Alex Chang
A Unified Definition of Hallucination, Or: It's the World Model, Stupid
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Despite numerous attempts to solve the issue of hallucination since the inception of neural language models, it remains a problem in even frontier large language models today. Why is this the case? We walk through definitions of hallucination used in the literature from a historical perspective up to the current day, and fold them into a single definition of hallucination, wherein different prior definitions focus on different aspects of our definition. At its core, we argue that hallucination is simply inaccurate (internal) world modeling, in a form where it is observable to the user (e.g., stating a fact which contradicts a knowledge base, or producing a summary which contradicts a known source). By varying the reference world model as well as the knowledge conflict policy (e.g., knowledge base vs. in-context), we arrive at the different existing definitions of hallucination present in the literature. We argue that this unified view is useful because it forces evaluations to make clear their assumed "world" or source of truth, clarifies what should and should not be called hallucination (as opposed to planning or reward/incentive-related errors), and provides a common language to compare benchmarks and mitigation techniques. Building on this definition, we outline plans for a family of benchmarks in which hallucinations are defined as mismatches with synthetic but fully specified world models in different environments, and sketch out how these benchmarks can use such settings to stress-test and improve the world modeling components of language models.
Toward Foundation Models for Earth Monitoring: Proposal for a Climate Change Benchmark
Dec 01, 2021
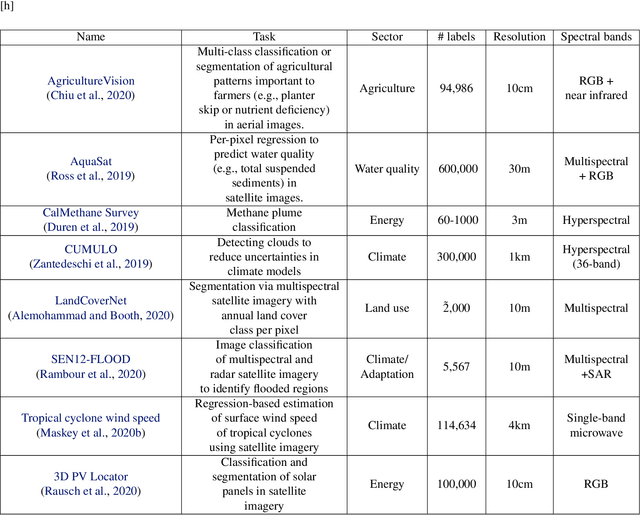
Abstract:Recent progress in self-supervision shows that pre-training large neural networks on vast amounts of unsupervised data can lead to impressive increases in generalisation for downstream tasks. Such models, recently coined as foundation models, have been transformational to the field of natural language processing. While similar models have also been trained on large corpuses of images, they are not well suited for remote sensing data. To stimulate the development of foundation models for Earth monitoring, we propose to develop a new benchmark comprised of a variety of downstream tasks related to climate change. We believe that this can lead to substantial improvements in many existing applications and facilitate the development of new applications. This proposal is also a call for collaboration with the aim of developing a better evaluation process to mitigate potential downsides of foundation models for Earth monitoring.
3D Reasoning for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in Pediatric WbMRI
Mar 24, 2021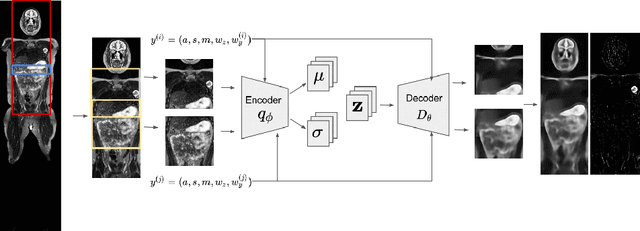
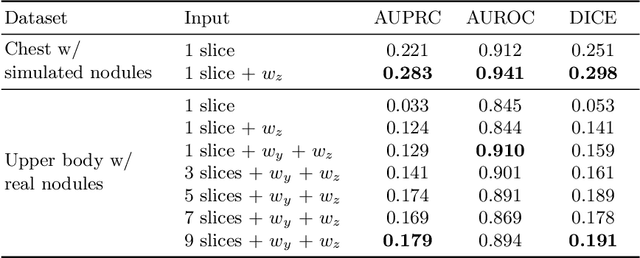
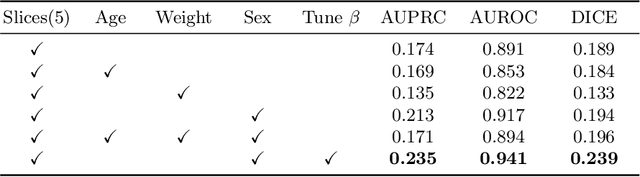
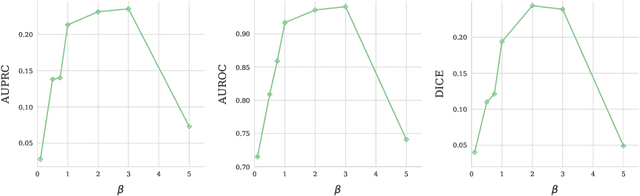
Abstract:Modern deep unsupervised learning methods have shown great promise for detecting diseases across a variety of medical imaging modalities. While previous generative modeling approaches successfully perform anomaly detection by learning the distribution of healthy 2D image slices, they process such slices independently and ignore the fact that they are correlated, all being sampled from a 3D volume. We show that incorporating the 3D context and processing whole-body MRI volumes is beneficial to distinguishing anomalies from their benign counterparts. In our work, we introduce a multi-channel sliding window generative model to perform lesion detection in whole-body MRI (wbMRI). Our experiments demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms processing individual images in isolation and our ablations clearly show the importance of 3D reasoning. Moreover, our work also shows that it is beneficial to include additional patient-specific features to further improve anomaly detection in pediatric scans.
Using Generative Models for Pediatric wbMRI
Jun 01, 2020

Abstract:Early detection of cancer is key to a good prognosis and requires frequent testing, especially in pediatrics. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (wbMRI) is an essential part of several well-established screening protocols, with screening starting in early childhood. To date, machine learning (ML) has been used on wbMRI images to stage adult cancer patients. It is not possible to use such tools in pediatrics due to the changing bone signal throughout growth, the difficulty of obtaining these images in young children due to movement and limited compliance, and the rarity of positive cases. We evaluate the quality of wbMRI images generated using generative adversarial networks (GANs) trained on wbMRI data from The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto. We use the Frchet Inception Distance (FID) metric, Domain Frchet Distance (DFD), and blind tests with a radiology fellow for evaluation. We demonstrate that StyleGAN2 provides the best performance in generating wbMRI images with respect to all three metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge