-Vocabulary Models Ready for Detection of MEP Elements on Construction Sites
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:The construction industry has long explored robotics and computer vision, yet their deployment on construction sites remains very limited. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize traditional workflows by enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and safety in construction management. Ground robots equipped with advanced vision systems could automate tasks such as monitoring mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems. The present research evaluates the applicability of open-vocabulary vision-language models compared to fine-tuned, lightweight, closed-set object detectors for detecting MEP components using a mobile ground robotic platform. A dataset collected with cameras mounted on a ground robot was manually annotated and analyzed to compare model performance. The results demonstrate that, despite the versatility of vision-language models, fine-tuned lightweight models still largely outperform them in specialized environments and for domain-specific tasks.
GNN-based Decentralized Perception in Multirobot Systems for Predicting Worker Actions
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:In industrial environments, predicting human actions is essential for ensuring safe and effective collaboration between humans and robots. This paper introduces a perception framework that enables mobile robots to understand and share information about human actions in a decentralized way. The framework first allows each robot to build a spatial graph representing its surroundings, which it then shares with other robots. This shared spatial data is combined with temporal information to track human behavior over time. A swarm-inspired decision-making process is used to ensure all robots agree on a unified interpretation of the human's actions. Results show that adding more robots and incorporating longer time sequences improve prediction accuracy. Additionally, the consensus mechanism increases system resilience, making the multi-robot setup more reliable in dynamic industrial settings.
From the Lab to the Theater: An Unconventional Field Robotics Journey
Apr 11, 2024Abstract:Artistic performances involving robotic systems present unique technical challenges akin to those encountered in other field deployments. In this paper, we delve into the orchestration of robotic artistic performances, focusing on the complexities inherent in communication protocols and localization methods. Through our case studies and experimental insights, we demonstrate the breadth of technical requirements for this type of deployment, and, most importantly, the significant contributions of working closely with non-experts.
An AI-enabled Bias-Free Respiratory Disease Diagnosis Model using Cough Audio: A Case Study for COVID-19
Jan 04, 2024


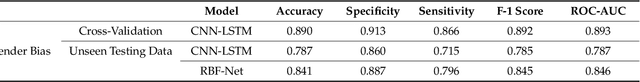
Abstract:Cough-based diagnosis for Respiratory Diseases (RDs) using Artificial Intelligence (AI) has attracted considerable attention, yet many existing studies overlook confounding variables in their predictive models. These variables can distort the relationship between cough recordings (input data) and RD status (output variable), leading to biased associations and unrealistic model performance. To address this gap, we propose the Bias Free Network (RBFNet), an end to end solution that effectively mitigates the impact of confounders in the training data distribution. RBFNet ensures accurate and unbiased RD diagnosis features, emphasizing its relevance by incorporating a COVID19 dataset in this study. This approach aims to enhance the reliability of AI based RD diagnosis models by navigating the challenges posed by confounding variables. A hybrid of a Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks is proposed for the feature encoder module of RBFNet. An additional bias predictor is incorporated in the classification scheme to formulate a conditional Generative Adversarial Network (cGAN) which helps in decorrelating the impact of confounding variables from RD prediction. The merit of RBFNet is demonstrated by comparing classification performance with State of The Art (SoTA) Deep Learning (DL) model (CNN LSTM) after training on different unbalanced COVID-19 data sets, created by using a large scale proprietary cough data set. RBF-Net proved its robustness against extremely biased training scenarios by achieving test set accuracies of 84.1%, 84.6%, and 80.5% for the following confounding variables gender, age, and smoking status, respectively. RBF-Net outperforms the CNN-LSTM model test set accuracies by 5.5%, 7.7%, and 8.2%, respectively
Towards using Cough for Respiratory Disease Diagnosis by leveraging Artificial Intelligence: A Survey
Sep 24, 2023
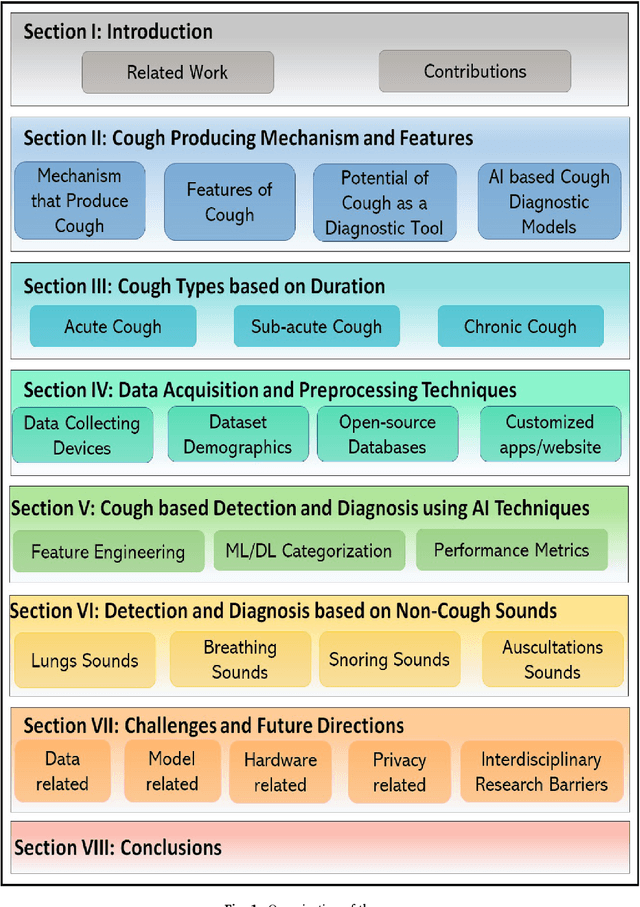
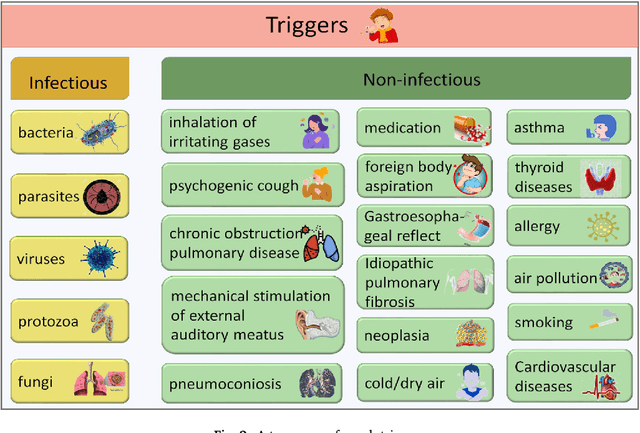
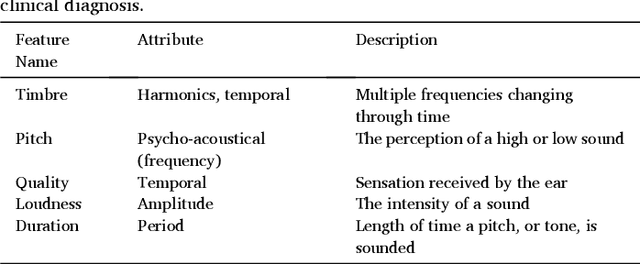
Abstract:Cough acoustics contain multitudes of vital information about pathomorphological alterations in the respiratory system. Reliable and accurate detection of cough events by investigating the underlying cough latent features and disease diagnosis can play an indispensable role in revitalizing the healthcare practices. The recent application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and advances of ubiquitous computing for respiratory disease prediction has created an auspicious trend and myriad of future possibilities in the medical domain. In particular, there is an expeditiously emerging trend of Machine learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL)-based diagnostic algorithms exploiting cough signatures. The enormous body of literature on cough-based AI algorithms demonstrate that these models can play a significant role for detecting the onset of a specific respiratory disease. However, it is pertinent to collect the information from all relevant studies in an exhaustive manner for the medical experts and AI scientists to analyze the decisive role of AI/ML. This survey offers a comprehensive overview of the cough data-driven ML/DL detection and preliminary diagnosis frameworks, along with a detailed list of significant features. We investigate the mechanism that causes cough and the latent cough features of the respiratory modalities. We also analyze the customized cough monitoring application, and their AI-powered recognition algorithms. Challenges and prospective future research directions to develop practical, robust, and ubiquitous solutions are also discussed in detail.
An AI-Enabled Framework to Defend Ingenious MDT-based Attacks on the Emerging Zero Touch Cellular Networks
Aug 05, 2023



Abstract:Deep automation provided by self-organizing network (SON) features and their emerging variants such as zero touch automation solutions is a key enabler for increasingly dense wireless networks and pervasive Internet of Things (IoT). To realize their objectives, most automation functionalities rely on the Minimization of Drive Test (MDT) reports. The MDT reports are used to generate inferences about network state and performance, thus dynamically change network parameters accordingly. However, the collection of MDT reports from commodity user devices, particularly low cost IoT devices, make them a vulnerable entry point to launch an adversarial attack on emerging deeply automated wireless networks. This adds a new dimension to the security threats in the IoT and cellular networks. Existing literature on IoT, SON, or zero touch automation does not address this important problem. In this paper, we investigate an impactful, first of its kind adversarial attack that can be launched by exploiting the malicious MDT reports from the compromised user equipment (UE). We highlight the detrimental repercussions of this attack on the performance of common network automation functions. We also propose a novel Malicious MDT Reports Identification framework (MRIF) as a countermeasure to detect and eliminate the malicious MDT reports using Machine Learning and verify it through a use-case. Thus, the defense mechanism can provide the resilience and robustness for zero touch automation SON engines against the adversarial MDT attacks
See as a Bee: UV Sensor for Aerial Strawberry Crop Monitoring
Oct 30, 2022Abstract:Precision agriculture aims to use technological tools for the agro-food sector to increase productivity, cut labor costs, and reduce the use of resources. This work takes inspiration from bees vision to design a remote sensing system tailored to incorporate UV-reflectance into a flower detector. We demonstrate how this approach can provide feature-rich images for deep learning strawberry flower detection and we apply it to a scalable, yet cost effective aerial monitoring robotic system in the field. We also compare the performance of our UV-G-B image detector with a similar work that utilizes RGB images.
Towards a Hybrid RF/Optical Lunar Communication System (LunarComm)
Mar 29, 2022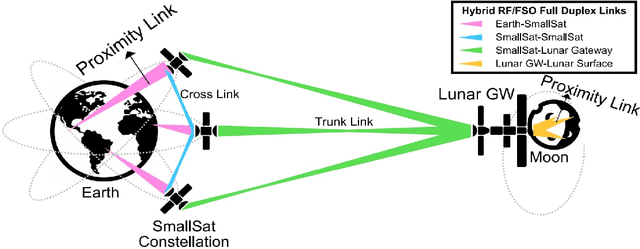
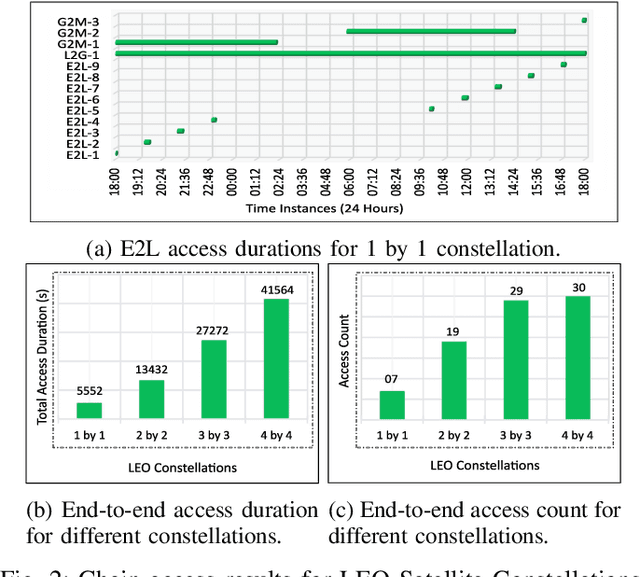
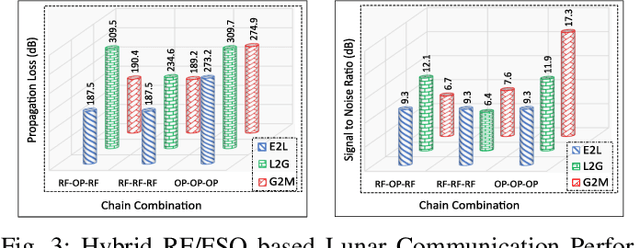
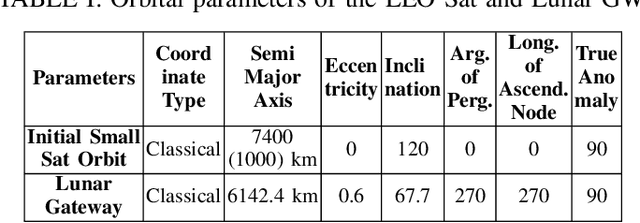
Abstract:The prospect of mankind returning to the Moon has garnered a great amount of attention in recent years. Dozens of lunar missions are planned for the coming decade which will require the development of a sustainable communication infrastructure with high data rates and minimal latency. Space communication systems thus far have relied on Radio Frequency (RF) links alone, but recent developments in laser communications have demonstrated that Free Space Optical (FSO) links can achieve much higher data rates. Upon considering the respective benefits and drawbacks of RF and FSO links, we make a case for the integration of these two technologies into a hybrid RF/FSO lunar communications architecture which leverages small satellites in a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellation. We include a case study for this technology designed in Analytical Graphics Systems Tool Kit (STK) software. Results are presented in terms of chain access duration, propagation delay, transmission loss, Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and Bit Error Rate (BER). This architecture shows potential to revolutionize extraterrestrial communications and pave the way for highly ambitious future missions in space.
Machine Learning Aided Holistic Handover Optimization for Emerging Networks
Feb 06, 2022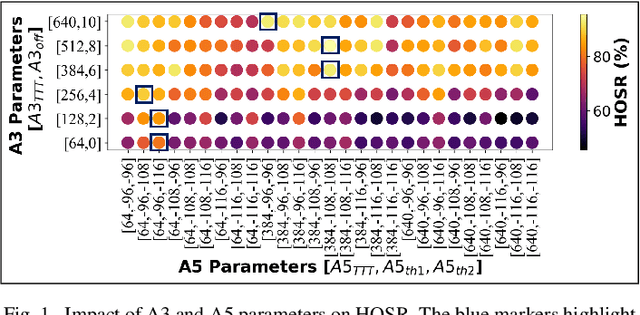

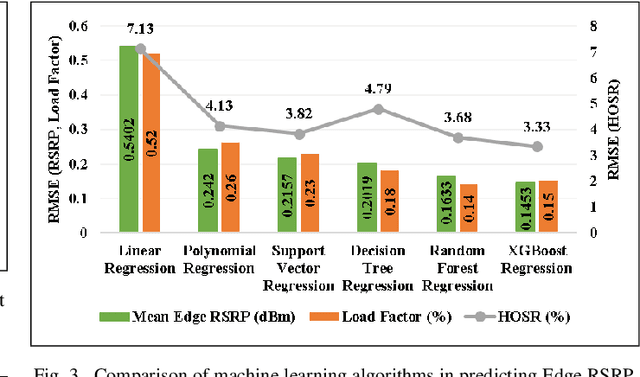
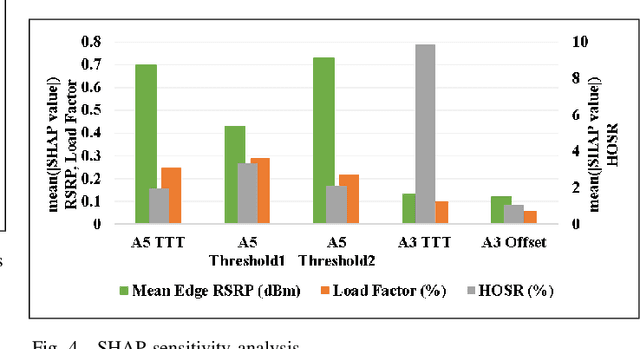
Abstract:In the wake of network densification and multi-band operation in emerging cellular networks, mobility and handover management is becoming a major bottleneck. The problem is further aggravated by the fact that holistic mobility management solutions for different types of handovers, namely inter-frequency and intra-frequency handovers, remain scarce. This paper presents a first mobility management solution that concurrently optimizes inter-frequency related A5 parameters and intra-frequency related A3 parameters. We analyze and optimize five parameters namely A5-time to trigger (TTT), A5-threshold1, A5-threshold2, A3-TTT, and A3-offset to jointly maximize three critical key performance indicators (KPIs): edge user reference signal received power (RSRP), handover success rate (HOSR) and load between frequency bands. In the absence of tractable analytical models due to system level complexity, we leverage machine learning to quantify the KPIs as a function of the mobility parameters. An XGBoost based model has the best performance for edge RSRP and HOSR while random forest outperforms others for load prediction. An analysis of the mobility parameters provides several insights: 1) there exists a strong coupling between A3 and A5 parameters; 2) an optimal set of parameters exists for each KPI; and 3) the optimal parameters vary for different KPIs. We also perform a SHAP based sensitivity to help resolve the parametric conflict between the KPIs. Finally, we formulate a maximization problem, show it is non-convex, and solve it utilizing simulated annealing (SA). Results indicate that ML-based SA-aided solution is more than 14x faster than the brute force approach with a slight loss in optimality.
Interpretable AI-based Large-scale 3D Pathloss Prediction Model for enabling Emerging Self-Driving Networks
Jan 30, 2022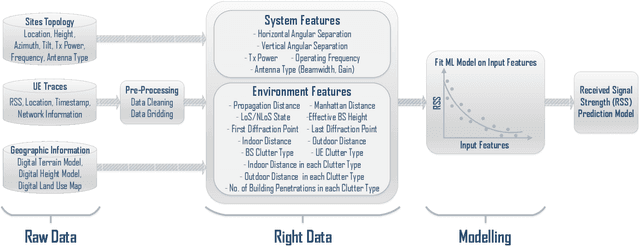
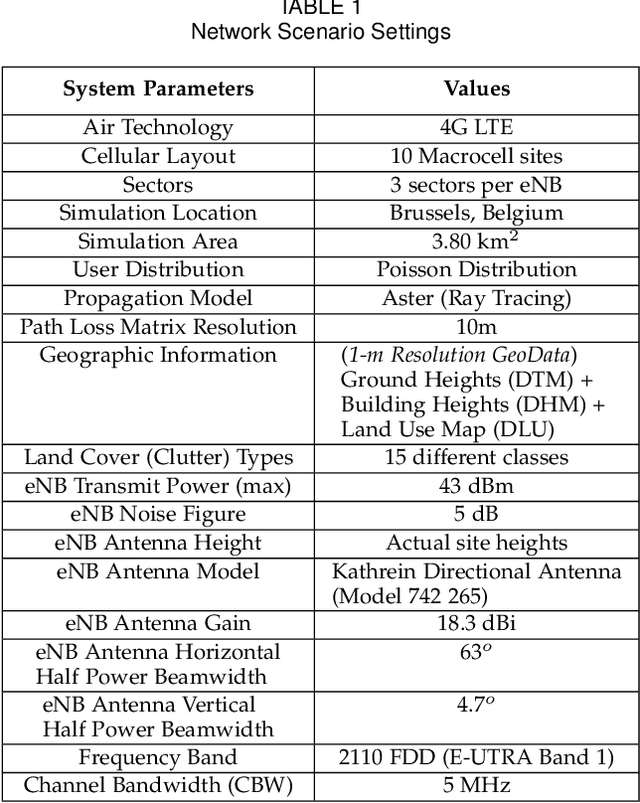
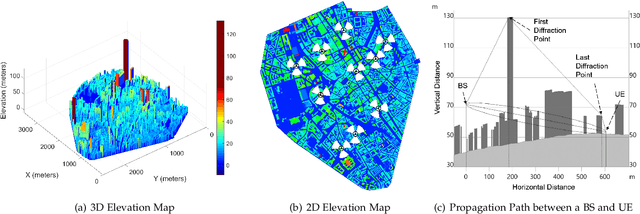
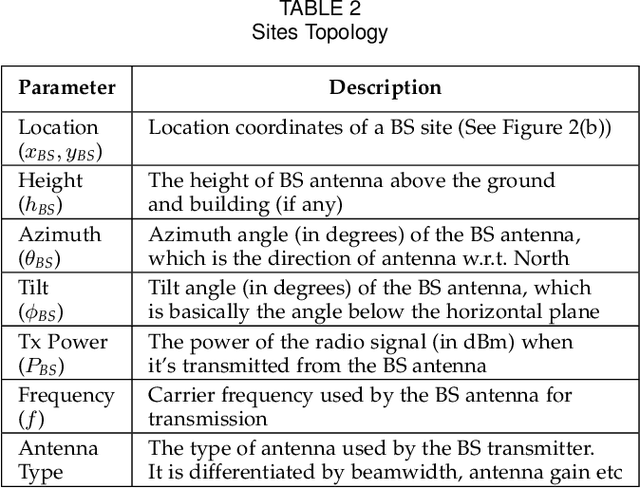
Abstract:In modern wireless communication systems, radio propagation modeling to estimate pathloss has always been a fundamental task in system design and optimization. The state-of-the-art empirical propagation models are based on measurements in specific environments and limited in their ability to capture idiosyncrasies of various propagation environments. To cope with this problem, ray-tracing based solutions are used in commercial planning tools, but they tend to be extremely time-consuming and expensive. We propose a Machine Learning (ML)-based model that leverages novel key predictors for estimating pathloss. By quantitatively evaluating the ability of various ML algorithms in terms of predictive, generalization and computational performance, our results show that Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM) algorithm overall outperforms others, even with sparse training data, by providing a 65% increase in prediction accuracy as compared to empirical models and 13x decrease in prediction time as compared to ray-tracing. To address the interpretability challenge that thwarts the adoption of most ML-based models, we perform extensive secondary analysis using SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) method, yielding many practically useful insights that can be leveraged for intelligently tuning the network configuration, selective enrichment of training data in real networks and for building lighter ML-based propagation model to enable low-latency use-cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge