Alexandra Hotti
Efficient Mixture Learning in Black-Box Variational Inference
Jun 11, 2024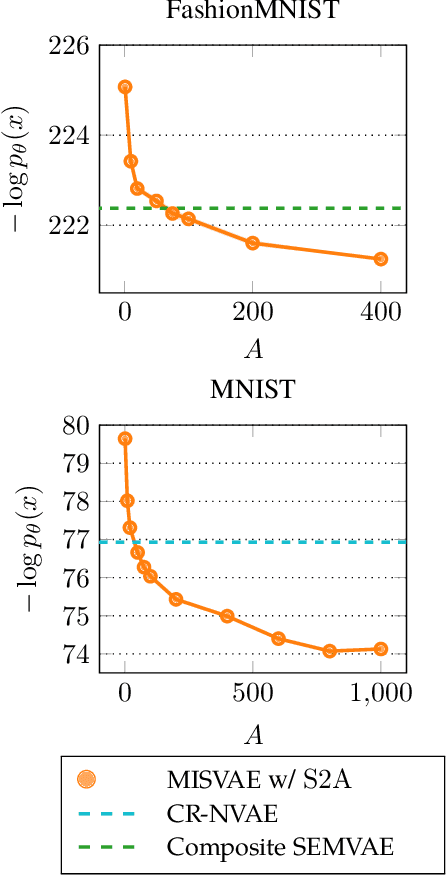
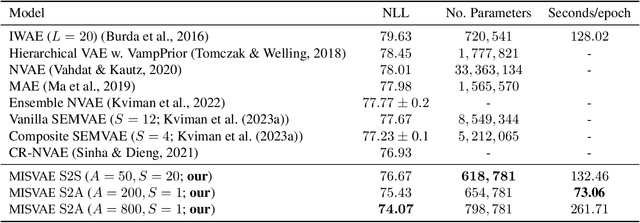
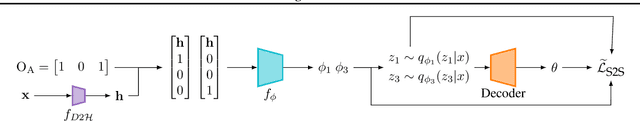
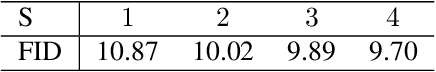
Abstract:Mixture variational distributions in black box variational inference (BBVI) have demonstrated impressive results in challenging density estimation tasks. However, currently scaling the number of mixture components can lead to a linear increase in the number of learnable parameters and a quadratic increase in inference time due to the evaluation of the evidence lower bound (ELBO). Our two key contributions address these limitations. First, we introduce the novel Multiple Importance Sampling Variational Autoencoder (MISVAE), which amortizes the mapping from input to mixture-parameter space using one-hot encodings. Fortunately, with MISVAE, each additional mixture component incurs a negligible increase in network parameters. Second, we construct two new estimators of the ELBO for mixtures in BBVI, enabling a tremendous reduction in inference time with marginal or even improved impact on performance. Collectively, our contributions enable scalability to hundreds of mixture components and provide superior estimation performance in shorter time, with fewer network parameters compared to previous Mixture VAEs. Experimenting with MISVAE, we achieve astonishing, SOTA results on MNIST. Furthermore, we empirically validate our estimators in other BBVI settings, including Bayesian phylogenetic inference, where we improve inference times for the SOTA mixture model on eight data sets.
Indirectly Parameterized Concrete Autoencoders
Mar 01, 2024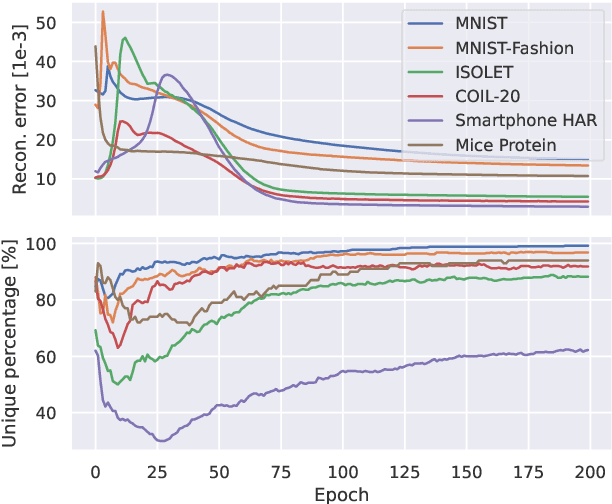
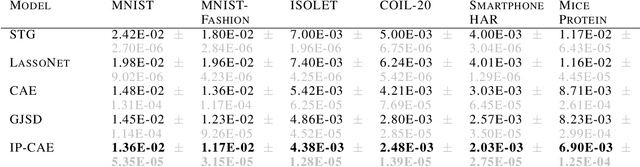
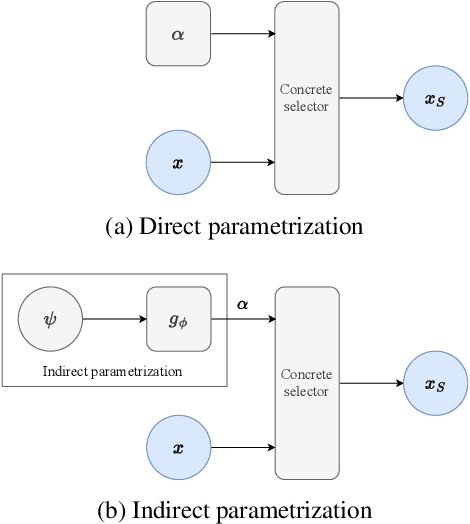
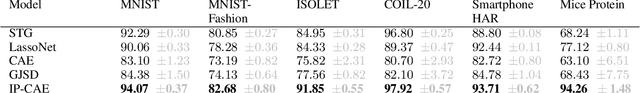
Abstract:Feature selection is a crucial task in settings where data is high-dimensional or acquiring the full set of features is costly. Recent developments in neural network-based embedded feature selection show promising results across a wide range of applications. Concrete Autoencoders (CAEs), considered state-of-the-art in embedded feature selection, may struggle to achieve stable joint optimization, hurting their training time and generalization. In this work, we identify that this instability is correlated with the CAE learning duplicate selections. To remedy this, we propose a simple and effective improvement: Indirectly Parameterized CAEs (IP-CAEs). IP-CAEs learn an embedding and a mapping from it to the Gumbel-Softmax distributions' parameters. Despite being simple to implement, IP-CAE exhibits significant and consistent improvements over CAE in both generalization and training time across several datasets for reconstruction and classification. Unlike CAE, IP-CAE effectively leverages non-linear relationships and does not require retraining the jointly optimized decoder. Furthermore, our approach is, in principle, generalizable to Gumbel-Softmax distributions beyond feature selection.
Learning with MISELBO: The Mixture Cookbook
Sep 30, 2022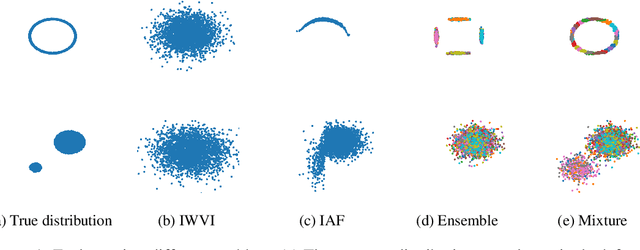
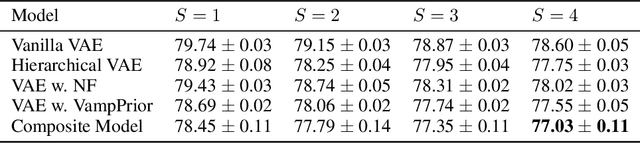
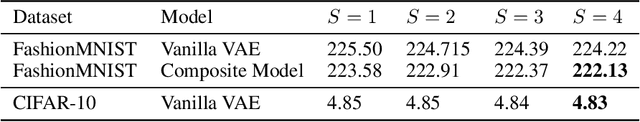
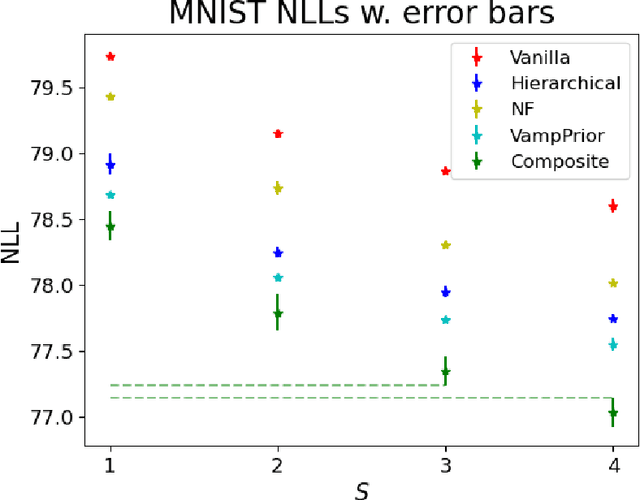
Abstract:Mixture models in variational inference (VI) is an active field of research. Recent works have established their connection to multiple importance sampling (MIS) through the MISELBO and advanced the use of ensemble approximations for large-scale problems. However, as we show here, an independent learning of the ensemble components can lead to suboptimal diversity. Hence, we study the effect of instead using MISELBO as an objective function for learning mixtures, and we propose the first ever mixture of variational approximations for a normalizing flow-based hierarchical variational autoencoder (VAE) with VampPrior and a PixelCNN decoder network. Two major insights led to the construction of this novel composite model. First, mixture models have potential to be off-the-shelf tools for practitioners to obtain more flexible posterior approximations in VAEs. Therefore, we make them more accessible by demonstrating how to apply them to four popular architectures. Second, the mixture components cooperate in order to cover the target distribution while trying to maximize their diversity when MISELBO is the objective function. We explain this cooperative behavior by drawing a novel connection between VI and adaptive importance sampling. Finally, we demonstrate the superiority of the Mixture VAEs' learned feature representations on both image and single-cell transcriptome data, and obtain state-of-the-art results among VAE architectures in terms of negative log-likelihood on the MNIST and FashionMNIST datasets. Code available here: \url{https://github.com/Lagergren-Lab/MixtureVAEs}.
The Klarna Product Page Dataset: A Realistic Benchmark for Web Representation Learning
Nov 09, 2021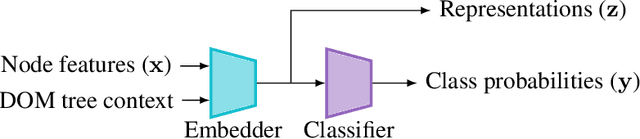
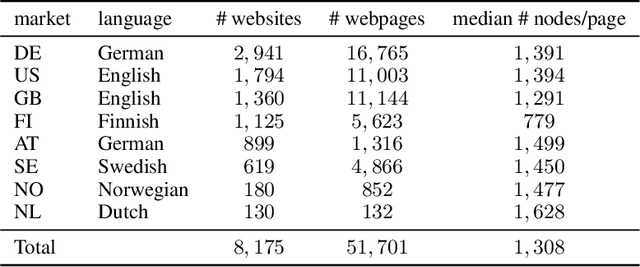
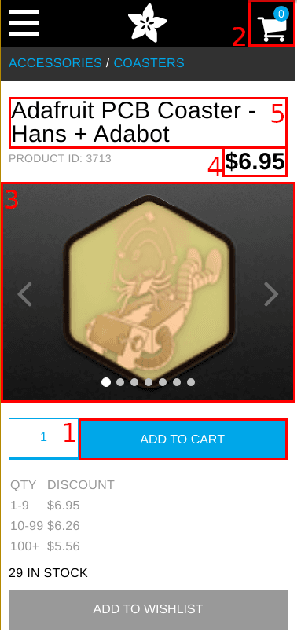
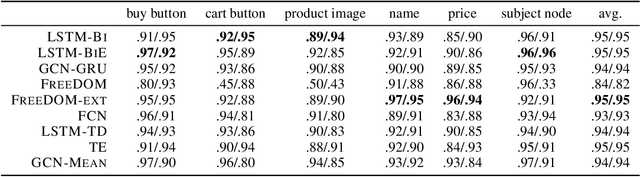
Abstract:This paper tackles the under-explored problem of DOM tree element representation learning. We advance the field of machine learning-based web automation and hope to spur further research regarding this crucial area with two contributions. First, we adapt several popular Graph-based Neural Network models and apply them to embed elements in website DOM trees. Second, we present a large-scale and realistic dataset of webpages. By providing this open-access resource, we lower the entry barrier to this area of research. The dataset contains $51,701$ manually labeled product pages from $8,175$ real e-commerce websites. The pages can be rendered entirely in a web browser and are suitable for computer vision applications. This makes it substantially richer and more diverse than other datasets proposed for element representation learning, classification and prediction on the web. Finally, using our proposed dataset, we show that the embeddings produced by a Graph Convolutional Neural Network outperform representations produced by other state-of-the-art methods in a web element prediction task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge