Alekh Karkada Ashok
The 3D-PC: a benchmark for visual perspective taking in humans and machines
Jun 06, 2024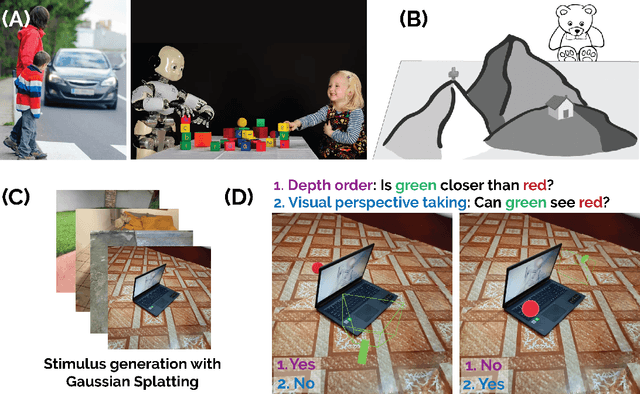

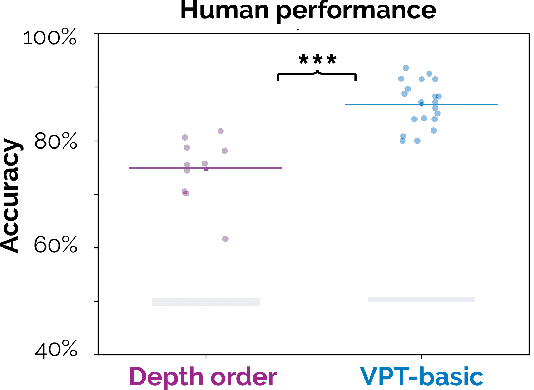
Abstract:Visual perspective taking (VPT) is the ability to perceive and reason about the perspectives of others. It is an essential feature of human intelligence, which develops over the first decade of life and requires an ability to process the 3D structure of visual scenes. A growing number of reports have indicated that deep neural networks (DNNs) become capable of analyzing 3D scenes after training on large image datasets. We investigated if this emergent ability for 3D analysis in DNNs is sufficient for VPT with the 3D perception challenge (3D-PC): a novel benchmark for 3D perception in humans and DNNs. The 3D-PC is comprised of three 3D-analysis tasks posed within natural scene images: 1. a simple test of object depth order, 2. a basic VPT task (VPT-basic), and 3. another version of VPT (VPT-Strategy) designed to limit the effectiveness of "shortcut" visual strategies. We tested human participants (N=33) and linearly probed or text-prompted over 300 DNNs on the challenge and found that nearly all of the DNNs approached or exceeded human accuracy in analyzing object depth order. Surprisingly, DNN accuracy on this task correlated with their object recognition performance. In contrast, there was an extraordinary gap between DNNs and humans on VPT-basic. Humans were nearly perfect, whereas most DNNs were near chance. Fine-tuning DNNs on VPT-basic brought them close to human performance, but they, unlike humans, dropped back to chance when tested on VPT-perturb. Our challenge demonstrates that the training routines and architectures of today's DNNs are well-suited for learning basic 3D properties of scenes and objects but are ill-suited for reasoning about these properties like humans do. We release our 3D-PC datasets and code to help bridge this gap in 3D perception between humans and machines.
Diagnosing and exploiting the computational demands of videos games for deep reinforcement learning
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:Humans learn by interacting with their environments and perceiving the outcomes of their actions. A landmark in artificial intelligence has been the development of deep reinforcement learning (dRL) algorithms capable of doing the same in video games, on par with or better than humans. However, it remains unclear whether the successes of dRL models reflect advances in visual representation learning, the effectiveness of reinforcement learning algorithms at discovering better policies, or both. To address this question, we introduce the Learning Challenge Diagnosticator (LCD), a tool that separately measures the perceptual and reinforcement learning demands of a task. We use LCD to discover a novel taxonomy of challenges in the Procgen benchmark, and demonstrate that these predictions are both highly reliable and can instruct algorithmic development. More broadly, the LCD reveals multiple failure cases that can occur when optimizing dRL algorithms over entire video game benchmarks like Procgen, and provides a pathway towards more efficient progress.
Computing a human-like reaction time metric from stable recurrent vision models
Jun 20, 2023Abstract:The meteoric rise in the adoption of deep neural networks as computational models of vision has inspired efforts to "align" these models with humans. One dimension of interest for alignment includes behavioral choices, but moving beyond characterizing choice patterns to capturing temporal aspects of visual decision-making has been challenging. Here, we sketch a general-purpose methodology to construct computational accounts of reaction times from a stimulus-computable, task-optimized model. Specifically, we introduce a novel metric leveraging insights from subjective logic theory summarizing evidence accumulation in recurrent vision models. We demonstrate that our metric aligns with patterns of human reaction times for stimulus manipulations across four disparate visual decision-making tasks spanning perceptual grouping, mental simulation, and scene categorization. This work paves the way for exploring the temporal alignment of model and human visual strategies in the context of various other cognitive tasks toward generating testable hypotheses for neuroscience.
Adversarial alignment: Breaking the trade-off between the strength of an attack and its relevance to human perception
Jun 05, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) are known to have a fundamental sensitivity to adversarial attacks, perturbations of the input that are imperceptible to humans yet powerful enough to change the visual decision of a model. Adversarial attacks have long been considered the "Achilles' heel" of deep learning, which may eventually force a shift in modeling paradigms. Nevertheless, the formidable capabilities of modern large-scale DNNs have somewhat eclipsed these early concerns. Do adversarial attacks continue to pose a threat to DNNs? Here, we investigate how the robustness of DNNs to adversarial attacks has evolved as their accuracy on ImageNet has continued to improve. We measure adversarial robustness in two different ways: First, we measure the smallest adversarial attack needed to cause a model to change its object categorization decision. Second, we measure how aligned successful attacks are with the features that humans find diagnostic for object recognition. We find that adversarial attacks are inducing bigger and more easily detectable changes to image pixels as DNNs grow better on ImageNet, but these attacks are also becoming less aligned with features that humans find diagnostic for recognition. To better understand the source of this trade-off, we turn to the neural harmonizer, a DNN training routine that encourages models to leverage the same features as humans to solve tasks. Harmonized DNNs achieve the best of both worlds and experience attacks that are detectable and affect features that humans find diagnostic for recognition, meaning that attacks on these models are more likely to be rendered ineffective by inducing similar effects on human perception. Our findings suggest that the sensitivity of DNNs to adversarial attacks can be mitigated by DNN scale, data scale, and training routines that align models with biological intelligence.
Stable and expressive recurrent vision models
May 22, 2020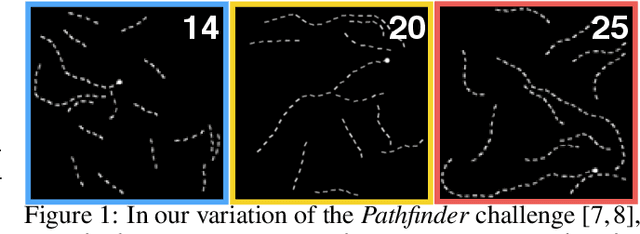
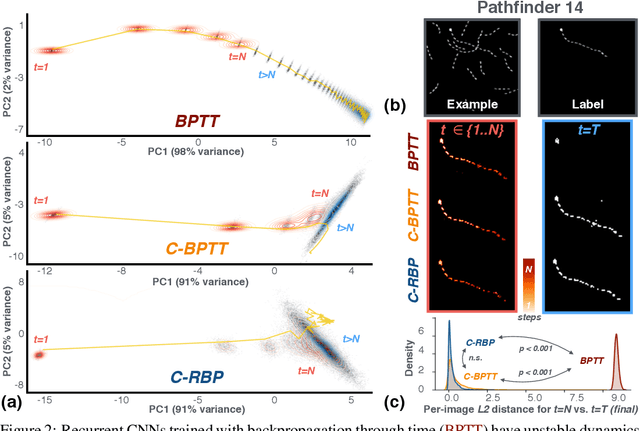
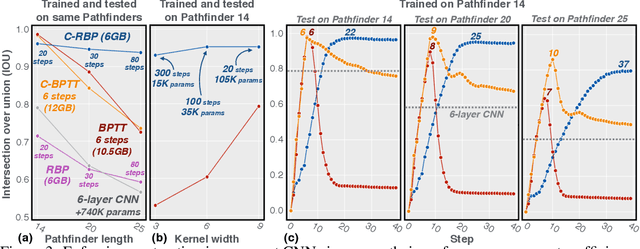
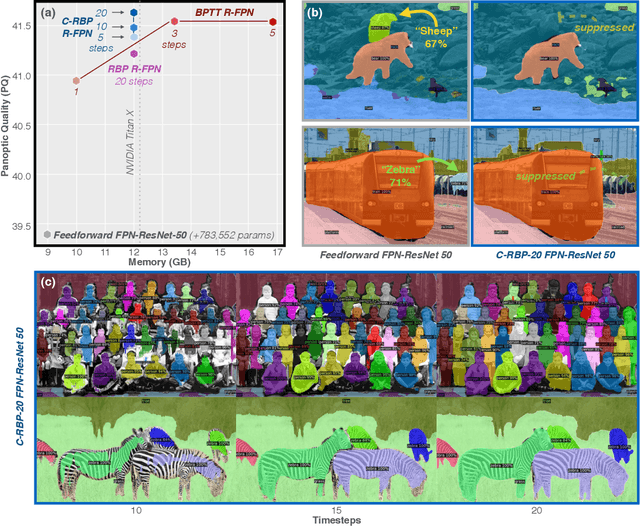
Abstract:Primate vision depends on recurrent processing for reliable perception (Gilbert & Li, 2013). At the same time, there is a growing body of literature demonstrating that recurrent connections improve the learning efficiency and generalization of vision models on classic computer vision challenges. Why then, are current large-scale challenges dominated by feedforward networks? We posit that the effectiveness of recurrent vision models is bottlenecked by the widespread algorithm used for training them, "back-propagation through time" (BPTT), which has O(N) memory-complexity for training an N step model. Thus, recurrent vision model design is bounded by memory constraints, forcing a choice between rivaling the enormous capacity of leading feedforward models or trying to compensate for this deficit through granular and complex dynamics. Here, we develop a new learning algorithm, "contractor recurrent back-propagation" (C-RBP), which alleviates these issues by achieving constant O(1) memory-complexity with steps of recurrent processing. We demonstrate that recurrent vision models trained with C-RBP can detect long-range spatial dependencies in a synthetic contour tracing task that BPTT-trained models cannot. We further demonstrate that recurrent vision models trained with C-RBP to solve the large-scale Panoptic Segmentation MS-COCO challenge outperform the leading feedforward approach. C-RBP is a general-purpose learning algorithm for any application that can benefit from expansive recurrent dynamics. Code and data are available at https://github.com/c-rbp.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge