Waseem Raza
An AI-Enabled Framework to Defend Ingenious MDT-based Attacks on the Emerging Zero Touch Cellular Networks
Aug 05, 2023



Abstract:Deep automation provided by self-organizing network (SON) features and their emerging variants such as zero touch automation solutions is a key enabler for increasingly dense wireless networks and pervasive Internet of Things (IoT). To realize their objectives, most automation functionalities rely on the Minimization of Drive Test (MDT) reports. The MDT reports are used to generate inferences about network state and performance, thus dynamically change network parameters accordingly. However, the collection of MDT reports from commodity user devices, particularly low cost IoT devices, make them a vulnerable entry point to launch an adversarial attack on emerging deeply automated wireless networks. This adds a new dimension to the security threats in the IoT and cellular networks. Existing literature on IoT, SON, or zero touch automation does not address this important problem. In this paper, we investigate an impactful, first of its kind adversarial attack that can be launched by exploiting the malicious MDT reports from the compromised user equipment (UE). We highlight the detrimental repercussions of this attack on the performance of common network automation functions. We also propose a novel Malicious MDT Reports Identification framework (MRIF) as a countermeasure to detect and eliminate the malicious MDT reports using Machine Learning and verify it through a use-case. Thus, the defense mechanism can provide the resilience and robustness for zero touch automation SON engines against the adversarial MDT attacks
Towards a Hybrid RF/Optical Lunar Communication System (LunarComm)
Mar 29, 2022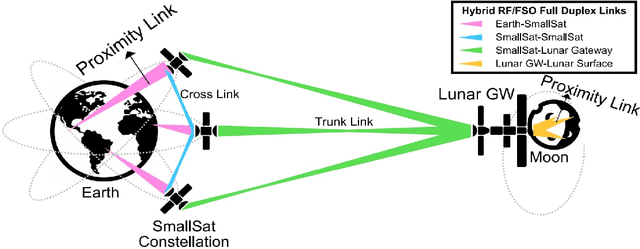
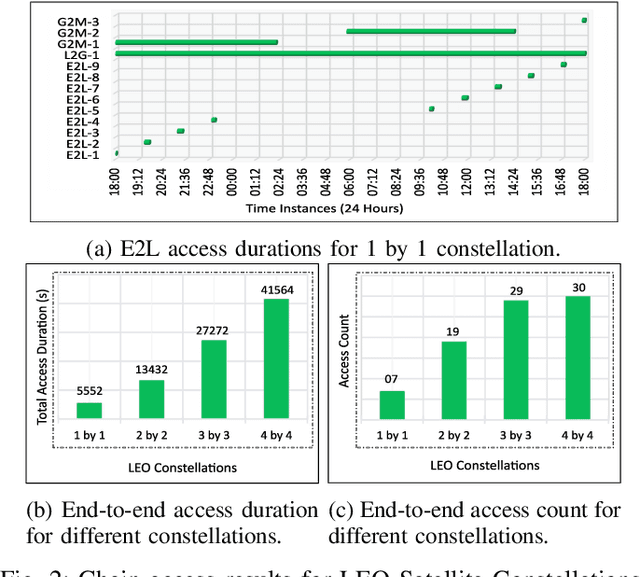
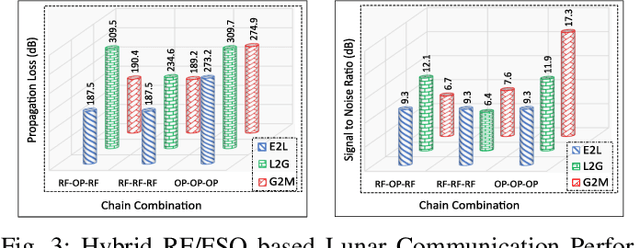
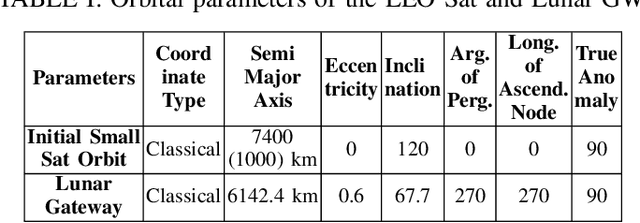
Abstract:The prospect of mankind returning to the Moon has garnered a great amount of attention in recent years. Dozens of lunar missions are planned for the coming decade which will require the development of a sustainable communication infrastructure with high data rates and minimal latency. Space communication systems thus far have relied on Radio Frequency (RF) links alone, but recent developments in laser communications have demonstrated that Free Space Optical (FSO) links can achieve much higher data rates. Upon considering the respective benefits and drawbacks of RF and FSO links, we make a case for the integration of these two technologies into a hybrid RF/FSO lunar communications architecture which leverages small satellites in a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellation. We include a case study for this technology designed in Analytical Graphics Systems Tool Kit (STK) software. Results are presented in terms of chain access duration, propagation delay, transmission loss, Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and Bit Error Rate (BER). This architecture shows potential to revolutionize extraterrestrial communications and pave the way for highly ambitious future missions in space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge