Ismail Sadiq
An AI-enabled Bias-Free Respiratory Disease Diagnosis Model using Cough Audio: A Case Study for COVID-19
Jan 04, 2024


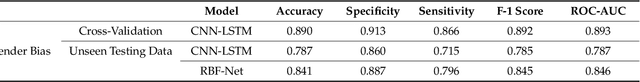
Abstract:Cough-based diagnosis for Respiratory Diseases (RDs) using Artificial Intelligence (AI) has attracted considerable attention, yet many existing studies overlook confounding variables in their predictive models. These variables can distort the relationship between cough recordings (input data) and RD status (output variable), leading to biased associations and unrealistic model performance. To address this gap, we propose the Bias Free Network (RBFNet), an end to end solution that effectively mitigates the impact of confounders in the training data distribution. RBFNet ensures accurate and unbiased RD diagnosis features, emphasizing its relevance by incorporating a COVID19 dataset in this study. This approach aims to enhance the reliability of AI based RD diagnosis models by navigating the challenges posed by confounding variables. A hybrid of a Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks is proposed for the feature encoder module of RBFNet. An additional bias predictor is incorporated in the classification scheme to formulate a conditional Generative Adversarial Network (cGAN) which helps in decorrelating the impact of confounding variables from RD prediction. The merit of RBFNet is demonstrated by comparing classification performance with State of The Art (SoTA) Deep Learning (DL) model (CNN LSTM) after training on different unbalanced COVID-19 data sets, created by using a large scale proprietary cough data set. RBF-Net proved its robustness against extremely biased training scenarios by achieving test set accuracies of 84.1%, 84.6%, and 80.5% for the following confounding variables gender, age, and smoking status, respectively. RBF-Net outperforms the CNN-LSTM model test set accuracies by 5.5%, 7.7%, and 8.2%, respectively
Mythological Medical Machine Learning: Boosting the Performance of a Deep Learning Medical Data Classifier Using Realistic Physiological Models
Dec 28, 2021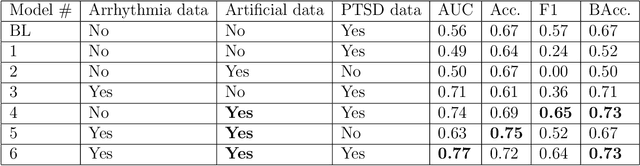
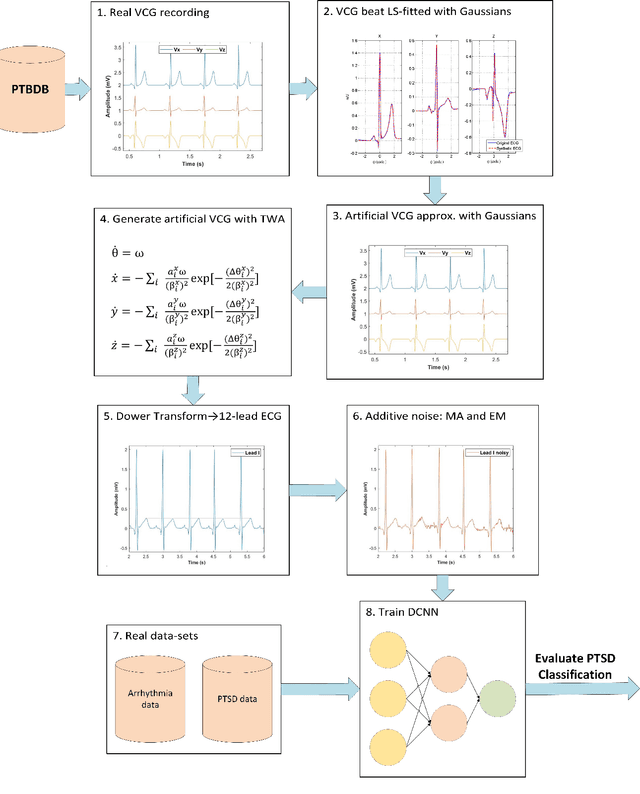
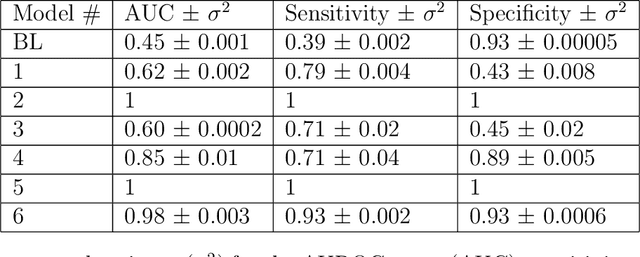
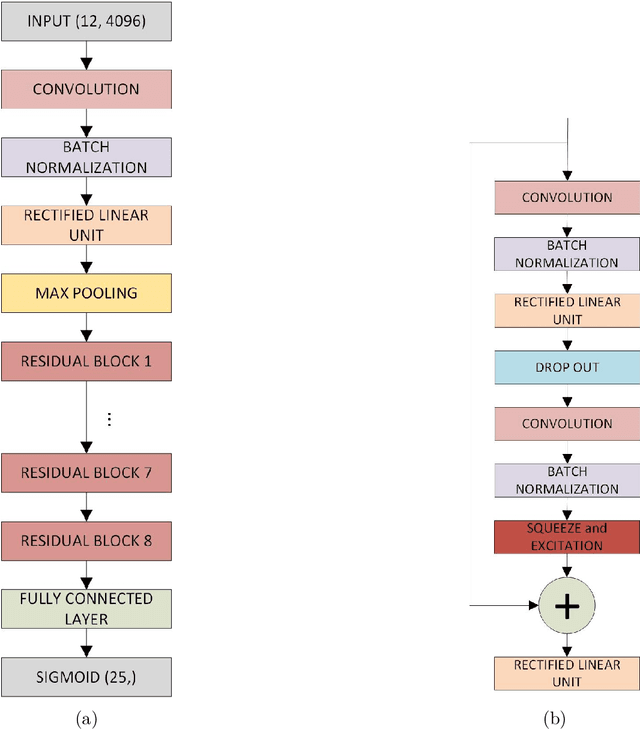
Abstract:Objective: To determine if a realistic, but computationally efficient model of the electrocardiogram can be used to pre-train a deep neural network (DNN) with a wide range of morphologies and abnormalities specific to a given condition - T-wave Alternans (TWA) as a result of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, or PTSD - and significantly boost performance on a small database of rare individuals. Approach: Using a previously validated artificial ECG model, we generated 180,000 artificial ECGs with or without significant TWA, with varying heart rate, breathing rate, TWA amplitude, and ECG morphology. A DNN, trained on over 70,000 patients to classify 25 different rhythms, was modified the output layer to a binary class (TWA or no-TWA, or equivalently, PTSD or no-PTSD), and transfer learning was performed on the artificial ECG. In a final transfer learning step, the DNN was trained and cross-validated on ECG from 12 PTSD and 24 controls for all combinations of using the three databases. Main results: The best performing approach (AUROC = 0.77, Accuracy = 0.72, F1-score = 0.64) was found by performing both transfer learning steps, using the pre-trained arrhythmia DNN, the artificial data and the real PTSD-related ECG data. Removing the artificial data from training led to the largest drop in performance. Removing the arrhythmia data from training provided a modest, but significant, drop in performance. The final model showed no significant drop in performance on the artificial data, indicating no overfitting. Significance: In healthcare, it is common to only have a small collection of high-quality data and labels, or a larger database with much lower quality (and less relevant) labels. The paradigm presented here, involving model-based performance boosting, provides a solution through transfer learning on a large realistic artificial database, and a partially relevant real database.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge