Adrian Hutter
InfAlign: Inference-aware language model alignment
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:Language model alignment has become a critical step in training modern generative language models. The goal of alignment is to finetune a reference model such that the win rate of a sample from the aligned model over a sample from the reference model is high, subject to a KL divergence constraint. Today, we are increasingly using inference-time algorithms (e.g., Best-of-N, controlled decoding, tree search) to decode from language models rather than standard sampling. However, the alignment objective does not capture such inference-time decoding procedures. We show that the existing alignment framework is sub-optimal in view of such inference-time methods. We then modify the alignment objective and propose a framework for inference-aware alignment (IAPO). We prove that for any inference-time decoding algorithm, the optimal solution that optimizes the inference-time win rate of the aligned policy against the reference policy is the solution to the typical RLHF problem with a transformation of the reward. This motivates us to provide the KL-regularized calibrate-and-transform RL (CTRL) algorithm to solve this problem, which involves a reward calibration step and a KL-regularized reward maximization step with a transformation of the calibrated reward. We particularize our study to two important inference-time strategies: best-of-N sampling and best-of-N jailbreaking, where N responses are sampled from the model and the one with the highest or lowest reward is selected. We propose specific transformations for these strategies and demonstrate that our framework offers significant improvements over existing state-of-the-art methods for language model alignment. Empirically, we outperform baselines that are designed without taking inference-time decoding into consideration by 8-12% and 4-9% on inference-time win rates over the Anthropic helpfulness and harmlessness dialog benchmark datasets.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Learning in two-player games between transparent opponents
Dec 04, 2020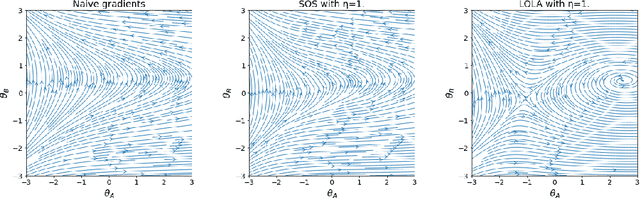
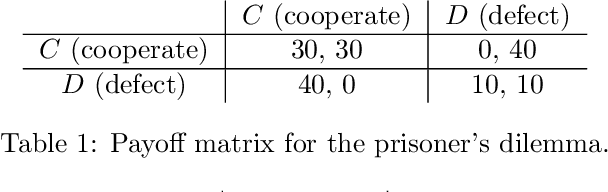
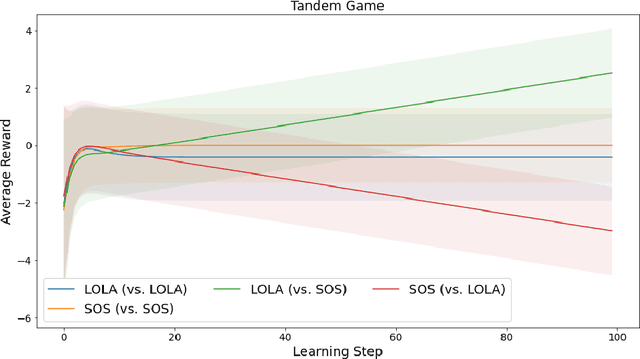
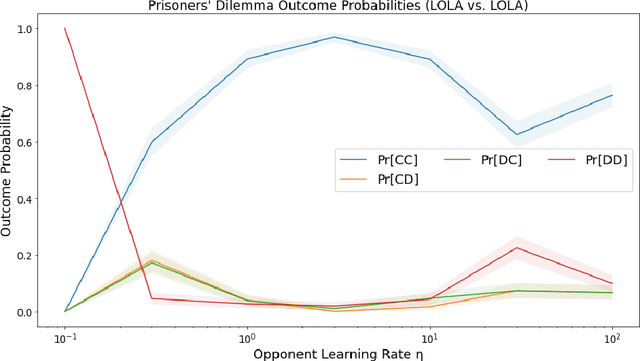
Abstract:We consider a scenario in which two reinforcement learning agents repeatedly play a matrix game against each other and update their parameters after each round. The agents' decision-making is transparent to each other, which allows each agent to predict how their opponent will play against them. To prevent an infinite regress of both agents recursively predicting each other indefinitely, each agent is required to give an opponent-independent response with some probability at least epsilon. Transparency also allows each agent to anticipate and shape the other agent's gradient step, i.e. to move to regions of parameter space in which the opponent's gradient points in a direction favourable to them. We study the resulting dynamics experimentally, using two algorithms from previous literature (LOLA and SOS) for opponent-aware learning. We find that the combination of mutually transparent decision-making and opponent-aware learning robustly leads to mutual cooperation in a single-shot prisoner's dilemma. In a game of chicken, in which both agents try to manoeuvre their opponent towards their preferred equilibrium, converging to a mutually beneficial outcome turns out to be much harder, and opponent-aware learning can even lead to worst-case outcomes for both agents. This highlights the need to develop opponent-aware learning algorithms that achieve acceptable outcomes in social dilemmas involving an equilibrium selection problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge